Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Hydraulic Lift System
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic lift system
In today’s global marketplace, the hydraulic lift system stands as a pivotal component in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and logistics. These systems enhance operational efficiency by providing reliable and powerful lifting solutions for heavy loads, enabling businesses to optimize their workflows and improve safety standards. As international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to streamline their operations, understanding the intricacies of hydraulic lift systems becomes essential.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed sourcing decisions. We will explore the different types of hydraulic lift systems, ranging from scissor lifts to vertical lifts, and discuss the materials used in their construction, ensuring durability and efficiency. Furthermore, we will delve into the manufacturing and quality control processes that guarantee product reliability, while also highlighting key suppliers within the global market.
Additionally, this guide will provide insights into cost considerations, market trends, and frequently asked questions that often arise in the procurement process. By equipping buyers with this critical information, we aim to foster strategic partnerships and support the growth of businesses across diverse regions, ultimately enhancing their competitive edge in the hydraulic lift system market.
Understanding hydraulic lift system Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scissor Lift | Compact design with crisscrossed supports; vertical lift | Warehousing, manufacturing, construction | Pros: High stability, excellent for vertical lifting. Cons: Limited horizontal reach. |
| Forklift Hydraulic Lift | Equipped with forks; designed for lifting pallets and loads | Logistics, shipping, retail | Pros: Versatile for various loads, great for tight spaces. Cons: Requires operator training. |
| Hydraulic Hoist | Uses a winch mechanism; vertical lifting capability | Heavy equipment maintenance, construction | Pros: Ideal for heavy loads, flexible installation. Cons: Slower lifting speed. |
| Platform Lift | Enclosed platform; suitable for transporting goods/people | Retail, hospitals, airports | Pros: Safe for passengers, space-efficient. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Mobile Hydraulic Lift | Portable design; can be moved easily across job sites | Maintenance, construction, outdoor events | Pros: Flexible use, easy to transport. Cons: Stability can be an issue on uneven ground. |
Scissor Lift
Scissor lifts are characterized by their crisscrossed support structure that allows for vertical lifting. They are particularly suitable for applications in warehousing, manufacturing, and construction, where stable elevation is required for tasks such as inventory management or overhead assembly work. When purchasing scissor lifts, buyers should consider factors such as load capacity, platform height, and whether the lift can be used indoors or outdoors.
Forklift Hydraulic Lift
This type of hydraulic lift features forks and is specifically designed to handle pallets and other loads. It is widely used in logistics, shipping, and retail environments. Buyers should evaluate the lift’s capacity, maneuverability, and compatibility with existing warehouse systems. Training for operators is essential to ensure safety and efficiency in operation.
Hydraulic Hoist
Hydraulic hoists utilize a winch mechanism to lift heavy loads vertically, making them ideal for heavy equipment maintenance and construction tasks. The flexibility in installation allows them to be used in various settings. Buyers need to consider the hoist’s lifting speed, load capacity, and installation space. While they can handle heavy weights, their slower lifting speed may not suit all operations.
Platform Lift
Platform lifts are enclosed systems designed for transporting goods or people vertically. They find applications in retail, hospitals, and airports, where safety and efficiency are paramount. When considering a platform lift, buyers should assess the initial investment costs, safety features, and space requirements. The higher upfront costs can be justified by the enhanced safety and efficiency they provide.
Mobile Hydraulic Lift
Mobile hydraulic lifts are designed for portability, allowing them to be easily moved across various job sites. They are commonly used in maintenance, construction, and outdoor events. Buyers should focus on the lift’s weight capacity, ease of transport, and stability on uneven surfaces. While their flexibility is a significant advantage, ensuring stability during operation is crucial for safety.
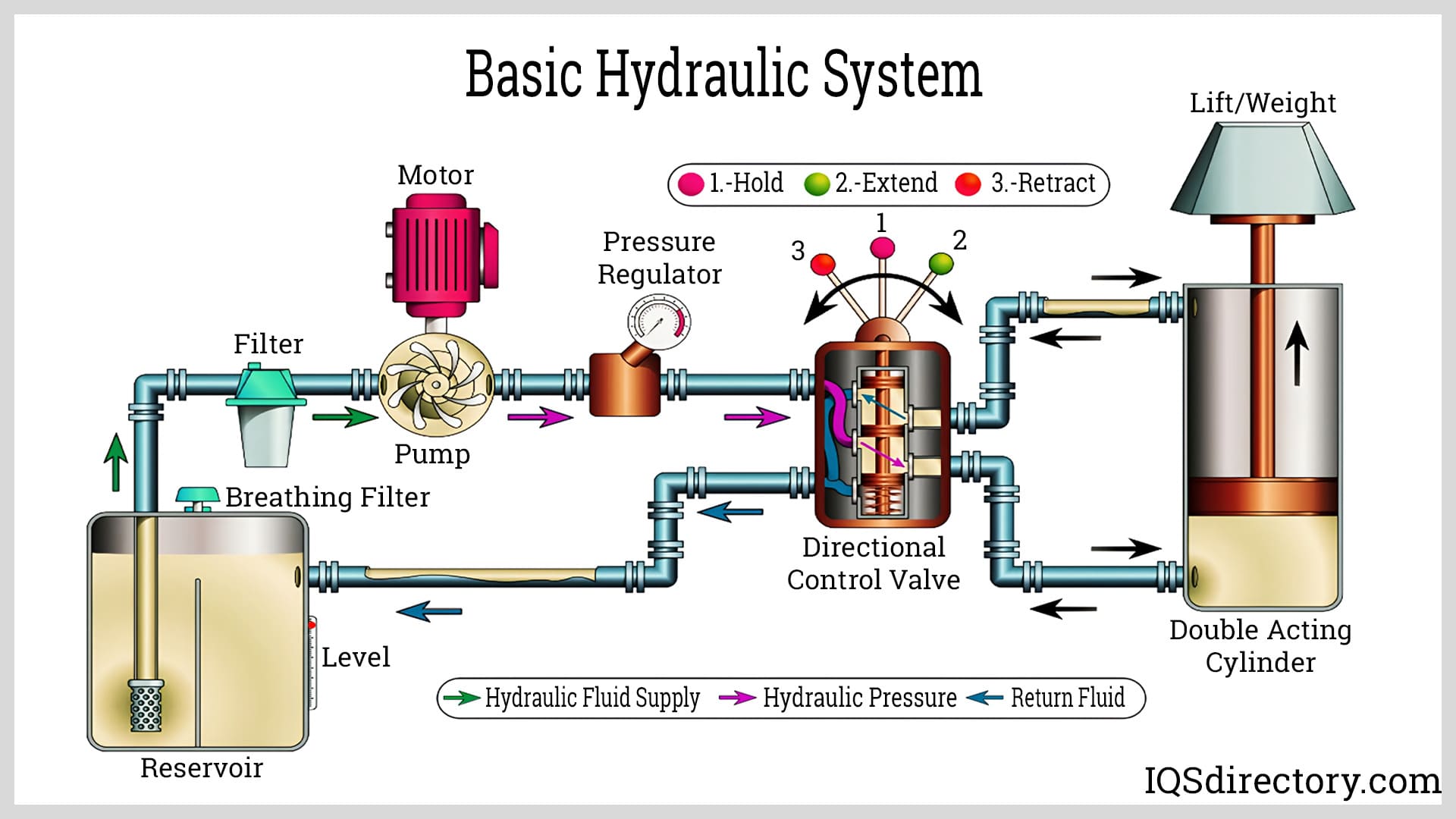
Related Video: Understanding a Basic Hydraulic System with Transparent Componenets
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic lift system
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Hydraulic Lift System | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated Material Handling | Increased efficiency in loading/unloading goods | Reliability of hydraulic components, maintenance support, cost of ownership |
| Construction | Elevating Heavy Equipment | Enhanced safety and productivity on job sites | Compliance with safety standards, load capacity, and durability |
| Logistics & Warehousing | Forklifts and Pallet Jacks | Streamlined operations for inventory management | Supplier reputation, service agreements, and part availability |
| Automotive | Vehicle Lifts for Repair | Improved service speed and customer satisfaction | Equipment warranty, hydraulic fluid compatibility, and service options |
| Aerospace | Aircraft Maintenance Stands | Precision in maintenance and reduced downtime | Certification standards, load testing, and safety features |
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, hydraulic lift systems are integral to automated material handling processes. They facilitate the efficient loading and unloading of goods, which is critical for maintaining production timelines. Buyers in this sector should focus on the reliability and performance of hydraulic components, as well as the availability of maintenance support. Ensuring that the lift systems are compatible with existing machinery and can handle the specific loads required is essential for maximizing operational efficiency.
Construction
In the construction industry, hydraulic lifts are used to elevate heavy equipment, providing a safer and more productive work environment. These systems allow workers to easily transport materials to various heights, reducing the risk of injuries associated with manual lifting. Buyers should consider compliance with local safety standards, as well as the load capacity and durability of the hydraulic lift systems, particularly in challenging environments. Understanding the operational demands of specific construction projects will help in selecting the right equipment.
Logistics & Warehousing
Hydraulic lift systems play a crucial role in logistics and warehousing, particularly in the form of forklifts and pallet jacks. These systems streamline operations for inventory management, allowing for the quick and efficient movement of goods. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their reputation, service agreements, and the availability of parts for maintenance. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements of warehouse layouts and load sizes can guide the selection of appropriate hydraulic systems.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, hydraulic lifts are essential for vehicle repair and maintenance. They enable technicians to elevate vehicles safely, improving service speed and enhancing customer satisfaction. When sourcing hydraulic lifts, buyers should pay attention to warranty options, hydraulic fluid compatibility, and the availability of service options. Ensuring that the lift can accommodate various vehicle sizes and weights is critical for meeting diverse service needs.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry employs hydraulic lift systems in aircraft maintenance stands, where precision and safety are paramount. These systems allow for efficient access to aircraft components, significantly reducing maintenance downtime. Buyers should consider certification standards and load testing results when sourcing these systems. Additionally, safety features are critical to ensure compliance with aviation regulations, making it essential for buyers to thoroughly assess the specifications and capabilities of hydraulic lift systems.
Related Video: Principle of hydraulic lift
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic lift system
When selecting materials for hydraulic lift systems, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in hydraulic lift systems: steel, aluminum, plastic (polymer), and composite materials. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and disadvantages that can significantly impact the application.
Steel
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and durability. It typically has a temperature rating up to 300°C and can withstand high pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel also offers excellent corrosion resistance when treated with protective coatings.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and longevity, which translates to a longer lifespan for hydraulic lift systems. However, steel is relatively heavy, which can complicate installation and increase operational costs. Additionally, the cost of high-quality steel can be significant, affecting the overall budget.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various hydraulic fluids, making it versatile for different applications. However, it is essential to ensure that the selected steel type is appropriate for the specific media used in the system.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN for steel quality. In Africa and South America, local sourcing may affect availability and pricing.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has a high strength-to-weight ratio, with a temperature rating up to 150°C. It is also naturally resistant to corrosion, which makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which facilitates easier handling and installation. However, it has a lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than steel, depending on market conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various hydraulic fluids, but care must be taken with certain aggressive media that may cause corrosion. This material is often used in applications where weight reduction is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may prefer aluminum for its aesthetic appeal and lightweight properties. Compliance with JIS standards is crucial for ensuring quality in these markets.
Plastic (Polymer)
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly high-performance polymers, offer excellent chemical resistance and can operate at temperatures up to 100°C. They are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its resistance to corrosion and chemical attack, making it suitable for specific hydraulic fluids. However, plastics generally have lower mechanical strength and can be less durable than metals. They are also sensitive to UV light, which can degrade performance over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are ideal for applications requiring chemical resistance but may not be suitable for high-pressure environments. Buyers should evaluate the compatibility of the chosen plastic with the hydraulic media.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary, selecting UV-stabilized plastics is crucial. Compliance with local standards for plastic materials is also important.
Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composite materials combine the strengths of different materials, typically featuring high strength and low weight. They can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°C and offer good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their tailored properties, allowing for high performance in specific applications. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized fabrication techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for high-performance hydraulic systems where weight and corrosion resistance are critical. However, they may not be compatible with all hydraulic fluids, necessitating careful selection.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe may find composites appealing for advanced applications, but they should ensure compliance with relevant standards. In emerging markets, the higher cost may be a barrier to adoption.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic lift system | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial lifts | High strength and durability | Heavy and potentially costly | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight lifts in automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Plastic (Polymer) | Chemical handling lifts | Excellent chemical resistance | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Composite Materials | Advanced aerospace applications | Tailored properties for performance | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for hydraulic lift systems, offering actionable insights for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic lift system
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance for hydraulic lift systems are critical for ensuring reliability and performance, particularly for international B2B buyers. Understanding these processes can help buyers make informed decisions when sourcing hydraulic systems.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of hydraulic lift systems typically involves several key stages, each with specific techniques and methodologies.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of materials. This involves selecting high-quality raw materials such as steel or aluminum, which are essential for the structural integrity of hydraulic lifts. Common techniques in this phase include:
- Cutting: Raw materials are cut to the required dimensions using laser cutting or plasma cutting for precision.
- Machining: Further shaping of components through processes like milling, turning, and drilling to achieve exact specifications.
Forming
After material preparation, the next stage is forming, where the raw materials are shaped into functional components. Key techniques include:
- Bending: Metal sheets are bent into desired shapes using hydraulic press brakes.
- Welding: Various welding techniques (MIG, TIG) are employed to join components, ensuring strong, leak-proof connections essential for hydraulic systems.
Assembly
The assembly stage involves putting together the individual components to create the hydraulic lift system. This includes:
- Integration of Hydraulic Components: Valves, cylinders, and pumps are assembled to form the hydraulic circuit.
- Mechanical Assembly: Structural components such as frames and platforms are assembled, ensuring that all parts fit together correctly.
Finishing
The final stage is finishing, which enhances the durability and aesthetics of the hydraulic lift system. Techniques used include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as powder coating or galvanizing protect against corrosion and wear.
- Quality Inspection: Each unit undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets design specifications and quality standards before it is shipped.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in manufacturing hydraulic lift systems is crucial to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards.
Relevant International Standards
Several standards govern the quality of hydraulic lift systems, including:
- ISO 9001: This international standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products.
- API Standards: For hydraulic equipment used in oil and gas applications, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is often required.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product before shipment, including functionality tests and dimensional checks.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the performance and reliability of hydraulic lift systems:
- Hydraulic Testing: Systems are pressurized to check for leaks and performance under operational conditions.
- Load Testing: Lifts are tested under maximum load to ensure stability and safety.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic and radiographic testing are used to detect internal flaws in materials without causing damage.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from international suppliers, verifying the quality control processes of manufacturers is essential. Here are actionable steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help ensure compliance with quality standards. Buyers should consider both on-site audits and remote assessments.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and product quality.
QC/Cert Nuances for International B2B Buyers
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regional Compliance: Understand the local regulations and standards in your region that may differ from international norms. This is particularly important for buyers in Europe where CE marking is mandatory.
- Documentation Requirements: Ensure that all necessary documentation for compliance is provided, including certificates of conformity and test reports.
- Cultural Considerations: Be aware of cultural differences that may impact communication and expectations regarding quality. Establishing clear lines of communication can help mitigate misunderstandings.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures specific to hydraulic lift systems, B2B buyers can better evaluate potential suppliers and ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
Related Video: Mass Production Processes and Modern Manufacturing Machines ▶4
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic lift system Sourcing
Cost Structure of Hydraulic Lift Systems
Understanding the cost structure of hydraulic lift systems is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This is typically the largest portion of the cost, encompassing hydraulic cylinders, pumps, hoses, and other structural components. The choice of materials significantly impacts both the price and the durability of the system.
-
Labor: Labor costs include wages for skilled workers involved in assembly and installation. This can vary based on the location of manufacturing and the complexity of the lift system.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: These costs cover utilities, maintenance of machinery, and facility expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, thus lowering overall costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specific hydraulic lift designs, which can add to initial costs. However, investing in quality tooling can lead to long-term savings through improved production efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a robust QC process is vital, especially for safety-critical systems like hydraulic lifts. The costs associated with QC can vary based on industry standards and certifications required.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can fluctuate based on distance, shipping method, and the size of the order. International buyers should consider these expenses in their total cost calculations.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin that reflects their profit expectations, which can vary widely depending on market conditions and competition.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of hydraulic lift systems:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders can often secure better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-built hydraulic lifts tailored to specific applications may incur higher costs. Clarity in specifications can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can affect durability and performance. High-quality materials may lead to higher upfront costs but can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with international safety and quality standards may lead to higher costs but is essential for ensuring operational safety and meeting regulatory requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and geographic location can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge premium prices for reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the final cost.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency
For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable insights to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms, especially when dealing with high-volume orders. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle cost of the hydraulic lift system, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences that can arise from local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and shipping costs. In some cases, sourcing from nearby suppliers may reduce logistics expenses.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from several suppliers to compare pricing, delivery times, and service offerings. This can help identify the best overall value rather than just the lowest price.
-
Be Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends and market conditions can provide leverage during negotiations and help anticipate price changes.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate pricing for their needs.
Spotlight on Potential hydraulic lift system Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘hydraulic lift system’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic lift system
Key Technical Properties of Hydraulic Lift Systems
Understanding the essential technical properties of hydraulic lift systems is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making procurement decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of hydraulic components, such as cylinders and hoses, significantly affects performance and durability. Common materials include high-strength steel and reinforced rubber, which provide resistance to pressure and wear. Selecting the appropriate material ensures that the lift system can withstand operational demands, thus minimizing maintenance costs and downtime. -
Load Capacity
Load capacity is a vital specification indicating the maximum weight the hydraulic lift can handle safely. This is typically expressed in tons or kilograms. Buyers must evaluate their operational needs to select a lift system with an adequate load capacity to avoid potential safety hazards and equipment failure.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating, usually measured in bar or psi, denotes the maximum pressure the hydraulic system can safely operate under. A higher pressure rating often correlates with a more powerful lift. Understanding this property helps buyers choose systems that align with their operational requirements while ensuring safety and efficiency. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the permissible limits of variation in dimensions and performance characteristics. High tolerance levels in hydraulic components ensure precise operation, which is essential for applications requiring exact positioning. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide detailed tolerance specifications to ensure compatibility and reliability. -
Cycle Time
Cycle time measures the duration required for the hydraulic lift to complete one full lift and lower cycle. This parameter is critical in high-volume operations, as shorter cycle times can lead to increased productivity. B2B buyers should assess cycle times to ensure that the lift system meets their operational efficiency goals.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency indicates how effectively the hydraulic system converts energy into lifting power. Systems with higher efficiency ratings reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Buyers should consider energy-efficient models to align with sustainability goals and reduce long-term expenses.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiations for international B2B buyers. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or systems that are sold under another company’s brand. Understanding this term helps buyers identify quality suppliers who can provide reliable components that meet their specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers must consider MOQs to ensure they can meet procurement budgets while avoiding excess inventory. Negotiating MOQs can lead to better pricing and supply chain efficiency. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This term is crucial for buyers to understand as it helps streamline the procurement process and ensures that they receive competitive offers.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is essential for international trade, as they help clarify obligations and reduce the risk of misunderstandings. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for planning operations and managing supply chain efficiency. Buyers should evaluate lead times during procurement to ensure timely delivery of hydraulic lift systems. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards refer to the compliance of products with specific safety and quality regulations. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who meet recognized certification standards to ensure the reliability and safety of hydraulic lift systems.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure the safety and reliability of hydraulic lift systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the hydraulic lift system Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The hydraulic lift system sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. Increased urbanization, particularly in Africa and South America, is leading to greater demand for efficient material handling solutions in construction and logistics. Additionally, advancements in automation and Industry 4.0 technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling the integration of smart hydraulic systems that enhance operational efficiency. B2B buyers must stay informed about these technological shifts to leverage opportunities that improve productivity and reduce costs.
Emerging trends include the adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) in hydraulic systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This shift not only enhances reliability but also decreases downtime, a critical factor for businesses in competitive markets. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on digital procurement platforms that streamline sourcing processes, making it easier for international buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and products, particularly from regions like Europe and the Middle East where quality standards are high.
Market dynamics are also influenced by global supply chain challenges, necessitating a shift towards local sourcing in certain regions to mitigate risks associated with transportation delays and tariffs. B2B buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to provide flexibility and responsiveness, ensuring a continuous flow of hydraulic lift systems and components.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the procurement of hydraulic lift systems. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or implementing energy-efficient technologies.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should engage with suppliers who adhere to international labor standards and environmental regulations, thereby minimizing risks associated with unethical practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and can serve as benchmarks for evaluating potential partners.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials in hydraulic lift systems—such as biodegradable hydraulic fluids and components made from recycled materials—can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of operations. B2B buyers should actively seek out these options as part of their sustainability strategy, aligning their procurement practices with broader corporate social responsibility goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The hydraulic lift system sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 19th century. Initially developed for industrial applications, hydraulic systems have expanded into various sectors, including construction, transportation, and logistics. The introduction of hydraulic fluid dynamics and advancements in materials science have led to more efficient and reliable systems.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards automation and integration with digital technologies, enabling smarter and more responsive hydraulic systems. Today, the sector is at the forefront of the sustainability movement, with ongoing innovations aimed at reducing environmental impact while enhancing performance. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with modern operational and ethical standards.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic lift system
-
How do I vet suppliers for hydraulic lift systems?
Supplier vetting is crucial for ensuring reliability and quality. Start by researching suppliers’ backgrounds, including their years in business, certifications, and customer reviews. Request references and case studies to assess their experience with similar projects. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility or arranging virtual tours to evaluate their manufacturing processes. For international suppliers, verify compliance with local and international standards relevant to hydraulic systems, such as ISO certifications. -
Can hydraulic lift systems be customized to meet specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for hydraulic lift systems. When discussing your requirements, provide detailed specifications such as load capacity, lift height, and operational environment. Engage in a dialogue with the supplier to understand their capabilities and limitations. It’s also advisable to review previous custom projects they have executed to gauge their expertise in delivering tailored solutions. Ensure that any customization aligns with safety standards and regulations in your region. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for hydraulic lift systems?
MOQs can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the hydraulic lift systems. Generally, suppliers may require a minimum order of one unit for customized solutions, while standard models might have higher MOQs. Lead times also vary based on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s current production capacity. On average, expect lead times of 4 to 12 weeks. Always confirm these details upfront to ensure they align with your project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing hydraulic lift systems?
Payment terms can differ among suppliers, but typical arrangements include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. It’s essential to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfers, letters of credit) and any potential additional costs, such as tariffs or taxes that might apply to international transactions. Ensure that all terms are documented in the contract. -
What quality assurance (QA) certifications should I look for?
When sourcing hydraulic lift systems, look for suppliers with recognized quality assurance certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Additionally, check for compliance with specific industry standards relevant to hydraulic systems, such as EN 1570 (for lifting platforms) or ANSI/ASME standards. Request documentation that demonstrates the supplier’s commitment to quality, including test reports, inspection certificates, and warranty details. This ensures that the products meet safety and performance expectations. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international orders of hydraulic lift systems?
Logistics for international orders involve several steps, including selecting a reliable freight forwarder and understanding import/export regulations. Discuss shipping methods (e.g., sea freight, air freight) with your supplier and obtain estimates for shipping costs and delivery timelines. Ensure that all necessary shipping documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, is prepared in advance. Consider insurance coverage for the shipment to protect against potential loss or damage during transit. -
What should I do if there’s a dispute with the supplier?
In the event of a dispute, the first step is to communicate directly with the supplier to resolve the issue amicably. Clearly outline your concerns and provide supporting documentation. If discussions do not yield a satisfactory resolution, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution. This may include mediation or arbitration processes. Having legal counsel familiar with international trade laws can also be beneficial for navigating complex disputes effectively. -
Are there any specific regulations I need to be aware of when importing hydraulic lift systems?
Yes, when importing hydraulic lift systems, you must comply with local regulations, which may include safety standards, environmental regulations, and import tariffs. Research the specific requirements in your country or region, as they can vary widely. For instance, the EU has stringent CE marking requirements for machinery, while other regions may have different compliance standards. Engaging with a customs broker can help ensure that all regulatory requirements are met, minimizing the risk of delays or penalties during the import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic lift system
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of hydraulic lift systems is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Key takeaways include the importance of developing a comprehensive procurement strategy that encompasses supplier segmentation, procurement catalog management, and ongoing market analysis. By leveraging these strategies, businesses can foster strong supplier relationships, ensure compliance, and achieve significant cost savings.
Furthermore, as industries increasingly adopt automation and advanced technologies, investing in innovative hydraulic solutions will position companies to meet evolving market demands. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize collaboration with reliable suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and sustainability.
Looking ahead, the market for hydraulic lift systems is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for efficient material handling solutions. International buyers are encouraged to stay informed about market trends and actively engage in sourcing strategies that align with their organizational goals. By taking proactive steps now, companies can secure a competitive edge in the global marketplace.