Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Leak Detection Device
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leak detection device
Leak detection devices play a pivotal role in ensuring product integrity and operational efficiency across various industries, from manufacturing to energy production. As global markets become increasingly interconnected, the demand for reliable leak detection solutions has surged, making it essential for international B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest technologies and best practices. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, equipping decision-makers with the necessary insights to navigate the complexities of sourcing leak detection devices.
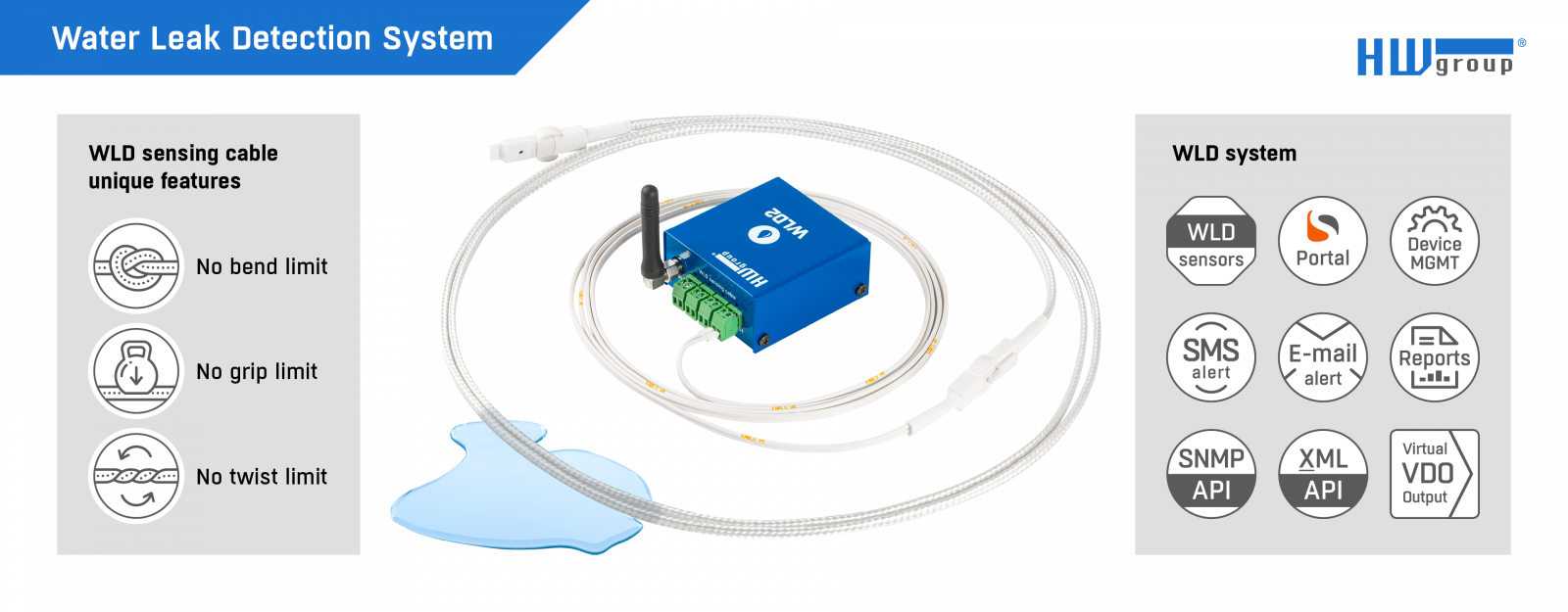
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In this guide, we delve into various types of leak detection methods, including underwater, air, and helium/tracer gas testing, while also examining the materials and technologies employed in these devices. We will highlight crucial manufacturing and quality control considerations, ensuring buyers understand the standards and certifications that underpin product reliability. Furthermore, we will provide an overview of leading suppliers and the competitive landscape across regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
By addressing cost factors and total cost of ownership, this guide empowers buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Additionally, a dedicated FAQ section will clarify common queries, enhancing the overall sourcing experience. With this knowledge, international B2B buyers can confidently select leak detection solutions that not only meet stringent quality standards but also drive efficiency and profitability in their operations.
Understanding leak detection device Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Underwater Leak Detection | Utilizes water immersion to visually inspect for bubbles or leaks. | HVAC systems, pipelines, and storage tanks. | Pros: Simple to implement, low cost. Cons: Limited to visible leaks, not suitable for all applications. |
| Helium Leak Detection | Employs helium as a tracer gas to identify very small leaks. | Aerospace, automotive, and high-precision industries. | Pros: Highly sensitive, detects minute leaks. Cons: Higher operational costs, requires specialized equipment. |
| Pressure Differential Testing | Measures pressure changes to detect leaks in sealed components. | Electronics, packaging, and medical devices. | Pros: Effective for various materials, quick results. Cons: May not detect all leak types, requires careful calibration. |
| Mass Flow Leak Testing | Measures the mass flow of gas through a leak over time. | Semiconductor manufacturing, fuel systems. | Pros: Accurate and quantitative, suitable for high-throughput testing. Cons: More complex setup, initial investment cost. |
| Burst Pressure Testing | Tests the integrity of components by applying pressure until failure. | Safety valves, tanks, and pressure vessels. | Pros: Ensures component safety, straightforward results. Cons: Destructive testing, not suitable for all components. |
Underwater Leak Detection
Underwater leak detection is a straightforward method that involves submerging components in water and observing for escaping bubbles. This technique is particularly effective for larger leaks and is commonly used in industries such as HVAC systems, pipelines, and storage tanks. When considering this method, buyers should evaluate the size and material of the components, as well as the environment in which testing will occur. While it is cost-effective and simple to implement, it is limited to visible leaks and may not detect smaller, more critical leaks.
Helium Leak Detection
Helium leak detection is renowned for its sensitivity, making it ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and high-precision industries where even the smallest leaks can lead to failures. This method uses helium as a tracer gas, which can easily escape through tiny leaks, allowing for accurate detection. Buyers should consider the operational costs and the need for specialized equipment when opting for this method. While it offers high precision, the investment can be significant, particularly for businesses with tight budgets.
Pressure Differential Testing
Pressure differential testing measures the changes in pressure within sealed components to identify leaks. This method is widely used in electronics, packaging, and medical devices, where maintaining integrity is paramount. It is generally quick and effective across various materials, but buyers must ensure careful calibration to achieve accurate results. While this method is versatile, it may not detect all types of leaks, necessitating a thorough understanding of the application to ensure reliability.
Mass Flow Leak Testing
Mass flow leak testing quantifies the amount of gas escaping through a leak over time, making it suitable for high-throughput environments such as semiconductor manufacturing and fuel systems. This method provides accurate and quantitative results, which can be crucial for compliance and safety standards. However, it requires a more complex setup and a higher initial investment. Buyers should weigh the accuracy and efficiency against the setup costs and complexity to determine its suitability for their operations.
Burst Pressure Testing
Burst pressure testing is a destructive method that assesses the integrity of components by applying pressure until failure occurs. It is commonly employed for safety valves, tanks, and pressure vessels to ensure they can withstand operational pressures. This method provides straightforward results and is essential for safety-critical components. However, because it is destructive, it is not suitable for all applications. Buyers should consider the trade-off between ensuring safety and the potential loss of components when selecting this testing method.
Related Video: Water Leak Detection | How It Works
Key Industrial Applications of leak detection device
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of leak detection device | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline Integrity Monitoring | Prevents leaks that can lead to environmental disasters and financial losses. | Compliance with international safety standards; robust technology for harsh environments. |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Fuel System Leak Testing | Ensures safety and performance, reducing recalls and warranty claims. | Accuracy in detecting small leaks; quick testing cycles; integration with existing production lines. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterility Testing of Packaging | Guarantees product safety and compliance with regulations, avoiding costly recalls. | High sensitivity for trace leaks; ability to handle various packaging materials. |
| HVAC Systems | Refrigerant Leak Detection | Enhances energy efficiency and compliance with environmental regulations. | Technology that detects low-level leaks; durability for long-term use in varying climates. |
| Food & Beverage | Quality Assurance in Packaging | Maintains product integrity, extending shelf life and reducing waste. | Versatility in testing methods; adaptability to different packaging types. |
Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas industry, leak detection devices are crucial for monitoring pipeline integrity. These devices help identify leaks early, minimizing the risk of environmental disasters and significant financial losses. Buyers should prioritize sourcing technologies that comply with international safety standards and can withstand the harsh conditions typical of oil and gas environments.
Automotive Manufacturing
In automotive manufacturing, leak detection is vital for fuel system testing. Ensuring that fuel systems are leak-free enhances vehicle safety and performance while reducing the likelihood of costly recalls. B2B buyers in this sector should seek devices that offer high accuracy in detecting small leaks and can integrate seamlessly into existing production lines to maintain efficiency.
Pharmaceuticals
Leak detection devices play a critical role in ensuring the sterility of packaging in the pharmaceutical industry. By identifying leaks that could compromise product safety, these devices help companies comply with stringent regulations and avoid costly product recalls. Buyers should focus on devices with high sensitivity capable of detecting trace leaks across various packaging materials.
HVAC Systems
In HVAC systems, leak detection devices are essential for monitoring refrigerant leaks. These devices enhance energy efficiency and ensure compliance with environmental regulations by preventing harmful refrigerants from escaping into the atmosphere. When sourcing equipment, buyers should consider technologies that can detect low-level leaks and are durable enough for long-term use in diverse climates.
Food & Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, leak detection devices are used to ensure the integrity of packaging, which is vital for maintaining product quality and extending shelf life. By preventing leaks, companies can significantly reduce waste and improve customer satisfaction. B2B buyers should look for versatile testing methods that can adapt to different packaging types and provide reliable results to meet industry standards.
Related Video: Our Disruptive Pipeline Leak Detection Technology
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leak detection device
When selecting materials for leak detection devices, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and the specific requirements of international markets. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in leak detection devices, focusing on their performance characteristics and implications for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C and can handle pressures exceeding 1000 psi, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can endure harsh environments and is less likely to degrade over time. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials and can be complex to manufacture, especially for intricate designs.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of fluids, including aggressive chemicals and gases, making it ideal for leak detection in industries such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Europe, preference may lean towards materials that meet stringent environmental regulations.
2. Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its chemical resistance and lightweight nature. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 100°C and is resistant to many acids and bases.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polypropylene is its low cost and ease of manufacturing, which allows for rapid prototyping and production. However, it has lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals, which may limit its application in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is suitable for leak detection in less aggressive environments, such as water and certain chemicals. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for portable leak detection devices.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should verify the material’s compliance with local environmental regulations, as well as its suitability for the specific chemicals it will encounter.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum offers a good balance of strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. It typically withstands temperatures up to 400°C and pressures around 300 psi.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is lightweight and relatively inexpensive, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not be suitable for highly corrosive environments.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used in applications where weight is a concern, such as in aerospace or automotive industries. Its compatibility with various fluids makes it a versatile option for leak detection.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the specific environmental conditions of their application and ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards, especially in regions with stringent quality requirements like Europe.
4. Glass
Key Properties:
Glass is inert and resistant to most chemicals, making it an excellent choice for leak detection in sensitive applications. It can withstand high temperatures but is generally more fragile than other materials.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of glass is its chemical resistance and transparency, allowing for visual inspection of leaks. However, its brittleness makes it less durable, and it can be costly to produce specialized glass components.
Impact on Application:
Glass is ideal for applications requiring high chemical resistance, such as in laboratories or pharmaceutical manufacturing. Its visibility can aid in quick leak detection.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of shipping and handling requirements due to the fragility of glass. Compliance with safety standards is also critical, especially in regions with strict regulations.
| Material | Typical Use Case for leak detection device | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, pharmaceuticals | Excellent durability and strength | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Polypropylene | Water and chemical leak detection | Low cost and easy to manufacture | Limited temperature and pressure ratings | Low |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable in corrosive environments | Medium |
| Glass | Laboratories and pharmaceuticals | High chemical resistance and visibility | Fragile and potentially high cost | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leak detection device
Manufacturing Processes for Leak Detection Devices
Manufacturing leak detection devices involves a series of meticulously coordinated stages, ensuring that each component meets stringent quality standards. The primary stages in the manufacturing process include:
Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting high-quality materials that can withstand various environmental factors and pressures. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and specialized plastics, each chosen based on the specific application of the leak detection device. Rigorous quality checks are conducted on incoming materials to ensure compliance with international standards.
Forming
During the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into the required components using techniques such as:
- CNC Machining: This precision method is crucial for creating intricate parts with high tolerances.
- Injection Molding: Often used for plastic components, this process allows for mass production while maintaining consistent quality.
- Stamping and Forging: These methods are employed for metal parts, ensuring strength and durability.
Each forming method is selected based on the desired characteristics of the final product, such as weight, strength, and resistance to corrosion.
Assembly
The assembly process integrates various components into a complete leak detection device. This stage typically involves:
- Automated Assembly Lines: These enhance efficiency and reduce the potential for human error.
- Manual Assembly: Skilled technicians may perform complex assemblies that require fine motor skills and experience.
Quality assurance during assembly includes visual inspections and functional testing to confirm that each device meets the specified design criteria.
Finishing
Finishing touches are applied to enhance the device’s performance and aesthetics. This may involve:
- Surface Treatments: Coatings such as anodizing or painting are applied to protect against corrosion and wear.
- Calibration: Devices are calibrated to ensure accurate leak detection, which is critical for their functionality.
Each finished product undergoes a final quality check before being packaged for distribution.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is pivotal in ensuring that leak detection devices perform reliably and meet the expectations of international B2B buyers. Key components of QA include:
International Standards
Compliance with recognized international standards is essential for credibility. Relevant standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, it signifies compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For devices used in oil and gas applications, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is critical.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses raw materials before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production ensures that any deviations from specifications are addressed immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough examination of the finished product to verify it meets all functional and aesthetic requirements.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to verify the integrity of leak detection devices, including:
- Pressure Testing: This method assesses the device’s ability to withstand specified pressures without leaking.
- Helium Leak Testing: A sensitive method that uses helium as a tracer gas to detect tiny leaks.
- Functional Testing: Ensures that the device operates correctly under real-world conditions.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are effective strategies to ensure supplier reliability:
Conducting Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. These audits should cover:
- Compliance with International Standards: Ensuring adherence to ISO, CE, and API standards.
- Documentation Practices: Reviewing quality records, testing results, and process control documents.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports that include:
- Inspection Results: Data on the performance of previous batches.
- Non-Conformance Reports: Documentation of any issues encountered and how they were resolved.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These inspectors can verify compliance with international standards and conduct independent testing of products.
Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers
When navigating the complexities of international trade, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to understand the nuances of quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of regional variations in quality expectations and manufacturing practices. This understanding can aid in establishing effective communication with suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements that impact product specifications and testing methods. Familiarity with these requirements is crucial for successful transactions.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Establishing a transparent supply chain can enhance trust and facilitate smoother transactions. Utilize technology for tracking and documenting each stage of the manufacturing process.
By focusing on these critical aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and high-quality leak detection devices that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Quality Testing: Leak Testing Methods
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leak detection device Sourcing
When sourcing leak detection devices, B2B buyers must navigate a complex cost structure that encompasses various components. Understanding these elements is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, particularly in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the materials used in manufacturing leak detection devices. Common materials include metals, plastics, and specialized sensors. The choice of materials can significantly affect both performance and price, with high-quality materials generally leading to higher costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often necessary for assembly and quality control, which can increase costs, especially in countries with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, providing a competitive edge in pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling for production can be substantial, particularly for custom or specialized devices. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating pricing, as they may be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that leak detection devices meet required specifications adds to the cost. Rigorous QC processes are essential, especially for devices used in critical applications, such as aerospace or medical devices.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can fluctuate based on the origin and destination of the product. Factors such as shipping method, distance, and import/export regulations can influence overall logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers often build in a profit margin that reflects the risk and investment associated with manufacturing. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions and supplier reputation.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant cost savings. Many manufacturers offer tiered pricing based on minimum order quantities (MOQs), incentivizing larger orders.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features can increase the price. Buyers should weigh the necessity of these features against their budget constraints.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the quality of materials directly affects pricing. Buyers should assess whether premium materials are necessary for their specific applications.
-
Quality/Certifications: Devices that meet international quality standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, CE marking) typically command higher prices due to the assurance of reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and experience can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better reliability but at a premium cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect total costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing. Leverage potential bulk orders or long-term contracts as bargaining chips.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A higher upfront investment may be justified by lower operational costs over time.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing disparities. For instance, sourcing from Europe may incur higher logistics costs than sourcing locally in Africa or South America.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough research on suppliers and pricing trends. Understanding the market landscape can provide leverage during negotiations.
Disclaimer
Prices for leak detection devices can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific device specifications. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct due diligence before finalizing purchases.
Spotlight on Potential leak detection device Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘leak detection device’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leak detection device
When evaluating leak detection devices, international B2B buyers need to understand essential technical properties and industry terminology to make informed purchasing decisions. Here, we explore key specifications and jargon that are critical in the context of leak detection technology.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The type of materials used in the construction of the leak detection device, often specified according to industry standards (e.g., stainless steel, plastic composites).
– B2B Importance: The material grade affects durability, resistance to corrosive substances, and overall performance in various environmental conditions. Buyers should consider material compatibility with the fluids being tested to ensure reliable operation. -
Leakage Rate
– Definition: A quantifiable measure of the volume of fluid that can pass through a leak over a specified time period, often expressed in units such as mbarl/s or ml/min.
– B2B Importance:* Understanding acceptable leakage rates is crucial for ensuring product safety and compliance with industry standards. Buyers must align leakage rate specifications with their application requirements to avoid costly failures. -
Test Pressure
– Definition: The maximum pressure at which the leak detection device can operate effectively during testing.
– B2B Importance: Test pressure influences the sensitivity and reliability of the leak detection process. Buyers should ensure that the device can withstand the operational pressures expected in their specific applications. -
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: The permissible limits of variation in the dimensions and performance of the leak detection device.
– B2B Importance: Tolerance levels are critical for ensuring that the device meets operational standards and fits correctly within the systems being tested. Tight tolerances may be necessary for high-precision applications. -
Automation Level
– Definition: The degree to which the leak detection process is automated, ranging from manual to fully automated systems.
– B2B Importance: Automation can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Buyers should assess their operational needs and consider the investment in automation for long-term savings and improved accuracy.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for quality components and facilitate smoother procurement processes. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategies and manage inventory effectively, especially in markets where demand may fluctuate.
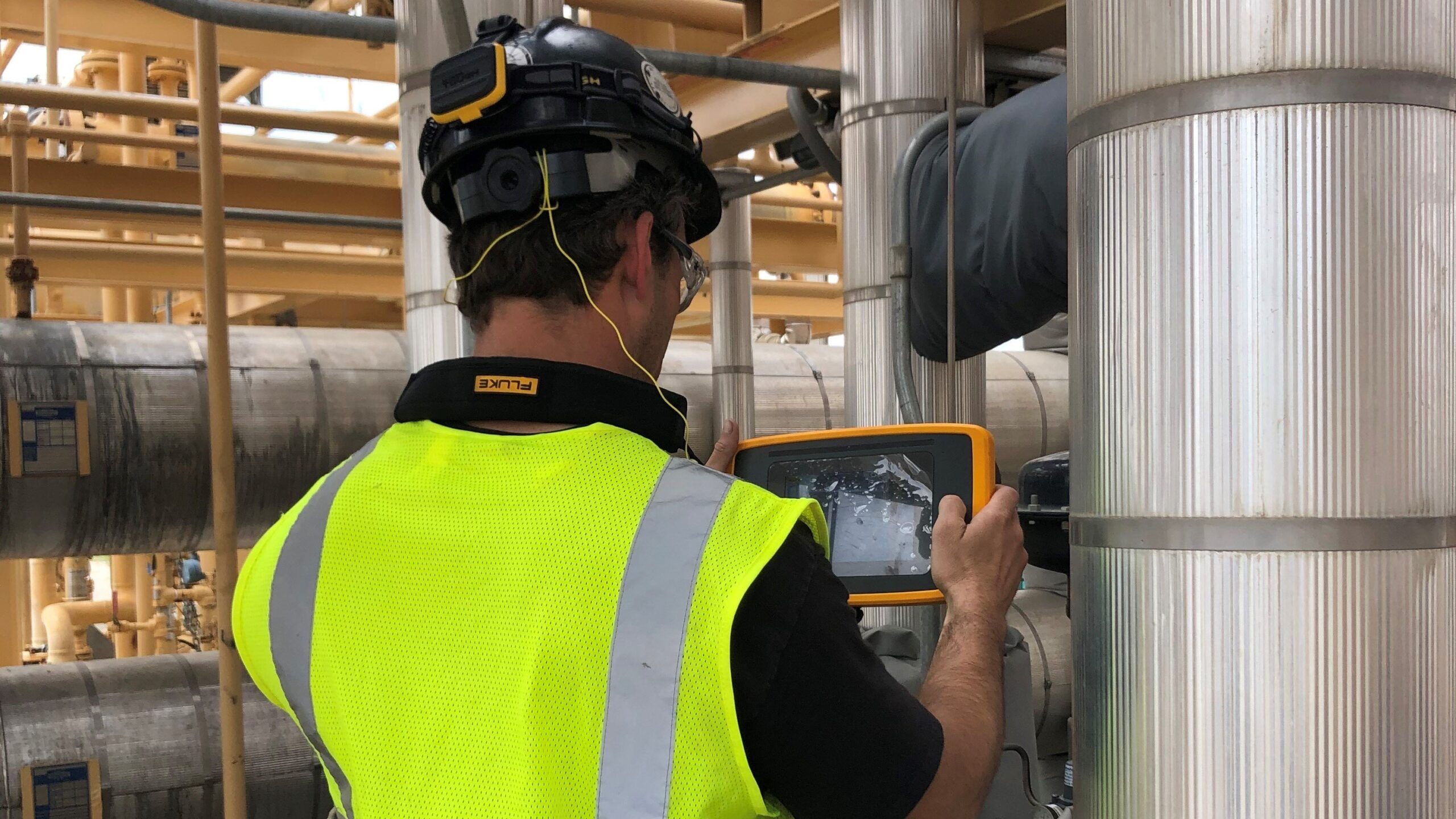

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ process allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from different suppliers, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods under sales contracts.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks involved in international transactions, aiding in smoother logistics planning. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– Definition: The total cost of purchasing and operating a product over its entire lifecycle.
– Relevance: Evaluating TCO helps buyers make informed decisions beyond the initial purchase price, considering maintenance, operation, and disposal costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make strategic decisions when investing in leak detection devices. Understanding these aspects will ensure compliance, enhance operational efficiency, and ultimately lead to better product quality and reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the leak detection device Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The leak detection device market is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing industrial automation, stringent regulatory requirements, and the need for improved safety and efficiency across various sectors, including oil and gas, manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals. As global industries strive to enhance operational efficiencies, the demand for reliable leak detection solutions continues to rise. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should note the following emerging trends:
-
Technological Advancements: The integration of IoT and AI in leak detection systems allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Buyers should explore suppliers offering smart devices that facilitate early leak detection and minimize downtime.
-
Diverse Testing Methods: Options such as underwater, air, and helium/tracer gas tests are gaining traction. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will help in selecting the most effective method, ensuring compliance and cost-effectiveness.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Stricter environmental regulations globally necessitate the adoption of advanced leak detection technologies. Buyers must prioritize vendors who can demonstrate compliance with international standards, particularly in sectors like oil, gas, and water utilities.
-
Sourcing Trends: An increasing number of international buyers are looking to source locally to reduce lead times and transportation costs. Establishing relationships with regional manufacturers can provide competitive advantages while enhancing supply chain resilience.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical factor in the procurement of leak detection devices. The environmental impact of industrial operations is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to consider the sustainability practices of their suppliers. Here are key considerations:
-
Environmental Impact: The manufacturing and disposal processes of leak detection devices can contribute to environmental degradation. Buyers should assess the lifecycle of products and opt for those with minimal ecological footprints.
-
Ethical Supply Chains: Engaging with suppliers committed to ethical sourcing practices is essential. This includes ensuring fair labor practices, responsible sourcing of raw materials, and transparency in supply chain operations.
-
Green Certifications: Look for products that come with environmental certifications such as ISO 14001 or EcoLabel. These certifications can provide assurance that the products meet specific environmental standards and contribute to sustainability goals.
-
Innovative Materials: The use of sustainable materials in the production of leak detection devices is on the rise. Buyers should seek out products made from recyclable or biodegradable materials to further enhance their sustainability profile.
Brief Evolution/History
The leak detection device sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, leak detection methods were rudimentary and often manual, relying heavily on visual inspections or basic pressure tests. However, as industries grew and the consequences of leaks became increasingly severe, the demand for more sophisticated technologies emerged.
With advancements in technology, methods such as helium leak testing and automated systems have become standard practice, allowing for greater precision and reliability. Today, the focus is not only on detection but also on prevention and sustainability, with an increasing number of manufacturers developing eco-friendly solutions to meet global environmental standards. This evolution presents an opportunity for international buyers to invest in state-of-the-art leak detection solutions that align with modern operational and sustainability goals.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leak detection device
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of leak detection devices?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, product certifications, and client references. Assess their manufacturing capabilities, including technology and quality control processes. Verify compliance with international standards, especially for specific markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Evaluate their customer support and responsiveness, which are critical for ongoing maintenance and service. Lastly, consider their logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery. -
Can leak detection devices be customized to meet specific operational needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor leak detection devices to your specific operational requirements. This can include adjustments in sensitivity, size, and functionality depending on the application. Engage with the supplier early in the process to discuss your needs and explore available modifications. Ensure that the supplier has a proven track record in providing customized solutions for similar industries. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for leak detection devices?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the device. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units to hundreds. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by factors such as customization, production capacity, and shipping logistics. It’s essential to discuss these details upfront with potential suppliers to align your procurement timelines with your operational needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing leak detection devices internationally?
Payment terms vary by supplier and can include options like advance payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Common practices involve a 30% deposit with the order and the remaining balance upon shipment. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of the payment terms, including any penalties for late payment and the currency used for transactions. Always consider the exchange rates and fees associated with international transfers. -
How can I ensure the quality and compliance of leak detection devices?
To ensure quality, request certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, as well as specific product certifications that meet international standards (e.g., CE marking in Europe). Ask for test reports and documentation demonstrating compliance with safety and performance standards. Regular audits and quality checks during the manufacturing process can also help maintain product integrity. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing leak detection devices?
Logistics are crucial in international trade. Consider the supplier’s shipping options, costs, and estimated delivery times. Evaluate potential customs duties and taxes applicable to your country, as these can significantly affect overall costs. It’s advisable to work with a freight forwarder familiar with your specific market to navigate import regulations and ensure smooth delivery. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding leak detection device quality or delivery?
Establish clear communication channels with your supplier to address issues promptly. Document all agreements and communications to support your claims. If disputes arise, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding quality assurance and delivery timelines. In cases of unresolved disputes, consider mediation or arbitration, as these methods can be less adversarial than litigation and often yield quicker resolutions. -
What after-sales support should I expect when purchasing leak detection devices?
After-sales support is vital for the effective operation of leak detection devices. Expect suppliers to provide training for your staff on device usage and maintenance. Inquire about warranty terms and the process for obtaining repairs or replacements. Additionally, assess the availability of technical support and spare parts, as well as resources for troubleshooting to ensure ongoing functionality and reliability of the devices.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leak detection device
In the rapidly evolving landscape of leak detection devices, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial component for international B2B buyers. By understanding diverse leak testing methods, such as underwater tests and helium tracer gas techniques, companies can select the most suitable solutions tailored to their specific applications. This ensures product integrity and compliance with industry standards, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Key Takeaways:
– Assess the required leakage rates and testing methods based on your product’s specifications and operational demands.
– Consider factors such as environmental conditions, degree of automation, and total cost of ownership when selecting a leak detection solution.
– Collaborate with experienced suppliers who understand regional market dynamics, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to leverage their expertise.
As we look to the future, embracing innovation in leak detection technology will be vital. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, buyers can not only safeguard their products but also gain a competitive edge in their respective markets. We encourage you to evaluate your sourcing strategies today, ensuring you are well-positioned to meet the challenges of tomorrow.