Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Industrial Steam Boiler
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial steam boiler
In today’s dynamic global market, the industrial steam boiler stands as a cornerstone for numerous sectors, including manufacturing, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and energy generation. These complex pressure vessels convert fuel or electrical energy into vital steam, facilitating processes that require heat and pressure. Understanding the intricacies of industrial steam boilers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those operating in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of industrial steam boilers, their construction materials, and manufacturing quality control standards. It outlines the essential factors to consider when selecting a supplier, including cost analysis, operational efficiency, and compliance with safety regulations. Additionally, it addresses common FAQs to ensure that buyers are well-informed about their options and obligations.
By providing a thorough understanding of these critical components, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. It equips them with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the industrial steam boiler market, ensuring that they can select the most appropriate solutions tailored to their operational needs. Whether you are a buyer in France seeking the latest technology or a Colombian firm looking to enhance production efficiency, this resource is designed to enhance your procurement strategy and drive business success.
Understanding industrial steam boiler Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fire-Tube Boiler | Hot gases pass through tubes surrounded by water. | Food processing, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. | Pros: Lower initial cost, compact design. Cons: Limited steam capacity, less efficient at high pressures. |
| Water-Tube Boiler | Water circulates in tubes heated by combustion gases. | Power generation, chemical processing. | Pros: High steam capacity, efficient at high pressures. Cons: Higher initial investment, complex maintenance. |
| Electric Boiler | Uses electric resistance to generate steam. | Small-scale operations, hospitals, and laboratories. | Pros: Clean energy source, easy installation. Cons: Higher operating costs, limited capacity. |
| Biomass Boiler | Utilizes organic materials as fuel. | Renewable energy projects, food processing. | Pros: Eco-friendly, reduces fossil fuel dependency. Cons: Variable fuel quality, requires more space. |
| Combination Boiler | Capable of using multiple fuel types (gas, oil, biomass). | Versatile applications across industries. | Pros: Flexibility in fuel choice, adaptable to market changes. Cons: More complex design, potential for higher maintenance costs. |
Fire-Tube Boiler
Fire-tube boilers are characterized by hot gases traveling through tubes, which are surrounded by water. This type is particularly suitable for lower pressure applications, making it popular in industries such as food processing and textiles. Buyers should consider the lower initial costs and compact design, but be mindful of the limitations in steam capacity and efficiency at high pressures.
Water-Tube Boiler
In water-tube boilers, water circulates within tubes heated by combustion gases. This design allows for a higher steam capacity and greater efficiency, especially at elevated pressures, making them ideal for power generation and chemical processing. While they require a higher initial investment and more complex maintenance, their operational efficiency can lead to long-term savings.
Electric Boiler
Electric boilers convert electrical energy into steam using resistance heating. These units are particularly advantageous for small-scale operations, such as hospitals or laboratories, due to their clean energy source and ease of installation. However, potential buyers should consider the higher operating costs and limited capacity compared to traditional fuel-fired boilers.
Biomass Boiler
Biomass boilers utilize organic materials, such as wood pellets or agricultural waste, as fuel. They are increasingly favored in renewable energy projects and food processing due to their eco-friendly nature and ability to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. However, buyers must account for the variable quality of biomass fuel and the need for more space for storage and operation.
Combination Boiler
Combination boilers can operate using multiple fuel types, such as gas, oil, or biomass, providing flexibility for various industrial applications. This adaptability can be particularly beneficial in fluctuating market conditions or when fuel prices vary. However, the complexity of their design may lead to higher maintenance costs, which buyers should factor into their purchasing decisions.
Related Video: How Steam Boiler Auxiliaries Operations?
Key Industrial Applications of industrial steam boiler
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industrial steam boiler | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Cooking and sterilization | Ensures food safety and quality, reduces production time | Compliance with hygiene standards, energy efficiency, and steam quality |
| Textile Manufacturing | Dyeing and finishing processes | Enhances color consistency and fabric quality | Temperature control, pressure requirements, and reliability of supply |
| Pharmaceutical | Sterilization and heating | Guarantees product safety and efficacy | Adherence to strict regulatory standards, water quality, and system automation |
| Chemical Processing | Chemical reactions and heating | Increases reaction efficiency and product yield | Customized boiler design, pressure and temperature specifications, and safety features |
| Power Generation | Steam-driven turbines for electricity production | Provides a renewable energy source, reduces carbon footprint | Fuel type compatibility, efficiency ratings, and maintenance support |
Food Processing
In the food processing industry, industrial steam boilers are essential for cooking, sterilizing, and drying various food products. The steam generated plays a critical role in maintaining food safety and quality, ensuring that products meet health regulations. Buyers should prioritize boilers that comply with hygiene standards and offer energy-efficient solutions, as this can significantly reduce operational costs. Additionally, steam quality is crucial, as impurities can affect food safety.
Textile Manufacturing
Steam boilers are widely used in textile manufacturing for dyeing and finishing processes. The controlled application of steam allows for consistent dye uptake, enhancing the overall quality of the fabric. For international buyers, particularly in regions like South America and Africa, it is vital to consider boilers that provide precise temperature control and meet the specific pressure requirements of their production processes. Reliability in steam supply is also essential to prevent production delays.
Pharmaceutical
In the pharmaceutical sector, steam is used for sterilization and heating processes, ensuring the safety and efficacy of products. The stringent regulatory environment necessitates that buyers select boilers that comply with local and international standards. Water quality is a significant consideration, as impurities can compromise product integrity. Furthermore, automation features in boiler systems can enhance operational efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Chemical Processing
Chemical processing industries utilize industrial steam boilers for facilitating various chemical reactions and heating processes. The efficiency of these reactions can be significantly improved with the right steam conditions. Buyers should focus on customized boiler designs that meet specific pressure and temperature specifications while incorporating essential safety features. This is particularly important in regions with varying regulatory requirements, such as the Middle East and Europe.
Power Generation
Industrial steam boilers are pivotal in power generation, where steam drives turbines to produce electricity. This application not only provides a renewable energy source but also helps in reducing the carbon footprint of power plants. When sourcing boilers for this application, buyers must consider fuel type compatibility, efficiency ratings, and the availability of maintenance support to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
Related Video: Steam Boiler Fundamentals, Basic and Operation
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial steam boiler
When selecting materials for industrial steam boilers, it is crucial to consider the properties and performance characteristics that align with specific operational requirements. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the construction of industrial steam boilers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its excellent tensile strength and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°C (752°F) and can handle pressures of around 20 bar.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and durability, making it a popular choice for many industrial applications. However, it is prone to corrosion, particularly in high-moisture environments, which can lead to maintenance challenges and a shorter lifespan.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications where steam quality is not critically high, such as in heating systems. However, it is less compatible with corrosive media, which may limit its use in certain industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A106 or equivalent. Understanding the local environment’s corrosion potential is essential for selecting carbon steel.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C or 1472°F) and pressures (up to 30 bar). Its composition includes chromium, which enhances its resistance to oxidation.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and low maintenance requirements due to its corrosion-resistant properties. However, it is significantly more expensive than carbon steel, which can impact project budgets.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications requiring high steam quality, such as in the pharmaceutical and food processing industries. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe, particularly in France, should be aware of compliance with EN standards for stainless steel grades. The higher initial investment may be justified by lower maintenance costs over time.
Alloy Steel
Key Properties: Alloy steel, which may contain elements like molybdenum or chromium, is designed for high-temperature applications, typically rated for temperatures above 500°C (932°F) and pressures exceeding 25 bar.
Pros & Cons: Alloy steel provides superior strength and resistance to thermal fatigue, making it suitable for high-performance applications. However, it is more complex to manufacture and can be more expensive than both carbon and stainless steel.
Impact on Application: This material is often used in power generation and heavy industrial processes where high pressure and temperature are critical. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions makes it a preferred choice in demanding environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should ensure that alloy steel components meet specific standards like ASTM A335 for seamless alloy steel pipes. Understanding local manufacturing capabilities is also essential.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper has excellent thermal conductivity, making it highly efficient for heat transfer applications. It can handle temperatures up to 300°C (572°F) and moderate pressures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior thermal efficiency and resistance to corrosion. However, it is less durable under high-pressure conditions and can be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Copper is often used in heat exchangers and low-pressure steam applications where efficiency is paramount. Its compatibility with various fluids makes it a versatile choice in specific industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for copper alloys in different regions. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B280 is crucial for ensuring product quality.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial steam boiler | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General heating applications | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-quality steam applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Alloy Steel | Power generation and heavy industrial processes | Superior strength at high temperatures | More complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Copper | Heat exchangers and low-pressure applications | Excellent thermal conductivity | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
This guide provides insights into material selection for industrial steam boilers, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial steam boiler
The manufacturing process and quality assurance of industrial steam boilers are critical elements that significantly impact their performance, safety, and longevity. International B2B buyers should have a clear understanding of these processes to ensure they are sourcing reliable and efficient products. Here, we delve into the typical manufacturing stages and quality assurance measures that buyers should consider.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process involves selecting high-quality raw materials. Common materials used for industrial steam boilers include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel due to their excellent strength and resistance to high temperatures and pressures.
-
Material Inspection: Before proceeding, suppliers must conduct a thorough inspection of incoming materials to ensure compliance with specifications. This is often governed by international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems.
-
Cutting and Shaping: The raw materials are then cut and shaped into required dimensions using techniques like plasma cutting or water jet cutting. This precision is crucial for ensuring proper fitting during assembly.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming, which involves shaping the components of the boiler.
-
Welding: This is a key technique used to join metal parts. Different welding methods such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) are employed depending on the material and required strength.
-
Bending and Rolling: Steel sheets are bent and rolled into cylindrical shapes to form the boiler shell. This stage requires specialized machinery to ensure accuracy and consistency.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage brings together all individual components to create a complete boiler.
-
Component Assembly: Major components such as the combustion chamber, heat exchanger, and pressure vessel are assembled. Each part must fit precisely to maintain the integrity of the pressure vessel.
-
Installation of Safety Features: Safety devices such as pressure relief valves, water level controls, and safety interlocks are installed during this phase to ensure the boiler operates safely.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves preparing the boiler for operation.
-
Surface Treatment: This includes painting and coating to prevent corrosion and enhance durability. Techniques such as sandblasting and powder coating are commonly used.
-
Final Assembly: Any remaining components, such as insulation and piping, are added. This step also includes the installation of control systems that monitor and manage boiler operations.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is essential to ensure that industrial steam boilers meet safety and performance standards. International B2B buyers should be aware of the following aspects of quality control.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking signifies that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. This is crucial for buyers in the European market.
-
API Standards: For buyers in the oil and gas sectors, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is vital for ensuring the reliability of steam boilers used in these applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to ensure each stage adheres to quality standards. This includes checking welds, dimensions, and alignment.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the boiler is fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes testing pressure levels, leak tests, and operational checks to ensure the boiler performs as expected.
Common Testing Methods
-
Hydrostatic Testing: This method involves filling the boiler with water and pressurizing it to check for leaks and structural integrity.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiographic testing are employed to detect internal flaws without damaging the components.
-
Performance Testing: This assesses the boiler’s efficiency in converting fuel to steam under various operating conditions.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must implement strategies to verify the quality assurance processes of potential suppliers:
-
Audits: Conducting supplier audits can help assess their manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards. This provides insight into their operational capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality control reports and documentation from suppliers can help buyers understand the testing methods used and the outcomes.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing process and final products can provide an unbiased assessment of quality.
Regional Considerations
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional regulatory requirements and industry practices is essential.
-
Local Regulations: Be aware of local safety and environmental regulations that may impact boiler specifications and operational standards.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding supplier communication, documentation, and service levels. Establishing clear communication channels can help navigate these differences.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for industrial steam boilers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and efficient equipment that meets their operational needs.
Related Video: Cochran – Boiler Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial steam boiler Sourcing
Understanding Cost Components in Industrial Steam Boiler Sourcing
When sourcing industrial steam boilers, it’s essential to grasp the cost structure that influences the final pricing. This structure typically includes several key components:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in the boiler significantly impact costs. Common materials include steel, insulation, and components like burners and heat exchangers. Higher quality materials enhance durability and efficiency but come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in the design, assembly, and installation of the boiler. Regions with higher labor costs may lead to increased pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the facilities, utilities, and equipment required for production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs, potentially lowering the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific boiler designs can add to the initial costs. However, this expense may be amortized over larger production runs, making it less significant on a per-unit basis.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are crucial, particularly for pressure vessels, to avoid costly failures and ensure operational safety.
-
Logistics: The costs associated with transporting the boilers from the manufacturing site to the buyer’s location can vary widely based on distance, shipping method, and Incoterms agreed upon.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin based on their operational costs, market conditions, and competition. Understanding this margin can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
Influencers on Pricing
Several factors influence the pricing of industrial steam boilers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often results in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs to meet specific operational needs can lead to higher costs. Standard models generally offer lower pricing due to streamlined production processes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Boilers that meet stringent international standards or certifications may command higher prices but provide better reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The agreed Incoterms can have significant implications for total costs. Buyers should ensure clarity on who bears responsibility for shipping, insurance, and tariffs to avoid unexpected expenses.
Strategic Buyer Tips
International B2B buyers should keep several strategies in mind to optimize their sourcing of industrial steam boilers:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Use your understanding of cost components and price influencers to negotiate better terms. Be prepared to discuss your purchasing volume and long-term needs, which can incentivize suppliers to offer discounts.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. A more expensive boiler may offer better energy efficiency, resulting in lower operating costs over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may experience varying pricing structures due to labor costs, material availability, and regulatory environments. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should research local market conditions to inform their negotiations.
-
Be Aware of Currency Fluctuations: For international transactions, currency exchange rates can impact overall costs. Buyers should consider locking in prices or exploring options to mitigate currency risk.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and can vary significantly based on specific project requirements, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. Always consult with multiple suppliers to obtain tailored quotes that accurately reflect your needs.
Spotlight on Potential industrial steam boiler Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘industrial steam boiler’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial steam boiler
Key Technical Properties of Industrial Steam Boilers
Understanding the essential technical properties of industrial steam boilers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in industries where efficiency and safety are paramount. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The material grade refers to the type of steel used in constructing the boiler. Common grades include Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, and Alloy Steel.
– Importance: The choice of material affects the boiler’s durability, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand high pressure and temperature. Selecting the appropriate material can significantly impact the lifespan and maintenance costs of the boiler. -
Pressure Rating
– Definition: This specification indicates the maximum pressure the boiler can safely operate under, typically measured in psi (pounds per square inch).
– Importance: Understanding pressure ratings is vital for compliance with safety standards. It helps buyers ensure that the boiler is suitable for their specific industrial applications, particularly in high-demand environments. -
Heat Transfer Efficiency
– Definition: This property measures how effectively the boiler converts energy from fuel into steam. It is often expressed as a percentage.
– Importance: High heat transfer efficiency leads to lower fuel consumption and reduced operating costs. For buyers, investing in a boiler with superior efficiency translates into long-term savings and a lower environmental footprint. -
Steam Quality
– Definition: Steam quality refers to the dryness fraction of steam, which indicates the amount of moisture present. High-quality steam is typically defined as having a dryness fraction of 0.95 or higher.
– Importance: The quality of steam affects production processes in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Ensuring high-quality steam is essential for maintaining product integrity and operational efficiency. -
Capacity
– Definition: This refers to the amount of steam the boiler can produce over a specific period, usually measured in pounds per hour (lb/hr) or tons per hour.
– Importance: Knowing the required steam capacity is critical for ensuring that the boiler meets the operational demands of the business. Oversizing can lead to unnecessary expenses, while undersizing can cause production delays.
Common Trade Terminology
Navigating the procurement process requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: For buyers, sourcing from an OEM can ensure that they are getting high-quality, compatible components that meet the specific requirements of their steam boiler systems.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQs is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate these terms to align with their operational needs and financial constraints. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific product or service.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs allows buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they obtain the best value and terms for their purchases. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, insurance, and risk management, which are essential for smooth international trade operations. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time is essential for planning and ensuring that production schedules are met. Buyers should consider lead times when making procurement decisions to avoid disruptions in operations. -
Warranty
– Definition: A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the product and the terms of repair or replacement if necessary.
– Importance: Understanding warranty terms is essential for buyers to protect their investment and ensure that they have recourse in case of equipment failure.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their industrial steam boiler investments are both efficient and cost-effective.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the industrial steam boiler Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The industrial steam boiler market is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. Key drivers include increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions across manufacturing sectors, a surge in industrial automation, and a growing emphasis on reducing carbon footprints. Regions such as Africa and South America are witnessing rapid industrialization, leading to higher steam demand for processes like food processing and textile manufacturing. In Europe, stringent regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions are compelling industries to adopt advanced boiler technologies.
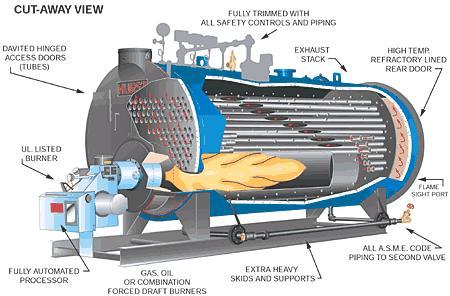
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing include the integration of smart technologies and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities within steam boilers. This enables real-time monitoring and optimization of boiler operations, leading to enhanced efficiency and reduced operational costs. Additionally, the shift towards modular and scalable boiler systems allows businesses to tailor their steam solutions to specific production needs, facilitating easier upgrades and maintenance.
International buyers should also consider the benefits of sourcing from local manufacturers to mitigate supply chain disruptions and tariffs, particularly in the current global economic climate. Understanding regional market dynamics, such as varying energy costs and regulatory requirements, will be crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical concern for businesses in the industrial steam boiler sector. The environmental impact of traditional boiler systems, particularly concerning emissions and resource consumption, is prompting manufacturers to innovate. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through the use of renewable energy sources, such as biomass or solar energy, and technologies that reduce emissions.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and demonstrate transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management can serve as benchmarks for evaluating supplier sustainability efforts. Moreover, opting for ‘green’ materials, such as low-carbon steel or recycled components, can significantly enhance the overall sustainability profile of steam boiler systems.
By focusing on sustainable and ethical sourcing, businesses not only comply with regulatory demands but also appeal to increasingly environmentally-conscious consumers, thereby enhancing brand reputation and market competitiveness.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of industrial steam boilers dates back to the early 18th century, marking a transformative period in manufacturing and energy production. Initially, steam boilers were simple devices, primarily used for powering early steam engines. Over the years, advancements in materials science and engineering led to the development of more efficient and safer pressure vessels.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the industrial revolution spurred the widespread adoption of steam boilers in various sectors, including textiles and food processing. The introduction of safety regulations and standards in the mid-20th century further shaped the industry, emphasizing the importance of safety and efficiency. Today, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and technological integration, with modern boilers designed to meet both operational and environmental standards, reflecting the industry’s continuous adaptation to global challenges.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial steam boiler
-
What key factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for industrial steam boilers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in manufacturing industrial steam boilers and their compliance with international safety standards. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 and ASME that ensure quality and reliability. Additionally, assess their track record by requesting references from other B2B buyers in your region. Evaluate their production capacity to meet your needs and inquire about their after-sales support and service capabilities to ensure you receive ongoing assistance. -
Can I customize the industrial steam boiler to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for industrial steam boilers. You can specify requirements such as steam pressure, temperature, fuel type, and size based on your operational needs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific applications and any industry regulations with the supplier during the initial consultation. Ensure that the supplier can provide documentation that confirms the boiler’s compliance with relevant safety and efficiency standards. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for industrial steam boilers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and boiler type. Generally, MOQs range from one unit to several, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and your customization requests. Lead times can also vary, often ranging from 8 to 16 weeks for standard models. For customized units, lead times may extend further, so it’s crucial to communicate your timeline needs early in the negotiation process to avoid delays. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of industrial steam boilers?
Payment terms vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms based on your relationship and order size. It’s essential to clarify all payment terms and conditions before finalizing the order to avoid misunderstandings later.
-
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for the industrial steam boiler I purchase?
Request detailed information about the supplier’s quality assurance processes, including any relevant certifications they hold, such as ISO, CE, or UL. Ask for copies of test reports and compliance certificates for the specific boiler models you are considering. Additionally, inquire about their quality control procedures during manufacturing and the testing process for boilers before shipment to ensure that they meet international standards and your operational requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing an industrial steam boiler internationally?
Logistics involve several key factors, including shipping methods, costs, and customs regulations. Discuss with your supplier whether they will handle shipping or if you need to arrange it independently. Understand the incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to clarify responsibility for shipping costs and risks. Additionally, familiarize yourself with customs requirements in your country to ensure a smooth import process and to avoid unexpected delays or fees. -
What should I do if a dispute arises with the supplier after purchasing the boiler?
In case of a dispute, the first step is to communicate directly with the supplier to resolve the issue amicably. Document all correspondence and keep records of agreements and contracts. If necessary, refer to the terms outlined in your purchase agreement, including any warranty or service clauses. Should informal negotiations fail, consider mediation or arbitration as a cost-effective way to resolve disputes without escalating to litigation, which can be time-consuming and expensive. -
How can I stay informed about the latest technology and trends in industrial steam boilers?
To stay updated, subscribe to industry publications, join relevant trade associations, and attend trade shows and conferences focused on industrial equipment. Engage with online forums and professional networks to exchange insights with other B2B buyers and suppliers. Additionally, follow leading manufacturers on social media platforms and sign up for newsletters to receive the latest news on technological advancements and best practices in steam boiler applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial steam boiler
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of industrial steam boilers is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring safety compliance across various industries. Key takeaways for international B2B buyers include the importance of understanding specific application requirements, selecting the right boiler type, and adhering to local regulations. By prioritizing customization and energy efficiency, companies can significantly enhance their production capabilities while reducing operational costs.
As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for reliable steam generation will only grow. Buyers should focus on building partnerships with reputable manufacturers who offer comprehensive support, including installation, maintenance, and operational training.
Looking ahead, the adoption of innovative technologies and sustainable practices will shape the future of industrial steam boilers. We encourage international buyers to stay informed on emerging trends and advancements in boiler technology, which will not only improve productivity but also contribute to environmental sustainability. Make strategic sourcing a priority to secure a competitive edge in your industry.