Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Iron Castings
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for iron castings
In an increasingly interconnected global market, the significance of iron castings cannot be overstated. These durable and versatile components are integral to various industries, including automotive, construction, and industrial machinery, serving as the backbone for countless applications. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable suppliers, understanding the intricacies of iron castings becomes essential for making informed procurement decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of iron castings, offering insights into the different types of castings—such as sand, permanent mold, and investment castings—as well as the materials used and manufacturing processes involved. Buyers will find valuable information on quality control practices, supplier selection criteria, and cost structures, equipping them with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing iron castings.
Furthermore, the guide addresses critical market trends, providing a holistic view of the competitive landscape and emerging technologies that shape the future of the iron casting industry. With FAQs tailored to the specific challenges faced by international buyers, this resource empowers decision-makers to build resilient supply chains, optimize sourcing strategies, and ultimately drive business success. By leveraging the insights presented here, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement processes and secure high-quality iron castings that meet their operational demands.
Understanding iron castings Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grey Iron Casting | High carbon content, excellent machinability | Automotive engine blocks, machine bases | Cost-effective; good wear resistance; prone to brittleness |
| Ductile Iron Casting | Enhanced ductility, can withstand impact | Automotive parts, pipe fittings, agricultural machinery | Superior strength; versatile; higher production costs |
| White Iron Casting | Hard and brittle, high wear resistance | Abrasive applications, grinding media | Exceptional hardness; limited ductility; complex machining required |
| Malleable Iron Casting | Heat-treated for improved ductility and toughness | Electrical fittings, automotive components | Good mechanical properties; higher processing costs |
| Ni-Resist Iron Casting | High nickel content for corrosion resistance | Marine applications, chemical processing | Excellent corrosion resistance; higher material costs |
Grey Iron Casting
Grey iron casting is characterized by its high carbon content and excellent machinability, making it a popular choice for various industrial applications. It is widely used in manufacturing automotive engine blocks, machine bases, and components requiring good wear resistance. For B2B buyers, the main considerations include cost-effectiveness and the ability to achieve intricate shapes. However, its brittleness can be a drawback, especially in applications where impact resistance is crucial.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ductile Iron Casting
Ductile iron casting, also known as spheroidal graphite iron, features enhanced ductility, allowing it to absorb impact without fracturing. This makes it suitable for applications such as automotive parts, pipe fittings, and agricultural machinery. Buyers must weigh the superior strength and versatility of ductile iron against its higher production costs. This type is especially relevant for industries looking for durable components that can withstand rigorous operational demands.
White Iron Casting
White iron casting is known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for abrasive applications such as grinding media and wear plates. However, its brittleness poses challenges for machining and requires careful handling. B2B buyers in sectors that prioritize durability must consider the trade-off between the exceptional hardness of white iron and the complexities involved in machining it to precise specifications.
Malleable Iron Casting
Malleable iron casting is produced by heat-treating white iron, resulting in improved ductility and toughness. It is commonly used in electrical fittings and automotive components. The key B2B purchasing considerations include the balance of good mechanical properties against higher processing costs. Buyers should also assess the specific performance requirements of their applications to determine if malleable iron is the right choice for their needs.
Ni-Resist Iron Casting
Ni-resist iron casting contains a high nickel content, providing excellent corrosion resistance, which is crucial for marine applications and chemical processing. While it offers significant advantages in terms of durability and longevity, the higher material costs can be a concern for budget-sensitive projects. B2B buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits of investing in ni-resist iron, particularly in environments where corrosion could lead to costly downtime or replacements.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of iron castings
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of iron castings | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine blocks and transmission housings | High strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness | Supplier reliability, production capacity, and quality |
| Construction | Structural components and machinery parts | Enhanced structural integrity and longevity | Compliance with local regulations and quality standards |
| Industrial Machinery | Pump housings and gearbox cases | Improved performance under heavy loads | Material sourcing and machining capabilities |
| Oil and Gas | Valve bodies and pipeline components | Resistance to harsh environments and high pressure | Supplier track record in the oil and gas sector |
| Agriculture | Equipment components such as plowshares and frames | Cost-effective solutions for rugged applications | Customization options and lead times |
Automotive Sector
Iron castings play a crucial role in the automotive industry, particularly in the production of engine blocks and transmission housings. These components require high strength and durability to withstand the demanding conditions of vehicle operation. For international buyers, especially those in regions like Europe and South America, sourcing from suppliers with proven reliability and the capability to meet stringent quality standards is essential. Additionally, understanding the production capacity of potential suppliers can help ensure timely delivery of large orders.
Construction Industry
In the construction sector, iron castings are utilized for various structural components and machinery parts. Their inherent strength and durability contribute to enhanced structural integrity, making them ideal for use in heavy-duty construction applications. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East should consider suppliers who comply with local building regulations and quality standards, ensuring that the castings can withstand environmental and load-bearing demands specific to their projects.
Industrial Machinery
Iron castings are integral to the manufacturing of industrial machinery, particularly in components such as pump housings and gearbox cases. These parts need to perform reliably under heavy loads, and iron’s robust properties make it a preferred choice. International B2B buyers must focus on suppliers’ material sourcing and machining capabilities, as these factors significantly influence the performance and longevity of the machinery components.
Oil and Gas Sector
In the oil and gas industry, iron castings are essential for producing valve bodies and pipeline components that can endure harsh environments and high pressure. The reliability of these components is critical to operational safety and efficiency. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers with a strong track record in the oil and gas market, as experience can be indicative of a supplier’s ability to meet specific operational requirements and compliance standards.
Agriculture
Iron castings are widely used in agricultural equipment, including components such as plowshares and frames. The rugged nature of these applications requires cost-effective solutions that do not compromise on quality. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, customization options are vital, as they often need specific designs to suit local agricultural practices. Lead times should also be carefully considered to ensure that the equipment is available during peak planting and harvesting seasons.
Related Video: Uses of Metals and Non Metals
Strategic Material Selection Guide for iron castings
When selecting materials for iron castings, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, cost, and application suitability. Here, we analyze four common materials used in iron castings: Gray Iron, Ductile Iron, White Iron, and Malleable Iron. Each material presents unique properties and considerations that can significantly influence procurement strategies.
Gray Iron
Key Properties: Gray iron is characterized by its excellent castability and machinability, with a temperature rating of up to 700°C. Its graphite microstructure provides good damping capacity and wear resistance, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of gray iron is its cost-effectiveness and ease of production, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing. However, its brittleness can be a limitation in applications requiring high impact resistance. Gray iron is typically used in automotive engine blocks and machine bases.
Impact on Application: Gray iron is compatible with a range of media, including water and oil, but has limited corrosion resistance, which may require protective coatings in some environments.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A48. They should also evaluate suppliers’ capabilities in producing consistent quality, given gray iron’s sensitivity to casting conditions.
Ductile Iron
Key Properties: Ductile iron, also known as spheroidal graphite iron, offers superior strength and ductility, with a temperature rating similar to gray iron but with enhanced impact resistance. It can withstand higher stress and strain without fracturing.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of ductile iron is its versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive components and heavy machinery. The downside is its higher production cost compared to gray iron, which can impact budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Ductile iron is highly resistant to fatigue and can handle various media, including corrosive fluids, making it ideal for applications in the automotive and construction sectors.
Considerations for Buyers: In Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards like EN 1563 is crucial. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate consistent quality and have a robust quality assurance process.
White Iron
Key Properties: White iron is known for its hardness and wear resistance, with a temperature rating exceeding that of gray and ductile iron. Its microstructure, characterized by cementite, makes it suitable for abrasive environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of white iron is its exceptional wear resistance, making it ideal for applications like grinding media and wear plates. However, its brittleness limits its use in applications requiring toughness.
Impact on Application: White iron is particularly effective in environments with high abrasion, such as mining and mineral processing. However, its low corrosion resistance necessitates protective coatings or alloying with other materials.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards applicable to white iron castings, such as ASTM A532. Ensuring that suppliers have the capability to produce white iron castings that meet these standards is essential for maintaining product integrity.
Malleable Iron
Key Properties: Malleable iron is produced through a heat treatment process that transforms white iron into a more ductile form. It offers good tensile strength and is suitable for applications requiring complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of malleable iron is its ability to be shaped into intricate designs while maintaining strength. However, the manufacturing process is more complex and costly compared to gray and ductile iron.
Impact on Application: Malleable iron is used in applications such as pipe fittings and automotive parts, where flexibility and strength are crucial. Its corrosion resistance is moderate, making it suitable for various environments.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM A47. It’s important to choose suppliers who can provide detailed documentation on the material properties and processing methods to ensure quality.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for iron castings | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gray Iron | Engine blocks, machine bases | Cost-effective, good castability | Brittle, limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Ductile Iron | Automotive components, heavy machinery | High strength, impact resistance | Higher production cost | Medium |
| White Iron | Grinding media, wear plates | Exceptional wear resistance | Brittle, low corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Malleable Iron | Pipe fittings, automotive parts | Good ductility, complex shapes | Complex manufacturing process | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights to make informed decisions when sourcing iron castings. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will facilitate better procurement strategies tailored to specific applications and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for iron castings
The manufacturing process for iron castings is intricate and requires a series of well-defined stages to ensure the final product meets the necessary specifications and quality standards. B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should familiarize themselves with these processes to make informed sourcing decisions.
Manufacturing Processes for Iron Castings
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process involves preparing the raw materials, primarily cast iron. This includes the selection and blending of the iron with other alloying elements such as carbon, silicon, and manganese to achieve desired properties. The quality of the raw materials significantly impacts the final casting. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s sourcing practices to ensure that high-quality raw materials are used.
Forming
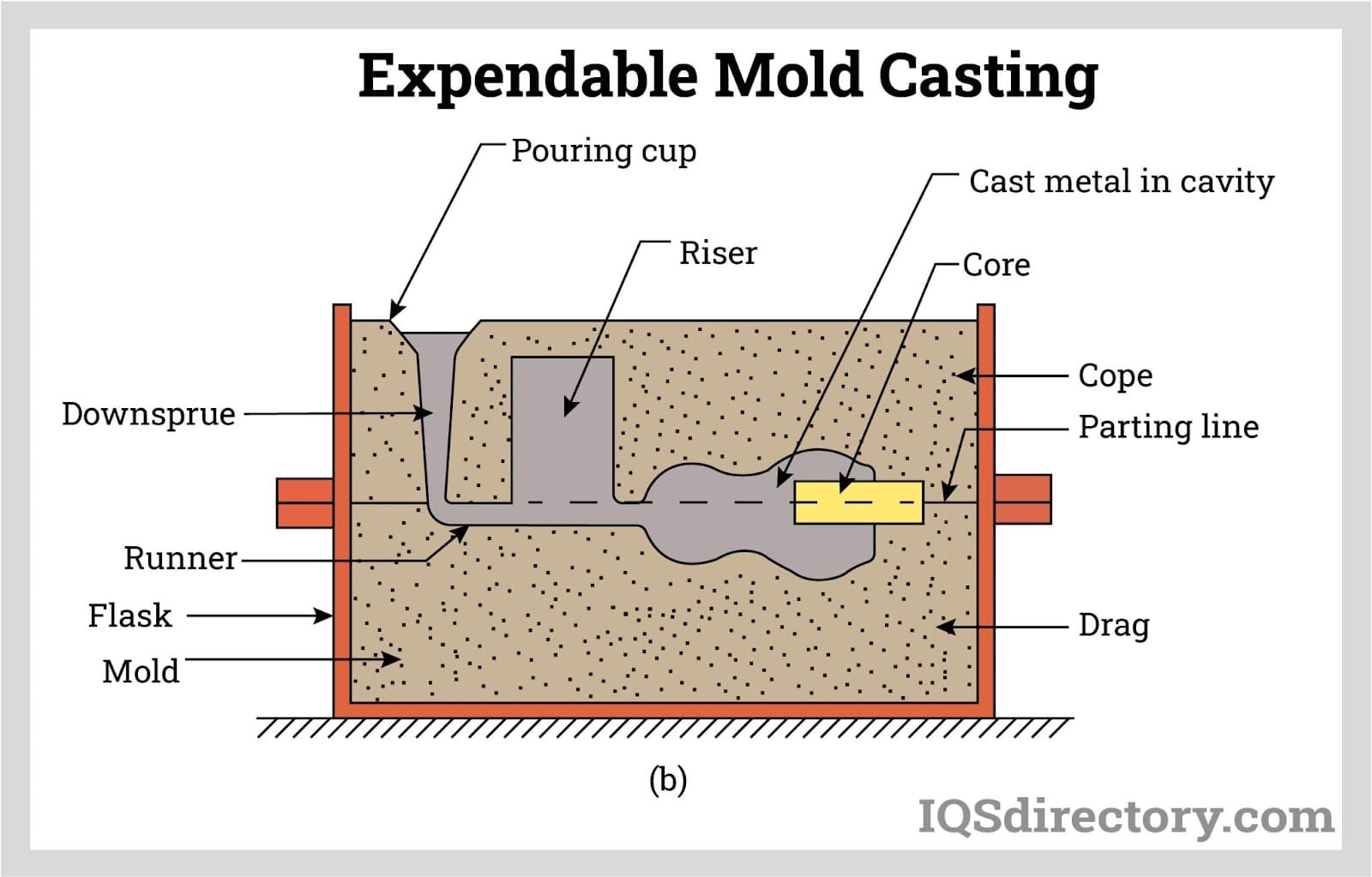
The forming stage is critical and involves creating molds into which the molten iron will be poured. The most common techniques used include:
- Sand Casting: This method utilizes sand molds that can accommodate complex geometries. It is cost-effective for small to medium production runs.
- Permanent Mold Casting: Employing reusable molds, this technique is ideal for high-volume production, offering better surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
- Investment Casting: Known for its precision, this method is suitable for complex designs and applications requiring high integrity.
Each forming technique has its advantages and should be matched to the specific application requirements of the buyer.
Assembly
Once the individual components are cast, they may need to be assembled. This can involve processes such as welding, machining, or fastening. Buyers should ensure that the supplier has the capability to handle these additional processes, particularly for components that require tight tolerances or specific functional attributes.
Finishing
Finishing processes are employed to enhance the surface quality and prepare the castings for their final application. Common finishing techniques include:
- Machining: To achieve precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
- Coating: Protective coatings can be applied to prevent corrosion and improve durability.
- Inspection: This is a critical step in the finishing process, where castings are examined for defects and compliance with specifications.
B2B buyers should assess whether the supplier has in-house finishing capabilities or if they rely on third-party services.
Quality Assurance in Iron Castings
Quality assurance is paramount in the iron casting industry, particularly for international B2B transactions where standards may vary significantly. Suppliers must adhere to both international and industry-specific quality standards.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant for European buyers, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Industry-Specific Standards
- API (American Petroleum Institute): Important for castings used in the oil and gas sector, ensuring products meet specific performance criteria.
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials): Provides specifications that many suppliers follow, particularly in North America.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To maintain product quality, several quality control (QC) checkpoints should be established:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection of the finished product before shipping to the buyer.
Common Testing Methods
Buyers should be aware of the various testing methods used to ensure product quality, including:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects or irregularities.
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and gauges to verify the dimensions of the casting.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection to detect internal defects without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, especially those in international markets, it is vital to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are actionable steps to ensure quality:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct thorough audits of the supplier’s facilities to assess their manufacturing and quality assurance processes.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for their quality control documentation, including inspection reports and certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to evaluate the supplier’s quality management system and product quality.
Navigating Quality Assurance Nuances
B2B buyers from diverse regions must navigate the nuances of quality assurance in international transactions. Factors such as cultural differences, regulatory requirements, and varying standards can complicate sourcing efforts. Here are some tips to address these challenges:
- Understand Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the local regulations that may affect product standards and quality assurance practices in the supplier’s country.
- Build Strong Relationships: Cultivating relationships with suppliers can lead to better communication regarding quality expectations and requirements.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize technology for real-time monitoring of production and quality assurance processes, enabling proactive management of any issues.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in the iron casting industry, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful partnerships and high-quality products. This knowledge is essential for navigating the complexities of sourcing iron castings on an international scale, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Related Video: Top 5 Mass Production Techniques: Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for iron castings Sourcing
The procurement of iron castings involves a multifaceted cost structure that B2B buyers must navigate effectively. Understanding the various components of cost and the factors influencing pricing can significantly enhance sourcing strategies, particularly for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Structure of Iron Castings
-
Materials: The raw materials constitute the largest portion of the cost structure, often accounting for 50-60% of the total expenses. The primary material is iron ore, and fluctuations in global prices can affect overall costs. Buyers should monitor market trends in iron ore pricing to better anticipate changes.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly by region. In regions with lower wage standards, such as parts of Africa and South America, labor can be a cost advantage. However, skilled labor for quality control and machining processes is critical, and sourcing from regions with higher labor costs, like Europe, may provide superior craftsmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Manufacturing overhead typically adds an additional 20-30% to the base costs, which buyers should consider in their total cost assessments.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs, which can range from USD 10,000 to USD 50,000 depending on complexity and volume, are a significant upfront investment. These costs are amortized over production runs, making them crucial for buyers to understand when negotiating prices for large orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is vital, especially for industries like automotive and aerospace. QC processes can add an additional 5-10% to the total cost. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s quality certifications and processes to mitigate risks associated with defective products.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the Incoterms used. International buyers must account for customs duties, freight, and insurance, which can substantially impact the overall price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up their costs to include a profit margin, which can range from 10-30%. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can provide leverage during negotiations.
Price Influencers
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of iron castings:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer tiered pricing based on the quantity ordered. Higher volumes can lead to discounts, so buyers should assess their needs carefully and consider bulk purchasing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized castings may incur additional costs due to unique tooling and processing requirements. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The type of iron and the presence of certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can also affect pricing. Higher-quality materials typically come at a premium but can result in lower failure rates and longer product lifespans.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capacity can impact pricing. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers may lead to better terms and pricing flexibility.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can influence the total cost by determining who is responsible for shipping costs, risk, and insurance. Buyers should negotiate terms that favor their logistical capabilities.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing. Presenting your buying volume and long-term partnership potential can provide leverage for better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), not just the initial purchase price. This includes factoring in logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime costs associated with lower-quality products.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and geopolitical factors that may impact pricing. Building a currency risk strategy can aid in budget planning.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers based on their cost structure, production capabilities, and quality assurance processes. A well-informed decision can lead to significant savings and value over time.
-
Market Intelligence: Stay updated on market trends and technological advancements in iron casting. This knowledge can help in anticipating price changes and identifying potential new suppliers.
By understanding these elements, international B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies for iron castings, ensuring they secure high-quality products at competitive prices.
Spotlight on Potential iron castings Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘iron castings’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for iron castings
Iron castings are integral to various industries, including automotive, construction, and machinery. Understanding their technical properties and trade terminology is essential for B2B buyers to make informed procurement decisions. Below are the key specifications and common industry terms that every buyer should be familiar with.
Critical Specifications for Iron Castings
- Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the classification of iron based on its composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include gray iron, ductile iron, and malleable iron.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial as it affects the strength, ductility, and machinability of the casting. Buyers must match material grades to specific applications to ensure product performance and durability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Dimensional Tolerance
– Definition: Dimensional tolerance specifies the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the casting. It is usually expressed as a range (e.g., ±0.5 mm).
– B2B Importance: Tighter tolerances often lead to higher production costs. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers negotiate pricing and ensure that the final product meets specifications for fit and function in assembly processes. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: Surface finish refers to the texture of the casting’s surface, which can range from rough to smooth. It is often measured in micrometers (µm).
– B2B Importance: The desired surface finish can impact the casting’s performance in applications. Buyers need to communicate their requirements clearly, as this can affect machining processes and overall product quality. -
Weight and Volume
– Definition: This specification encompasses the total weight and volume of the casting, which influences shipping and handling costs.
– B2B Importance: Understanding weight and volume helps in logistics planning and can influence cost calculations, especially for international shipments. Buyers should consider these factors when determining MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) and negotiating freight terms. -
Casting Method
– Definition: The casting method refers to the process used to create the iron casting, such as sand casting, investment casting, or permanent mold casting.
– B2B Importance: Different methods yield various quality and cost implications. Buyers should be aware of the method used to align their expectations regarding quality, lead times, and production costs.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers that provide high-quality components tailored to their specific needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers gauge the feasibility of their purchase plans and manage inventory effectively. It also influences pricing and negotiating power. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ is vital for comparing offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive pricing, and establishing clear expectations for delivery and quality. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping obligations, risk management, and cost responsibilities, ensuring smoother international trade operations. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Importance: Knowing lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing supply chain expectations. Buyers should consider lead times when sourcing from international suppliers to avoid production delays.
By mastering these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensure product quality, and build strong supplier relationships in the iron casting market.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the iron castings Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The iron castings market is poised for robust growth, driven by a projected CAGR of 6.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is largely fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing demand across sectors such as automotive, construction, and industrial machinery. Key drivers include the need for durable and cost-effective components like engine blocks and gearbox cases. For international B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional dynamics is crucial. For example, while the automotive sector is booming in Japan, similar trends are emerging in regions like Kenya and South America, where local manufacturing initiatives are gaining traction.
Emerging technologies such as additive manufacturing and digital twins are reshaping sourcing strategies. These innovations offer enhanced design capabilities and efficiency, allowing buyers to optimize their procurement processes. Additionally, the hybrid sourcing model is gaining popularity, where businesses integrate in-house processes with outsourced solutions. This approach provides flexibility and can lead to cost savings, particularly for buyers who manage high-volume purchases. Furthermore, the increasing globalization of supply chains necessitates a keen focus on logistics and compliance, especially for buyers navigating the diverse regulatory landscapes of different regions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the iron castings sector, with buyers increasingly prioritizing environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of casting processes—including energy consumption and waste generation—has prompted many companies to adopt greener techniques, such as green sand casting, which utilizes eco-friendly materials and processes. For B2B buyers, sourcing from suppliers committed to sustainable practices not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also enhances brand reputation.
Ethical supply chains are essential for maintaining product integrity and consumer trust. Buyers should seek suppliers with certifications that demonstrate adherence to sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications. The use of recycled materials in casting processes is also a growing trend, allowing manufacturers to reduce their carbon footprint while meeting quality standards. By prioritizing suppliers who emphasize sustainability, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance and enhance their market competitiveness.
Brief Evolution/History
The iron castings industry has evolved significantly since its inception, transitioning from rudimentary methods of production to advanced techniques that emphasize precision and efficiency. Historically, casting processes were labor-intensive and time-consuming, primarily utilizing sand molds. The introduction of permanent mold and investment casting methods revolutionized the industry by enabling higher production rates and improved surface finishes.
In recent decades, technological advancements such as computer-aided design (CAD) and automated machinery have further refined casting processes, allowing for greater complexity and customization. As global markets have expanded, the focus has shifted toward sustainable practices and ethical sourcing, reflecting the industry’s response to contemporary environmental and social challenges. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with both quality and sustainability objectives.
Related Video: International Trade 101 | Economics Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of iron castings
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of iron castings?
When vetting suppliers, focus on several key criteria: quality certifications (such as ISO 9001), production capabilities (capacity and technology), material sourcing practices, and reputation within the industry. Verify their experience in your specific application area, and ask for references or case studies from previous clients. Additionally, assess their financial stability and compliance with international trade regulations to ensure they can meet your needs reliably. -
Can I customize iron castings to suit my specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for iron castings. You can specify dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes based on your application needs. It’s crucial to communicate your requirements clearly during the initial discussions. Some suppliers may also provide design assistance to optimize your casting for performance and manufacturability. Be aware that customization may affect lead times and pricing, so ensure these factors are discussed upfront. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for iron castings?
Minimum order quantities vary by supplier and depend on factors like production capacity and the complexity of the casting. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times can also differ significantly, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks for standard products. For customized orders, lead times may extend further. It’s advisable to discuss these aspects with potential suppliers to align expectations and production schedules. -
What payment terms and options should I expect when sourcing iron castings?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include 30% upfront payment with the balance due upon delivery, or net 30/60 terms post-delivery. Some suppliers may accept letters of credit, especially for international transactions. Always clarify payment terms before committing to an order and consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow and financial strategy. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications from my supplier?
Request documentation of quality assurance processes, including any relevant certifications like ISO 9001 or AS9100, depending on your industry needs. Inquire about their quality control measures throughout the production process, including material testing and final inspections. Establishing a quality agreement can also help set clear expectations regarding tolerances, testing protocols, and remedies for any defects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing iron castings?
When importing iron castings, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance procedures. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling industrial goods to navigate potential challenges. Factor in shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs that may apply to your specific imports. Additionally, ensure you have a clear agreement on who is responsible for logistics and customs duties to avoid unexpected costs. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers of iron castings?
To manage disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements and expectations in a contract. If a dispute arises, attempt to resolve it directly with the supplier first. If that fails, consider mediation or arbitration as outlined in your contract. Having a well-defined escalation process can help ensure that issues are addressed promptly and satisfactorily, minimizing disruption to your operations. -
What are the emerging trends in the iron casting industry that I should be aware of?
Stay informed about trends such as the shift towards sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly casting methods like green sand casting. Additionally, advancements in automation and AI-driven processes are improving efficiency and quality in production. Understanding these trends can help you make informed decisions about suppliers and technologies that align with your corporate sustainability goals and operational needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for iron castings
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing of iron castings is pivotal for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The anticipated CAGR of 6.1% highlights the growing demand driven by sectors such as automotive, construction, and industrial machinery. By prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate eco-friendly practices and robust quality assurance, buyers can secure a competitive edge while contributing to sustainability efforts.
Understanding the diverse casting methods—ranging from sand to investment casting—enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their production needs and budget constraints. Buyers should focus on establishing strong partnerships with reliable suppliers, as these relationships foster consistent quality and supply chain resilience.
As the global market continues to evolve, embracing innovation and sustainability will be crucial. International B2B buyers are encouraged to proactively engage with suppliers who can adapt to changing demands and leverage emerging technologies. By prioritizing strategic sourcing today, you can position your business for success in the dynamic landscape of iron castings tomorrow.