Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Jib Crane Components
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for jib crane components
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, jib crane components play a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency and safety across various sectors. These versatile lifting devices are essential for streamlining production processes, particularly in environments where space is limited and precision is paramount. For B2B buyers, understanding the intricacies of jib crane components is not just beneficial; it is critical for making informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of jib cranes, including freestanding, wall-mounted, and mast-type systems, while outlining the materials and manufacturing quality control standards that ensure durability and reliability. Additionally, we will explore the landscape of suppliers, providing insights into sourcing strategies tailored for international markets, specifically targeting buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Vietnam.
Understanding the cost implications and market dynamics surrounding jib crane components is crucial for optimizing budgets and maximizing return on investment. Furthermore, we address frequently asked questions to clarify common uncertainties and provide actionable insights that empower buyers to navigate the global market effectively.
By leveraging the information presented in this guide, international B2B buyers will be equipped to make well-informed decisions, ultimately enhancing their operational capabilities and ensuring they remain competitive in their respective industries.
Understanding jib crane components Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freestanding Jib Cranes | 360° rotation, spans up to 50’, capacities up to 15 tons | Manufacturing, warehousing, marinas | Pros: High capacity, versatile location; Cons: Higher cost, requires solid foundation. |
| Mast Type Jib Cranes | 360° rotation, requires minimal foundation support | Factories with overhead beams, assembly lines | Pros: Cost-effective, flexible installation; Cons: Limited to existing structures, lower capacity than freestanding. |
| Wall-Mounted Jib Cranes | Mounted on walls, limited rotation (180-200°) | Tight spaces, small workshops | Pros: Space-saving, easy installation; Cons: Limited mobility, lower lifting capacity. |
| Articulating Jib Cranes | Multi-jointed arms for extended reach | Loading docks, shipyards | Pros: Enhanced reach, adaptable to varied environments; Cons: More complex design, requires more maintenance. |
| Portable Jib Cranes | Lightweight, can be moved easily, often on wheels | Construction sites, temporary setups | Pros: Flexibility, quick setup; Cons: Lower capacity, less stability under heavy loads. |
Freestanding Jib Cranes
Freestanding jib cranes are notable for their ability to provide 360° rotation, accommodating spans of up to 50 feet and lifting capacities reaching 15 tons. They are ideal for manufacturing and warehousing environments where heavy loads need to be moved efficiently. When considering a freestanding jib crane, buyers should evaluate the installation site for a solid foundation, as these cranes require a robust base. Although they represent a higher investment, their versatility and operational efficiency can justify the cost in high-demand settings.
Mast Type Jib Cranes
Mast type jib cranes are designed to be anchored to existing structures, requiring only a minimal concrete foundation for support. They offer 360° rotation and are suitable for factories with overhead beams and assembly lines, where space is often at a premium. Buyers should consider their existing infrastructure when opting for this type, as it leverages existing support while maintaining reasonable lifting capacities of up to 10 tons. Their cost-effectiveness makes them an attractive option, though they are limited by the structural integrity of the supporting beam.
Wall-Mounted Jib Cranes
Wall-mounted jib cranes are perfect for operations in tight spaces, providing a compact solution with limited rotation of 180-200°. These cranes are typically installed in small workshops or areas where floor space is a concern. Buyers should assess wall strength and clearance height before installation, as these factors will dictate the crane’s effectiveness. While they save space and are relatively easy to install, their mobility and lifting capacity are restricted compared to freestanding options.
Articulating Jib Cranes
Articulating jib cranes feature multi-jointed arms that allow for extended reach and flexibility in positioning. This design is particularly beneficial in loading docks and shipyards, where loads need to be maneuvered around obstacles. When purchasing an articulating jib crane, businesses should consider the complexity of the design, which may require more maintenance and operational training. The enhanced reach and adaptability can significantly improve workflow efficiency in dynamic environments, making them a valuable investment for specialized applications.
Portable Jib Cranes
Portable jib cranes are lightweight and designed for easy mobility, often featuring wheels for quick relocation. They are ideal for construction sites or temporary setups where flexibility is paramount. Buyers should keep in mind that while these cranes offer quick setup and adaptability, they typically have lower lifting capacities and stability under heavy loads. For businesses that require a versatile lifting solution without the need for permanent installation, portable jib cranes can be a practical choice, albeit with limitations on their maximum load capabilities.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of jib crane components
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of jib crane components | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Assembly line operations | Increases efficiency by enabling quick lifting and positioning of components, reducing downtime. | Ensure load capacity matches production needs; consider ergonomic designs to enhance worker safety. |
| Construction | Material handling on job sites | Facilitates the lifting of heavy materials, improving workflow and reducing manual labor costs. | Assess mobility requirements; select corrosion-resistant materials for outdoor use. |
| Maritime | Loading and unloading of cargo | Streamlines cargo operations, enhancing turnaround time at ports and docks. | Evaluate space constraints; consider jibs with high rotation capabilities for tight spaces. |
| Warehousing | Inventory management and order fulfillment | Boosts productivity by simplifying the retrieval and placement of goods, leading to faster order processing. | Look for customizable solutions that fit existing warehouse layouts; prioritize ease of installation. |
| Automotive | Engine assembly and heavy part positioning | Reduces assembly time and improves precision, leading to higher production quality. | Focus on systems that can handle varying load sizes; consider integrated control systems for automation. |
Industry Applications Explained
Manufacturing: In manufacturing settings, jib crane components are integral for assembly line operations. They allow workers to lift and position heavy components with ease, significantly reducing the time spent on manual handling. International buyers should prioritize cranes with appropriate load capacities and ergonomic designs to enhance worker safety and productivity, especially in high-volume production environments.
Construction: Jib cranes play a vital role in construction by facilitating the lifting of heavy materials on job sites. Their ability to maneuver loads efficiently minimizes manual labor, which can lead to cost savings and improved safety. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider the crane’s mobility and durability, particularly in outdoor environments where weather conditions can affect performance.
Maritime: In the maritime sector, jib cranes are used for loading and unloading cargo at docks and ports. Their ability to operate in confined spaces allows for efficient handling of heavy loads, thereby improving overall turnaround times. For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East where port operations are critical, sourcing cranes with high rotation capabilities can enhance operational flexibility.
Warehousing: In warehousing, jib crane components streamline inventory management and order fulfillment processes. They enable quick retrieval and placement of goods, which accelerates order processing and enhances productivity. Buyers should look for customizable jib systems that can fit seamlessly into their existing layouts, as well as solutions that are easy to install and maintain.
Automotive: In the automotive industry, jib cranes are essential for engine assembly and the positioning of heavy parts. They help reduce assembly time and enhance precision, which ultimately leads to higher production quality. Buyers should focus on systems capable of handling varying load sizes and those that offer integrated control systems for greater automation and efficiency in their operations.
Related Video: DIY Jib Crane Part 2 of 2
Strategic Material Selection Guide for jib crane components
When selecting materials for jib crane components, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis will focus on four common materials: Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, and Composite Materials. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and suitability of jib cranes in various applications.
Steel
Steel is the most widely used material for jib crane components due to its high strength and durability. It typically has a high tensile strength, making it suitable for heavy loads. Steel components can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is beneficial in industrial environments.
Pros:
– Durability: Steel offers exceptional strength and longevity, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
– Cost-Effective: Compared to other materials, steel is relatively inexpensive, which can lower overall project costs.
– Manufacturing Flexibility: Steel can be easily welded and shaped, allowing for customized designs.
Cons:
– Corrosion Susceptibility: Steel is prone to rusting if not properly coated or maintained, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
– Weight: Steel components are heavier, which can increase installation complexity and require more robust support structures.
Impact on Application: Steel is well-suited for environments where high load capacities are required. However, in coastal or humid regions, buyers must consider protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
Aluminum
Aluminum is increasingly popular in jib crane applications due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. It is often used in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as portable or mobile cranes.
Pros:
– Lightweight: Aluminum’s low density allows for easier handling and installation, reducing labor costs.
– Corrosion Resistance: Naturally resistant to corrosion, aluminum is ideal for outdoor applications without additional coatings.
Cons:
– Lower Strength: While aluminum is strong for its weight, it does not have the same load-bearing capacity as steel.
– Higher Cost: Aluminum is generally more expensive than steel, which can impact budget considerations.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications requiring mobility and where weight savings are crucial. However, it may not be the best choice for heavy lifting tasks.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a premium material known for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It is often used in environments where hygiene is paramount, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Pros:
– Corrosion Resistance: Excellent for harsh environments, stainless steel maintains its integrity over time.
– Strength: Offers good strength, making it suitable for various lifting applications.
Cons:
– Cost: Stainless steel is significantly more expensive than both carbon steel and aluminum, which can be a limiting factor for budget-conscious buyers.
– Manufacturing Complexity: Requires specialized tools and techniques for cutting and welding, increasing manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications in corrosive or hygienic environments, stainless steel components can enhance the longevity and safety of jib cranes but at a higher cost.
Composite Materials
Composite materials, such as fiberglass or reinforced plastics, are emerging as alternatives for certain jib crane components. They offer unique benefits, particularly in specific niche applications.
Pros:
– Weight Savings: Composites are lightweight, which can reduce the overall weight of the crane.
– Corrosion Resistance: Many composites are resistant to environmental degradation, making them suitable for outdoor use.
Cons:
– Limited Load Capacity: Generally not suitable for heavy lifting applications due to lower strength compared to metals.
– Higher Manufacturing Costs: The production process for composites can be more complex and costly.
Impact on Application: Composites are best suited for specialized applications where weight and corrosion resistance are prioritized over load capacity.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for jib crane components | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Exceptional strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Aluminum | Portable or mobile cranes | Lightweight and easy to handle | Lower load-bearing capacity | Med |
| Stainless Steel | Hygienic or corrosive environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | High cost | High |
| Composite Materials | Niche applications with weight constraints | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Limited load capacity | Med |
This material selection guide aims to provide international B2B buyers with actionable insights into the suitability of various materials for jib crane components, considering specific regional needs and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for jib crane components
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance for jib crane components are critical for ensuring safety, reliability, and performance in various industrial applications. Understanding these processes and the associated quality standards is essential for B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section delves into the main stages of manufacturing, key techniques employed, and the quality assurance measures that should be in place when sourcing jib crane components.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Processes
Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing jib crane components involves selecting the right materials. Common materials include high-strength steel and aluminum alloys, chosen for their durability and weight-bearing capabilities.
- Material Selection: Steel grades, such as S235 and S355, are popular due to their excellent weldability and strength. For lighter applications, aluminum alloys may be used.
- Cutting: After selection, materials are cut to specified dimensions using methods like plasma cutting, laser cutting, or water jet cutting. Precision in this stage is crucial to avoid excess waste and ensure proper fit during assembly.
Forming
The forming stage transforms raw materials into usable shapes. This can include bending, rolling, and forging.
- Bending: The steel sheets are bent into the desired shapes for components like the mast and boom using hydraulic press brakes.
- Rolling: Larger components may require rolling processes to achieve curves, particularly in the design of the boom.
- Forging: Critical load-bearing components such as hooks and latches may undergo forging to enhance strength through grain alignment.
Assembly
Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final jib crane system.
- Welding: Key joints are welded using techniques such as MIG or TIG welding, which provide strong, durable connections.
- Fastening: Mechanical fasteners may be used in conjunction with welding for added strength and to facilitate future disassembly if necessary.
- Integration of Electrical Components: If the jib crane is motorized, the electrical systems, including controls and sensors, are integrated at this stage.
Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the durability and appearance of jib crane components.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as galvanization or powder coating are applied to protect against corrosion, especially for outdoor applications.
- Painting: A final coat of paint may be applied for aesthetic purposes and additional protection.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of jib crane components is paramount to ensure safety and compliance with international standards.
International Standards
B2B buyers should be familiar with the following standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance indicates that the manufacturer consistently provides products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), CE marking demonstrates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For specialized applications, especially in oil and gas, manufacturers may adhere to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards for specific components.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspection during the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Techniques may include dimensional checks and weld inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the assembled jib crane components to ensure they meet all specifications before shipping.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods employed in QC can include:
- Load Testing: Ensuring that components can handle the maximum load they are rated for, often performed by applying a load greater than the maximum expected.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle testing to detect flaws without damaging the components.
- Functional Testing: Verifying that electrical systems and controls operate as intended.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities to review quality management practices and compliance with standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Asking for documentation of past inspections and testing results can provide insight into the supplier’s reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the quality of products before shipment can help mitigate risks.
Quality Certification Nuances for International Buyers
For international buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa and South America, understanding the nuances of quality certification is crucial:
- Local Regulations: Ensure that suppliers are familiar with and compliant with local regulations, as these can differ significantly from international standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices vary across regions; establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication can aid in successful collaboration.
- Documentation: Ensure that all certifications and quality assurance documents are available in a language that is understandable to both parties, facilitating smoother negotiations and confirmations.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for jib crane components are vital for ensuring operational safety and efficiency. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should focus on understanding these processes and verifying the quality of suppliers through audits, reports, and third-party inspections. By prioritizing quality, buyers can enhance their operational capabilities and safeguard their investments in jib crane systems.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing – Lean Factory Tour – FastCap
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for jib crane components Sourcing
When sourcing jib crane components, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The cost structure typically encompasses several key components, including materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin. Each of these elements contributes to the final price of the components.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The raw materials used in jib crane components such as steel, aluminum, and synthetic materials can vary widely in price based on quality and sourcing location. For instance, high-grade steel may be more expensive but offers better durability, which can lead to lower maintenance costs over time.
-
Labor: Labor costs are often dictated by the manufacturing location. Regions with higher wage standards, like parts of Europe, may have higher labor costs compared to countries in Africa or South America. Additionally, the complexity of the components can affect the amount of labor required for assembly.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs, impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for manufacturing jib crane components can represent a significant investment. Custom tooling for specialized parts will increase costs, while standardized tooling can help keep expenses lower.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring components meet safety and performance standards is essential. Rigorous QC processes can add to costs but are critical for ensuring the reliability and safety of the cranes.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer. Incoterms play a significant role in determining who is responsible for shipping and handling costs, which can significantly affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand and competition.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the price of jib crane components:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to lower unit prices. Negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) can yield cost savings for larger orders.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom components tailored to specific applications generally cost more than standard parts. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of customization versus the potential for cost savings with off-the-shelf solutions.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly affect pricing. Higher quality materials may incur higher upfront costs but could reduce long-term maintenance expenses.
-
Quality/Certifications: Components that meet international safety standards (such as ISO certifications) may come at a premium. However, these certifications can enhance reliability and reduce risk, especially in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer companies may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding and negotiating Incoterms can lead to cost savings. For instance, choosing DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) can simplify logistics but may increase costs compared to EXW (Ex Works), where the buyer assumes more responsibility.
Buyer Tips
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms and prices. Suppliers often have flexibility, especially for larger orders.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, operation, and downtime costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations and import tariffs that could affect total costs. Having a clear understanding of local regulations and requirements can prevent unexpected expenses.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service over time.
Disclaimer
Prices for jib crane components can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. It’s advisable to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential jib crane components Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘jib crane components’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for jib crane components
Critical Technical Properties of Jib Crane Components
Understanding the technical specifications of jib crane components is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
- Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the quality of materials used in the construction of jib crane components, such as structural steel or aluminum.
– Importance: High-grade materials enhance durability and load-bearing capacity, which is critical for safety and longevity in demanding environments. For buyers, ensuring compliance with local and international standards is vital to avoid operational risks.
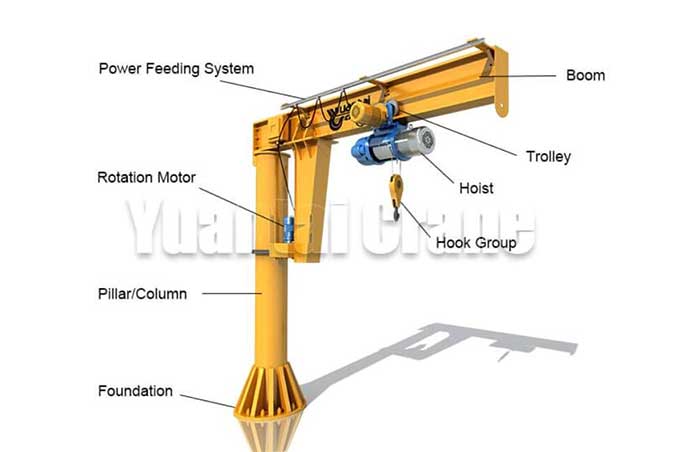
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Load Capacity
– Definition: This specification indicates the maximum weight the jib crane can safely lift and move, typically measured in tons.
– Importance: Knowing the load capacity is essential for selecting the right jib crane for specific applications. Overloading can lead to equipment failure and serious safety hazards, impacting production and incurring additional costs. -
Boom Length and Reach
– Definition: Boom length refers to the horizontal distance from the mast to the tip of the boom, while reach encompasses the total distance the crane can extend to lift loads.
– Importance: The boom length affects the crane’s operational range. Buyers must assess their workspace and the necessary reach to ensure the crane meets their operational needs without compromising safety. -
Rotation Range
– Definition: This refers to the extent to which the jib crane’s boom can rotate, typically measured in degrees (e.g., 360° or 180°).
– Importance: A greater rotation range allows for more flexible operation, minimizing the need for repositioning. Buyers should consider their facility layout and the potential for multi-directional lifting tasks. -
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: Tolerance levels specify the permissible deviation from nominal dimensions in the crane components.
– Importance: Precise tolerances are crucial for ensuring that all parts fit together correctly, which directly influences the crane’s operational efficiency and safety. Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to industry standards. -
Safety Features
– Definition: These are built-in systems or components designed to prevent accidents, such as overload sensors and emergency stop mechanisms.
– Importance: Safety features are non-negotiable in crane operations. Buyers must prioritize suppliers that provide robust safety mechanisms to protect both personnel and equipment.
Common Trade Terminology in Jib Crane Procurement
Familiarity with industry jargon can greatly enhance communication and negotiation processes. Here are key terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces components that are used in another company’s end product.
– Importance: Buyers often seek OEM parts for reliability and compatibility, ensuring that the components meet the original design specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and budget. It is crucial for negotiating terms that align with their operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Importance: Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal possible. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities, which can significantly affect overall procurement costs. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to delivery.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time is critical for project planning and minimizing downtime. Buyers should consider lead times when selecting suppliers to ensure timely delivery of components. -
Warranty Terms
– Definition: The conditions under which a supplier agrees to repair or replace defective parts.
– Importance: Buyers must carefully evaluate warranty terms to protect their investment and ensure adequate support in case of component failure.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and safety in their lifting operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the jib crane components Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global jib crane components market is shaped by several dynamic factors, including technological advancements, increasing industrial automation, and the need for enhanced operational efficiency. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a growing demand for versatile lifting solutions that can improve productivity and reduce workplace injuries. The rise of smart manufacturing technologies is also influencing sourcing trends, as companies increasingly seek components that integrate with IoT systems, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing highlight a shift towards modular and customizable jib crane systems. Buyers are looking for suppliers that offer tailored solutions to meet specific operational needs while ensuring quick turnaround times. Additionally, digital platforms for sourcing components are becoming more prevalent, providing buyers with access to a wider range of suppliers and comparative pricing. This digital transformation is particularly beneficial for international buyers, allowing them to navigate global supply chains more efficiently.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration. With a growing emphasis on reducing carbon footprints, buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that incorporate eco-friendly practices in their manufacturing processes. This includes the use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies. The combination of these market dynamics creates opportunities for international buyers to enhance their operational efficiencies while aligning with global sustainability goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, ethical sourcing and environmental impact are paramount for B2B buyers in the jib crane components sector. The production and lifecycle of jib crane components can significantly affect the environment, making it essential for businesses to consider the sustainability practices of their suppliers. This includes evaluating the carbon emissions associated with manufacturing processes, waste management practices, and the sourcing of raw materials.
Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications, which validate their commitment to sustainable practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) provide assurance that the supplier adheres to rigorous environmental standards. Additionally, using recyclable or biodegradable materials in the manufacturing of jib crane components is gaining traction, as businesses strive to minimize their ecological footprint.
Ethical supply chains are also critical, particularly in regions where labor practices may be scrutinized. Buyers are encouraged to conduct due diligence on their suppliers to ensure fair labor practices and compliance with local regulations. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can enhance their brand reputation, meet regulatory requirements, and respond to the increasing consumer demand for responsible corporate practices.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of jib cranes dates back to ancient times, with their origins linked to the need for efficient lifting solutions in construction and shipping. Over the centuries, advancements in materials and engineering led to the development of more sophisticated designs. The industrial revolution marked a significant turning point, as the introduction of powered hoists and mechanized systems increased lifting capabilities and efficiency.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing safety and ergonomics, with modern jib cranes designed to minimize operator strain and improve workplace safety. The integration of technology, such as automation and IoT connectivity, reflects the growing demand for smarter, more efficient lifting solutions. This historical progression underscores the importance of innovation in meeting the evolving needs of international B2B buyers across various industries.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of jib crane components
-
How do I vet suppliers for jib crane components?
When sourcing jib crane components, it’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Start by checking their business credentials, such as registration and industry certifications. Look for online reviews and testimonials from previous clients, particularly those in your region. Request references and evaluate their responsiveness and willingness to provide detailed product information. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if feasible, or utilize third-party inspection services to verify quality and capacity. -
Can I customize jib crane components to suit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for jib crane components. When discussing your requirements, be clear about your operational needs, including load capacity, reach, and environmental conditions. Suppliers often provide tailored solutions, such as specialized hoists or unique mounting configurations. Be prepared to share technical drawings and specifications, and ensure that any customization aligns with safety standards and regulations in your region. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for jib crane components?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers. Generally, MOQs for jib crane components may range from one unit for standard parts to larger quantities for customized solutions. Lead times depend on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production capacity, typically ranging from a few weeks to several months. Always confirm these details upfront to align your procurement schedule with your operational needs and project timelines.
-
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing jib crane components internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and your relationship with them. Common practices include upfront payments, deposits, or letters of credit for larger orders. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods, such as PayPal or escrow services, to mitigate risks. Ensure you clarify payment terms and conditions in your contract to avoid misunderstandings, particularly regarding currency exchange rates and potential additional fees. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for jib crane components?
To ensure quality, request copies of relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking, which indicate compliance with international standards. Inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing and inspection protocols for their components. It’s also beneficial to establish a formal quality assurance agreement that outlines your expectations for product quality and performance, including provisions for addressing any defects or non-conformance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing jib crane components?
Logistics play a crucial role in international procurement. Assess shipping options based on cost, speed, and reliability, considering both sea and air freight. Be aware of customs regulations and tariffs that may apply when importing goods into your country, as these can affect overall costs. Collaborate with your supplier to understand packaging requirements and ensure safe transport of components, minimizing the risk of damage during transit. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding jib crane components?
Dispute resolution should be addressed in your contract. Establish clear terms for handling conflicts, including mediation and arbitration procedures. Maintain open lines of communication with your supplier to resolve issues promptly before they escalate. Document all interactions and agreements in writing to create a clear record. If necessary, seek legal advice to understand your rights and obligations under international trade laws. -
What are the key factors to consider for after-sales support when sourcing jib crane components?
After-sales support is critical for ensuring the long-term functionality of your jib crane components. Inquire about warranty terms, maintenance services, and availability of spare parts. Assess the supplier’s responsiveness to service inquiries and their capability to provide technical support remotely or onsite. Establishing a clear understanding of after-sales support will help you minimize downtime and maintain operational efficiency in your facility.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for jib crane components
As the demand for efficient and versatile lifting solutions continues to rise globally, strategic sourcing of jib crane components presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers. By understanding the intricacies of jib crane design and components—such as the reach/boom, mast, and hoist—buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
Investing in high-quality components not only minimizes maintenance costs but also maximizes productivity, particularly in industries that rely on repetitive lifting tasks. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, focusing on suppliers who offer customized solutions and robust support can lead to a competitive edge in the market.
Looking ahead, the evolution of jib crane technology, including advancements in automation and smart controls, is set to transform material handling processes. Now is the time to explore partnerships with reputable manufacturers that prioritize innovation and sustainability. Engage with suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that align with your operational needs, and position your business for future growth in an increasingly automated world.