Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Industries With Oems
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industries with oems
Navigating the global market for industries with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) is essential for B2B buyers aiming to leverage innovation, efficiency, and competitive pricing in their sourcing strategies. As the demand for high-quality components and products escalates, understanding the intricacies of OEM partnerships becomes critical. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of industries utilizing OEMs, offering invaluable insights for international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
With a focus on diverse sectors such as electronics, automotive, and consumer goods, this comprehensive resource covers key aspects including types of OEMs, materials used, and manufacturing and quality control processes. It also highlights top suppliers, provides cost analysis, and explores market trends that influence sourcing decisions.
By empowering buyers with actionable information and addressing frequently asked questions, this guide equips decision-makers to navigate the complexities of global sourcing effectively. Whether you are a buyer in Colombia looking for reliable suppliers in China or a procurement officer in Vietnam seeking cost-effective production solutions, understanding the dynamics of OEM industries will enhance your sourcing capabilities and drive business success.
Understanding industries with oems Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics OEMs | Focus on high-tech components, rapid prototyping, and scalability. | Consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices. | Pros: Access to advanced technology; Cons: Potential IP risks. |
| Textile OEMs | Specialization in fabric production, dyeing, and garment assembly. | Apparel, home textiles, industrial fabrics. | Pros: Cost-effective production; Cons: Quality variability. |
| Automotive OEMs | Expertise in vehicle components, compliance with safety standards. | Auto parts manufacturing, assembly lines. | Pros: High-quality standards; Cons: Long lead times. |
| Consumer Goods OEMs | Broad range of products, often leveraging brand partnerships. | Household items, personal care products. | Pros: Flexibility in product design; Cons: Less control over production. |
| Pharmaceutical OEMs | Strict adherence to regulatory standards, focus on drug formulation. | Drug manufacturing, medical devices. | Pros: High compliance assurance; Cons: Higher costs due to regulations. |
Electronics OEMs
Electronics OEMs are characterized by their focus on high-tech components, rapid prototyping, and the ability to scale production quickly. They are suitable for businesses in sectors like consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices. Key purchasing considerations include the manufacturer’s technological capabilities, compliance with international standards, and the potential risks associated with intellectual property protection.
Textile OEMs
Textile OEMs specialize in fabric production, dyeing, and garment assembly, making them ideal for the apparel, home textiles, and industrial fabrics sectors. When purchasing from textile OEMs, buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of production, the quality of materials, and the potential for variability in product quality. It’s crucial to establish clear quality standards to mitigate risks.
Automotive OEMs
Automotive OEMs possess expertise in vehicle components and compliance with stringent safety standards. They are primarily engaged in auto parts manufacturing and assembly lines. Buyers in this sector should prioritize manufacturers with proven track records in quality assurance and timely delivery, while also being aware of potential long lead times that can affect inventory management.
Consumer Goods OEMs
Consumer goods OEMs produce a broad range of products and often work closely with brand partners. They are suitable for businesses in the household items and personal care sectors. Buyers should look for flexibility in product design and the ability to adapt to market trends. However, they may experience less control over production processes, which can lead to inconsistencies.
Pharmaceutical OEMs
Pharmaceutical OEMs are distinguished by their strict adherence to regulatory standards and a focus on drug formulation. They cater to drug manufacturing and medical device production. Buyers must consider the high compliance assurance provided by these manufacturers, but they should also be prepared for higher costs associated with regulatory compliance. Establishing strong communication about quality expectations is essential in this sector.
Related Video: Economic models | Basic economics concepts | AP Macroeconomics and Microeconomics | Khan Academy
Key Industrial Applications of industries with oems
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Industries with OEMs | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of automotive parts and assemblies | Enhanced production efficiency and cost reduction | Supplier reliability, compliance with safety standards |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of electronic components and devices | Access to advanced technology and reduced time-to-market | Quality certifications (ISO, IPC), prototyping capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Production of medical instruments and equipment | Compliance with regulatory standards and enhanced quality | FDA compliance, material sourcing, and testing protocols |
| Consumer Goods | Assembly of consumer products like appliances and furniture | Increased scalability and flexibility in production | Customization options, lead times, and logistics |
| Renewable Energy | Manufacturing of solar panels and wind turbine components | Cost savings and sustainability in production | Material sourcing, technological expertise, and certifications |
Automotive
In the automotive sector, OEMs collaborate with specialized manufacturers to produce various components such as engines, transmission systems, and electronic control units. This partnership not only boosts production efficiency but also significantly reduces operational costs. For international buyers, especially those in Africa and South America, it’s crucial to ensure suppliers meet safety and quality standards, as well as to evaluate their capacity for timely delivery amid fluctuating demand.
Electronics
The electronics industry relies heavily on OEMs for the production of components like printed circuit boards (PCBs) and consumer electronics. By outsourcing these manufacturing processes, companies can leverage advanced technologies and expertise, which helps in accelerating product development and reducing time-to-market. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers with strong quality certifications and prototyping capabilities to ensure that the final products meet stringent performance standards.
Medical Devices
OEM partnerships are vital in the medical device sector, where precision and compliance with regulatory standards are paramount. Manufacturers produce everything from diagnostic equipment to surgical instruments, ensuring that they adhere to rigorous quality and safety protocols. For international B2B buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, it is essential to verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications, such as FDA approval, and robust testing protocols to ensure product reliability.
Consumer Goods
In the consumer goods industry, OEMs facilitate the assembly of a wide range of products, including home appliances and furniture. This collaboration allows businesses to scale operations rapidly and adapt to changing market demands without significant capital investment. Buyers should consider customization options offered by manufacturers, as well as lead times and logistics capabilities, to maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector benefits greatly from OEM relationships, particularly in the production of solar panels and wind turbine components. These partnerships enable companies to achieve cost savings while promoting sustainability. For international buyers, sourcing considerations should include the availability of high-quality materials, technological expertise, and adherence to relevant environmental certifications, which are crucial for ensuring long-term viability and compliance in this rapidly evolving industry.
Related Video: Uses of Aluminium | Environmental Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industries with oems
When selecting materials for industries that rely on Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), it is essential to consider the specific properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials. This guide analyzes four common materials used in OEM applications, focusing on their performance characteristics, suitability for different products, and strategic considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and possesses excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and is often used in applications requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its durability and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for outdoor applications. However, it can be more expensive than other metals and may require specialized manufacturing processes like welding or anodizing.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries for components such as frames, panels, and heat exchangers due to its lightweight nature and strength.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local regulations regarding aluminum recycling and manufacturing standards, such as ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum products.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its high corrosion resistance, strength, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures (up to 1000°C). It is available in various grades, each tailored for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, it is generally more costly than carbon steel and can be challenging to machine.
Impact on Application: This material is widely used in the food processing, medical, and chemical industries, where hygiene and resistance to corrosion are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM A240 for stainless steel sheets and plates. Understanding local sourcing options in Europe or the Middle East can also provide cost advantages.
3. Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity. It can operate effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of polycarbonate is its lightweight nature and high strength, making it an excellent choice for transparent applications like safety glasses and protective shields. However, it can be more expensive than traditional plastics and may be prone to scratching without proper coatings.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is often used in the electronics and automotive industries for components like lenses, covers, and housings due to its transparency and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ISO 11469 for plastics. Understanding the local market dynamics in regions like Vietnam can help in sourcing polycarbonate at competitive prices.
4. Carbon Fiber
Key Properties: Carbon fiber is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and is resistant to corrosion and fatigue.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon fiber is its exceptional strength and lightweight properties, making it ideal for high-performance applications. However, it is expensive and requires specialized manufacturing techniques, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: This material is primarily used in the aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries, where performance and weight savings are crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of carbon fiber suppliers and compliance with standards such as ASTM D7260 for composite materials. Additionally, understanding the import regulations in their respective regions is vital for smooth transactions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for industries with oems | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive frames, aerospace panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than other metals | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment, medical devices | High corrosion resistance | More expensive and hard to machine | High |
| Polycarbonate | Electronics housings, safety glasses | Impact resistance and clarity | Prone to scratching | Medium |
| Carbon Fiber | Aerospace components, high-performance sports gear | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into material properties, advantages, and considerations, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional market dynamics.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industries with oems
Manufacturing Processes in OEM Industries
Understanding the manufacturing processes involved in Original Equipment Manufacturing (OEM) is crucial for B2B buyers. Each stage is designed to ensure efficiency and quality, enabling companies to deliver high-caliber products. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the main stages of manufacturing:
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. This stage is critical as the quality of raw materials directly impacts the final product. Buyers should ensure that suppliers adhere to international standards for material quality. Techniques such as material inspection and testing for compliance with specifications are vital at this stage.
Forming
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes, which may include methods like casting, machining, or molding. Each method has its advantages depending on the material and desired product characteristics. For example:
- Casting is often used for metals and allows complex shapes.
- Machining provides high precision and is typically used for metals and plastics.
- Injection molding is a key technique in plastic manufacturing, enabling high-volume production with consistent quality.
Buyers should inquire about the specific forming techniques used by their suppliers and assess their capabilities based on the complexity of the products they intend to source.
Assembly
The assembly stage combines various components into a finished product. This can involve manual labor or automated processes, depending on the complexity and scale of production. Quality checks should be integrated into the assembly line, such as:
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the assembly process to detect defects early.
- Final Assembly Checks: Ensuring all parts fit and function as intended.
B2B buyers should evaluate how assembly processes align with their product specifications and ensure that suppliers maintain rigorous assembly standards.
Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the product’s appearance and protect it from environmental factors. Techniques include painting, coating, and polishing. Quality control during this phase is essential to ensure that the product meets aesthetic and functional requirements. Buyers should request samples of finished products to assess quality before committing to large orders.
Quality Assurance in OEM Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, especially in industries with OEMs. It ensures that products meet predetermined standards and specifications. Here are the key elements of QA relevant to B2B buyers:
International Standards
Many industries adhere to international quality standards, with ISO 9001 being one of the most recognized. This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system and emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Other industry-specific certifications may include:
- CE Marking for products sold in the European Economic Area.
- API Standards for products in the oil and gas industry.
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers hold relevant certifications, as this reflects their commitment to quality.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with quality standards. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting thorough checks of the finished product before shipment.
Implementing these checkpoints can significantly reduce the risk of defects reaching the market.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to verify product quality, including:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects.
- Dimensional Testing: Ensuring products meet specified dimensions.
- Functional Testing: Verifying that products operate as intended.
Buyers should discuss testing methodologies with potential suppliers to understand their approach to quality assurance.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers meet quality standards, B2B buyers should implement verification strategies, including:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site evaluations of the manufacturing processes and quality systems.
- Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of previous QC results, including non-conformance reports and corrective action plans.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to assess product quality before shipment.
These steps provide buyers with confidence in their suppliers’ ability to deliver high-quality products consistently.
Navigating QC and Certification Nuances
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial. Each region may have specific regulations and standards that affect product compliance.
- Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with local regulatory requirements and standards, such as the GCC certification in the Middle East or SANS standards in South Africa.
- Cultural Considerations: Recognize that quality perceptions may vary across regions, affecting buyer-supplier relationships. Open communication about quality expectations can bridge these gaps.
- Documentation and Traceability: Ensure that suppliers maintain detailed records of their QC processes, allowing for traceability in case of defects or recalls.
By taking these factors into account, B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of working with OEMs and ensure that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: Top 5 Mass Production Techniques: Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industries with oems Sourcing
In the realm of industries leveraging Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge enables buyers to make informed decisions, optimize sourcing strategies, and enhance overall cost-efficiency.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant component of the overall production cost. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand, regional availability, and specific material characteristics. Buyers should consider sourcing materials from suppliers with stable pricing or those located in regions with lower production costs to mitigate risks.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly across different regions. For instance, average hourly wages in manufacturing are approximately $6.50 in China and $3.50 in Vietnam as of 2023. Understanding local labor markets can help buyers negotiate better rates and identify suitable manufacturing locations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative costs. Buyers should inquire about overhead percentages when negotiating contracts, as these can vary widely between suppliers.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are essential for custom parts and can be substantial, especially for complex designs. Buyers should factor in these costs early in the negotiation process, as they can significantly impact the total cost of ownership (TCO).
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes is vital for maintaining product standards. Buyers should assess the QC measures in place at potential suppliers and consider how these costs are integrated into pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can influence the overall price significantly. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and any tariffs or duties applicable to imports should be evaluated. Utilizing Incoterms effectively can help clarify responsibilities regarding shipping and reduce unforeseen expenses.
-
Margin: The manufacturer’s profit margin is influenced by competition, market demand, and the perceived value of the product. Understanding typical margins within specific industries can aid buyers in assessing fair pricing.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Price Influencers
Several factors can affect pricing when sourcing from OEMs:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should evaluate their demand forecasts to negotiate better pricing structures.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom products usually command higher prices due to the additional resources required for design and production. Clearly defining product specifications can help mitigate these costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts both cost and quality. Buyers should consider alternatives that provide similar performance at a lower price point.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products meeting specific quality standards or certifications may incur higher costs. Buyers should balance the need for quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can often yield better terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding and negotiating Incoterms is vital for cost management. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the total cost.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open dialogue with suppliers. Discussing cost breakdowns can lead to more favorable terms and greater transparency in pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider not just the unit price but the total cost of ownership, including logistics, tariffs, and potential costs associated with defects or delays.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of regional market dynamics that affect pricing. For instance, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact the final costs when sourcing from countries like China or Vietnam.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Prices are subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and geopolitical factors. It is advisable for buyers to continuously monitor market trends and engage in periodic reviews of supplier contracts.
By understanding the intricate cost structures and pricing influencers in OEM sourcing, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they achieve the best possible value for their investments.
Spotlight on Potential industries with oems Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘industries with oems’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industries with oems
In the context of industries with OEMs, understanding key technical properties and trade terminology is essential for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only facilitates better communication but also ensures that decision-makers can effectively evaluate products and services offered by suppliers.
Critical Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the classification of materials based on their properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity.
– Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that products meet specific performance standards and regulatory requirements. For example, in the automotive industry, using high-grade steel can enhance safety and durability. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance is the allowable deviation from a specified dimension or property in manufactured parts.
– Importance: Precise tolerances are crucial for ensuring that components fit together correctly, especially in assemblies where multiple parts interact. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to increased costs due to rework or product failures. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: Surface finish describes the texture and smoothness of a material’s surface after manufacturing processes.
– Importance: A proper surface finish can influence the performance of a product, affecting factors like friction, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Industries such as electronics and medical devices often require specific finishes to ensure functionality and compliance with health standards. -
Load Capacity
– Definition: Load capacity indicates the maximum load a component can safely support without failure.
– Importance: Understanding load capacity is vital for applications in construction, machinery, and automotive industries. Insufficient load capacity can lead to catastrophic failures, safety hazards, and financial losses. -
Cycle Time
– Definition: Cycle time is the total time taken to complete one cycle of manufacturing, from start to finish.
– Importance: Reducing cycle time is essential for improving efficiency and meeting market demands. Shorter cycle times enable faster product launches, which can be a competitive advantage in rapidly evolving markets.
Common Trade Terminology
-
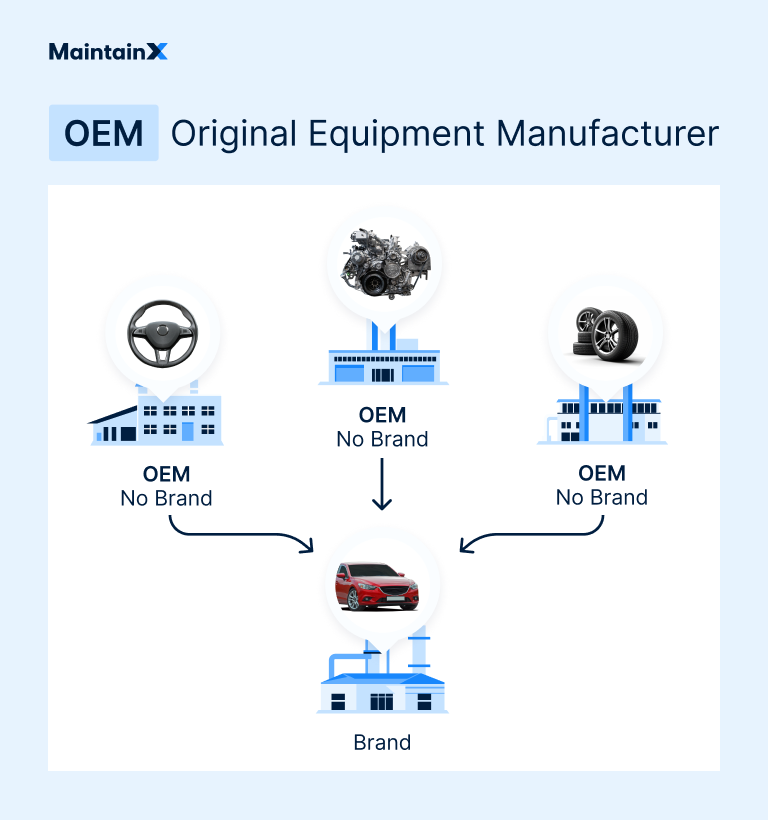
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding the role of OEMs is critical for buyers as it helps in identifying suppliers who can provide quality components tailored to specific needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess their purchasing needs and budget constraints. It also influences inventory management decisions and production planning. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from different suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers for the delivery of goods.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for managing shipping logistics, as they clarify who bears the risk and costs associated with transportation, thereby reducing disputes. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for supply chain management and inventory control. It enables buyers to plan production schedules and meet customer demands effectively.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their negotiation capabilities, ensure quality compliance, and streamline their purchasing processes. This knowledge ultimately contributes to building strong supplier relationships and achieving business objectives.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the industries with oems Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The landscape of industries with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) is evolving rapidly, driven by globalization, technological advancement, and shifting consumer demands. In recent years, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, have experienced significant changes in sourcing dynamics. The growth of e-commerce and digital platforms has streamlined the procurement process, enabling buyers to connect directly with manufacturers worldwide. Notably, the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies—including IoT, AI, and automation—has enhanced production efficiency and product quality, making these solutions attractive to OEMs seeking to optimize their operations.
Emerging trends such as sustainable manufacturing and ethical sourcing are becoming critical for buyers. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmental sustainability and social responsibility. This shift is accompanied by a growing demand for transparency in supply chains, compelling OEMs to adopt more responsible sourcing practices. Additionally, the ongoing geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have prompted many businesses to diversify their sourcing strategies, favoring suppliers closer to home or in politically stable regions.
With contract manufacturing projected to reach a market value of $1.2 trillion by 2027, international buyers must remain agile, adapting to these trends to maintain competitive advantage. Understanding regional differences in manufacturing capabilities and labor costs, particularly in emerging markets like Vietnam and Colombia, can also inform strategic sourcing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer a secondary concern for B2B buyers; it has become a critical factor in supplier selection and procurement strategies. Industries with OEMs are increasingly recognizing the environmental impacts of their operations and the importance of minimizing their carbon footprint. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who utilize sustainable materials and practices, such as recycled or biodegradable components, to meet both regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
The significance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. Consumers are increasingly aware of the social and environmental implications of their purchases, leading companies to adopt more rigorous ethical standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade for ethical labor practices are becoming essential benchmarks for suppliers. By prioritizing partners that uphold these standards, international buyers can not only mitigate risks associated with unethical practices but also enhance their brand reputation.
Moreover, the integration of sustainability into the supply chain can lead to cost savings and operational efficiencies. For instance, adopting energy-efficient manufacturing processes and reducing waste can lower production costs while appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Therefore, establishing a sustainable sourcing strategy is vital for OEMs looking to thrive in today’s market.
Brief Evolution/History
The concept of OEMs has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, OEMs primarily focused on manufacturing components for larger companies, often with little involvement in product development. However, as globalization took hold, the role of OEMs expanded to include more complex and integrated manufacturing processes. The rise of contract manufacturing emerged as a strategic response to the growing demand for cost-effective and efficient production solutions. Today, OEMs are not only seen as suppliers but as key partners in innovation and product development, enabling businesses to enhance their competitive edge in an increasingly interconnected world.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industries with oems
-
How do I vet potential OEM suppliers?
Vetting potential OEM suppliers requires a thorough due diligence process. Start by assessing their industry experience and reputation through online reviews and references. Request documentation on certifications such as ISO or specific industry standards. Conduct factory visits, if possible, to inspect production capabilities, quality control processes, and working conditions. Additionally, verify their financial stability and ability to meet your order requirements. Establishing clear communication channels and asking detailed questions about their processes can further enhance your confidence in the supplier. -
Can OEM suppliers customize products to my specifications?
Most OEM suppliers are equipped to customize products based on your specifications. When initiating discussions, provide detailed product requirements, including materials, design, and functionality. It’s essential to inquire about their capabilities in prototyping and design adjustments. Some suppliers may have minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom products, so clarify these terms early on. Establishing a collaborative relationship can facilitate smoother customization processes and ensure that the final product aligns with your expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times can vary significantly among OEM suppliers and depend on the product type and complexity. MOQs may range from a few hundred units to several thousand, particularly for custom items. Lead times are typically influenced by production schedules, material availability, and shipping logistics. It’s advisable to discuss these factors upfront, as they can impact your inventory management and planning. Consider negotiating terms that align with your business needs to ensure flexibility in your supply chain. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with OEM suppliers?
Payment terms for OEM suppliers often vary based on the supplier’s policies, your relationship with them, and the order size. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or before shipping. Some suppliers may also offer credit terms for established relationships. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods, currency, and any potential additional fees, such as transaction charges or taxes. Ensuring that both parties agree on these terms in the contract can help avoid disputes later. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance?
To ensure quality assurance and compliance with certifications, establish clear quality standards in your contract with the OEM supplier. Request documentation of their quality management systems and certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Implement regular quality checks during production and upon receipt of goods. Consider conducting third-party inspections or audits to validate compliance. Clear communication regarding your quality expectations can significantly reduce risks associated with product defects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing from OEMs?
Logistics play a critical role in the success of your supply chain with OEMs. Key considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and costs associated with transportation. Assess the supplier’s location and proximity to major shipping routes to optimize delivery times and costs. Inquire about their experience in handling customs and international shipping regulations, especially when sourcing from countries with specific trade policies. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can enhance efficiency and reduce delays. -
How can I handle disputes with OEM suppliers effectively?
Dispute resolution with OEM suppliers should begin with a clear contract that outlines responsibilities, quality standards, and communication protocols. In case of a disagreement, initiate open communication to discuss the issue and seek a mutually beneficial solution. If informal discussions do not resolve the dispute, consider mediation or arbitration as stipulated in your contract. Keeping records of all communications and agreements can serve as evidence if the situation escalates. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother conflict resolution. -
What are the potential risks of sourcing from international OEM suppliers?
Sourcing from international OEM suppliers involves several risks, including supply chain disruptions, quality inconsistencies, and regulatory compliance issues. Political instability or changes in trade policies can affect delivery times and costs. Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences may complicate communication. To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, maintain regular communication, and establish contingency plans. Diversifying your supplier base can also provide alternative options in case of unforeseen challenges, enhancing your overall supply chain resilience.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industries with oems
In conclusion, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency and innovation across industries that rely on OEM partnerships. By leveraging contract manufacturing, businesses can achieve significant cost reductions, scalability, and access to specialized expertise, allowing them to focus on core competencies such as design and marketing.
Key takeaways for international B2B buyers include the importance of thorough needs assessment and clear contract negotiations to mitigate risks and ensure alignment with production standards. Additionally, tapping into cost-effective manufacturing regions can unlock competitive advantages, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Looking ahead, the landscape of global manufacturing is evolving rapidly, presenting both challenges and opportunities. As markets continue to diversify, it is essential for B2B buyers to remain agile and informed. Embrace strategic sourcing as a pathway to not only enhance operational capabilities but also foster innovation and growth. Engage with reputable OEM partners and consider emerging markets to maximize your competitive edge in an increasingly interconnected world.