Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Linear Guide Rail
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for linear guide rail
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, the role of linear guide rails cannot be overstated. These essential components provide the precision and reliability necessary for smooth linear motion across various applications, from automation systems to CNC machinery. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key players in Poland and Italy—understanding the nuances of linear guide rails is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and product quality.
This guide will delve into the comprehensive scope of linear guide rails, covering critical aspects such as types, materials, and manufacturing quality control processes. It will also explore the landscape of suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends that influence purchasing decisions. Additionally, a section addressing frequently asked questions will empower buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate this complex market confidently.
By providing actionable insights and data-driven analysis, this guide is designed to equip international buyers with the tools to make informed sourcing decisions. Whether you are assessing the suitability of different linear guide configurations or evaluating supplier reliability, this resource will enhance your procurement strategy, ultimately leading to improved performance and competitiveness in your operations. Embrace the opportunity to refine your sourcing approach with a deeper understanding of linear guide rails—an investment that can drive significant returns in your business.
Understanding linear guide rail Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sliding Contact Bearings | Simple design, low cost, and good for light loads | Packaging, woodworking, and light machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, easy installation. Cons: Higher friction, less precision over time. |
| Rolling Element Bearings | Utilizes ball or roller elements for reduced friction | Robotics, automation, and CNC machines | Pros: High precision, smooth motion. Cons: Higher cost, requires regular maintenance. |
| Profile Rails | Modular design, customizable lengths and shapes | Automotive assembly, aerospace, and heavy machinery | Pros: Versatile, strong load capacity. Cons: Can be expensive, complex installation. |
| Miniature Guide Rails | Compact size, designed for tight spaces | Medical devices, electronics, and automation | Pros: Space-saving, lightweight. Cons: Limited load capacity, may not suit heavy-duty applications. |
| Linear Modules | Integrated system with rail and drive components | Automated assembly lines, packaging systems | Pros: All-in-one solution, reduced assembly time. Cons: Higher upfront investment, less flexibility. |
Sliding Contact Bearings
Sliding contact bearings are characterized by their straightforward design and affordability. They excel in applications requiring low-load capacities, such as packaging and woodworking industries. Buyers should consider the lower initial investment, but also be aware that these bearings may exhibit increased friction over time, leading to reduced precision. Regular maintenance is essential to extend their service life.
Rolling Element Bearings
Rolling element bearings are designed with balls or rollers that minimize friction, making them suitable for high-precision applications like robotics and CNC machines. These bearings offer exceptional smoothness and accuracy, making them a preferred choice in automation sectors. While their performance is superior, the higher cost and need for regular lubrication and maintenance must be factored into purchasing decisions.
Profile Rails
Profile rails are modular linear guides that can be customized to various lengths and shapes, catering to diverse applications in automotive assembly and aerospace industries. Their robust construction allows for high load capacities, making them suitable for heavy machinery. However, buyers should be prepared for potentially higher costs and a more complex installation process compared to simpler systems.
Miniature Guide Rails
Miniature guide rails are designed for applications with space constraints, such as in medical devices and electronic assemblies. Their compact size and lightweight nature make them ideal for tight environments. However, they generally have limited load capacities, so buyers must ensure that their applications do not exceed these limits. This type is best suited for precision tasks where space is at a premium.
Linear Modules
Linear modules combine rail and drive components into a single integrated system, streamlining the assembly process for automated systems. Commonly used in automated assembly lines and packaging systems, these modules offer a comprehensive solution that can significantly reduce setup time. While they provide an all-in-one advantage, the initial investment can be higher, and buyers should consider the trade-off between upfront costs and operational efficiency.
Related Video: Linear Guide Transformation on a Handmade Lathe – How I Replaced the Rails Step by Step
Key Industrial Applications of linear guide rail
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of linear guide rail | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | CNC Machining Centers | Enhanced precision in machining processes | Material quality (carbon vs. stainless steel), load capacity |
| Automotive | Robotic Assembly Lines | Increased efficiency and reduced cycle times | Compatibility with existing systems, maintenance support |
| Healthcare | Medical Device Production | Consistent quality and reliability in production | Cleanroom standards, corrosion resistance |
| Aerospace | Test Equipment for Aircraft Components | High accuracy and durability under extreme conditions | Certifications (ISO, AS9100), traceability of materials |
| Food & Beverage | Automated Packaging Systems | Improved hygiene and operational efficiency | Food-grade materials, ease of cleaning |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, linear guide rails are integral to CNC machining centers. They provide the necessary precision for cutting, drilling, and milling operations. By ensuring smooth motion along the X and Y axes, these systems minimize errors and enhance productivity. International buyers must consider the material quality—carbon steel may suffice for light loads, while stainless steel is preferred for heavy-duty applications. Additionally, understanding the specific load capacity requirements is crucial to avoid operational failures.
Automotive
Robotic assembly lines in the automotive industry utilize linear guide rails to facilitate the movement of robotic arms and tools. This application significantly boosts efficiency by reducing cycle times and improving consistency in assembly processes. Buyers should prioritize sourcing rails that are compatible with existing robotic systems and ensure that maintenance support is readily available. The ability to integrate seamlessly with automation technologies is essential for optimizing production lines.
Healthcare
In healthcare, linear guide rails are employed in the production of medical devices, where reliability and precision are paramount. These systems help maintain consistent quality throughout the manufacturing process, which is critical in a highly regulated industry. Buyers should ensure that the linear guides meet cleanroom standards and possess corrosion-resistant properties to withstand sterilization processes. Understanding the specific environmental requirements for medical applications will guide effective sourcing decisions.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies on linear guide rails for test equipment used in evaluating aircraft components. Given the extreme conditions these components face, high accuracy and durability are vital. International buyers should seek suppliers that offer products with relevant certifications, such as ISO and AS9100, to ensure compliance with industry standards. Additionally, traceability of materials used in manufacturing is crucial for maintaining safety and reliability in aerospace applications.
Food & Beverage
In automated packaging systems within the food and beverage sector, linear guide rails play a key role in enhancing hygiene and operational efficiency. They allow for smooth, reliable movement of packaging machinery, which is essential for maintaining product integrity. Buyers should focus on sourcing food-grade materials that comply with health regulations and facilitate easy cleaning. This ensures that operations remain efficient while adhering to strict industry hygiene standards.
Related Video: Redi-Rail Linear Guide Overview
Strategic Material Selection Guide for linear guide rail
When selecting materials for linear guide rails, it is essential to consider various factors such as environmental conditions, load requirements, and application specifics. Here, we analyze four common materials used in linear guide rails: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and plastic. Each material has unique properties that can significantly impact performance and suitability for specific applications.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and hardness, making it suitable for heavy load applications. It typically has a temperature rating up to 300°C and can withstand significant pressure. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its durability and cost-effectiveness, particularly for applications requiring robust support. However, its susceptibility to rust can be a significant drawback, necessitating protective coatings or regular maintenance, which can add to long-term costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is ideal for environments where exposure to moisture is minimal. It is commonly used in manufacturing and industrial machinery. Buyers in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, should consider protective treatments to enhance longevity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is crucial. Buyers should also be aware of local regulations regarding material coatings and treatments.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating that can exceed 800°C. It maintains its integrity under various environmental conditions, making it suitable for diverse applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and minimal maintenance requirements due to its resistance to rust and wear. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel, which can impact budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suitable for applications in the food and beverage industry, pharmaceuticals, and environments where hygiene is paramount. Its compatibility with various media makes it a preferred choice in healthcare and chemical processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A276 for stainless steel bars and shapes. In Europe, EN 10088 is relevant, while in the Middle East, buyers may need to consider local certifications.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating typically around 150°C. It is less robust than steel but compensates with its low weight and ease of machining.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, making it easier to handle and install. However, it has lower load-bearing capacity compared to steel, which limits its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring portability or where weight is a concern, such as in robotics or lightweight machinery. Its compatibility with various environments makes it versatile, though it may not be suitable for high-load scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is essential. Buyers should also consider the local availability of aluminum, as sourcing can vary significantly between regions.
Plastic
Key Properties: Plastic linear guide rails are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 80°C. They are less durable under heavy loads but are suitable for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of plastic is its resistance to corrosion and low friction properties, which can enhance performance in specific environments. However, its limited load capacity and susceptibility to wear under heavy loads can be significant drawbacks.
Impact on Application: Plastic is ideal for applications in clean rooms or environments where metal contamination must be avoided, such as in electronics or food processing. Its lightweight nature also makes it suitable for portable equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties of plastics. Understanding local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact is also crucial.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for linear guide rail | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Heavy machinery, industrial equipment | High durability and strength | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Aluminum | Robotics, lightweight machinery | Lightweight and easy to handle | Lower load capacity | Medium |
| Plastic | Clean rooms, electronics | Corrosion-resistant, low friction | Limited load capacity | Low |
This guide provides a clear overview of material options for linear guide rails, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for linear guide rail
Manufacturing Processes for Linear Guide Rail
The manufacturing process of linear guide rails is a complex operation that involves several key stages, each contributing to the overall quality and performance of the final product. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing linear guide rails is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Typically, high-grade carbon steel or stainless steel is used due to their durability and ability to withstand mechanical stress. The material is usually sourced from reputable suppliers who adhere to international standards to ensure quality.
- Material Inspection: Before processing, incoming materials undergo rigorous inspection (Incoming Quality Control – IQC) to verify compliance with specified standards, such as tensile strength and hardness.
- Cutting: The prepared steel is cut to the required lengths using precision cutting tools, ensuring minimal waste and exact dimensions for further processing.
2. Forming
After material preparation, the next phase is forming, which shapes the guide rail into its final profile. This can be achieved through various techniques:
- Machining: Precision machining processes, such as CNC turning and milling, are employed to create the rail’s precise dimensions and features. This step is critical for achieving the necessary tolerances.
- Heat Treatment: To enhance material properties, especially hardness and wear resistance, heat treatment processes (like quenching and tempering) are performed. This is essential for extending the operational lifespan of the linear guide.
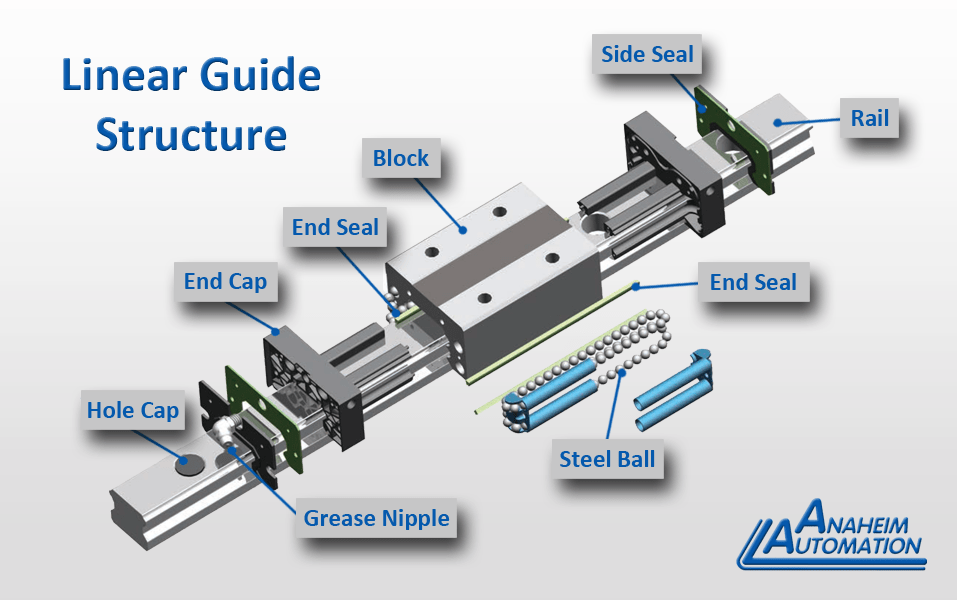
3. Assembly
In the assembly stage, various components of the linear guide system are brought together:
- Linear Blocks and Rails: The linear blocks (carriages) are assembled onto the rails. This involves ensuring that the internal steel ball bearings are correctly positioned to minimize friction during operation.
- Lubrication Systems: Integrated lubrication systems are installed to ensure smooth operation and longevity. Proper lubrication is vital to reduce wear and tear, especially in harsh environments.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves several processes that enhance the performance and aesthetic quality of the linear guide rails:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques like anodizing or coating are applied to protect against corrosion and improve wear resistance. This is particularly important for applications in humid or corrosive environments.
- Final Inspection and Cleaning: Before packaging, the rails are cleaned and subjected to final inspections to check for surface imperfections and dimensional accuracy.
Quality Assurance Processes
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for linear guide rails, ensuring that products meet specified standards and customer expectations. Here’s how QA is typically implemented:
International and Industry Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the international standards that guide the manufacturing of linear guide rails:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For applications in oil and gas, adherence to API standards is essential, particularly for components subject to high stress.
Quality Control Checkpoints
The QA process typically includes several key checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify defects early. This includes monitoring machining tolerances and ensuring proper assembly techniques.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product to confirm it meets all specifications and standards before shipping.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and reliability of linear guide rails:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using precision measurement tools to verify that the dimensions of the rails and blocks meet design specifications.
- Load Testing: Subjecting the rails to maximum load conditions to assess performance and failure points.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection to detect internal defects without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, verifying supplier quality control is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This could include reviewing their ISO certifications and quality management systems.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for detailed quality control reports that outline their testing procedures, inspection results, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to independently verify the quality of the products before shipment. This adds an extra layer of assurance, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital for B2B buyers:
- Regional Standards Variability: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards applicable to their specific markets.
- Documentation Requirements: Ensure that all necessary documentation, including certificates of conformity, inspection reports, and test results, are provided by the supplier. This documentation is often required for customs clearance and compliance with local regulations.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with linear guide rails, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and high-quality components for their applications.
Related Video: The Production Planning Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for linear guide rail Sourcing
In the competitive landscape of linear guide rail sourcing, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the key cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips to optimize procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Linear guide rails are commonly made from carbon steel or stainless steel. Higher-grade materials can enhance performance but also increase costs. Buyers should assess the material properties relevant to their specific applications to balance performance with expenditure.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing linear guide rails. Skilled labor is essential for precision engineering, particularly for custom specifications. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and administrative functions. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, benefiting both the supplier and the buyer.
-
Tooling: For custom or high-volume orders, tooling costs (such as molds and dies) can be significant. Buyers should inquire about tooling fees, especially if a large initial investment is required for specialized designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of linear guide rails involves rigorous testing and inspection processes. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the complexity of the product and the certifications required. Buyers should consider the value of certifications like ISO or industry-specific standards that may impact pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are influenced by distance, mode of transportation, and volume. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements, which can affect total landed costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on market conditions, competitive landscape, and individual business strategies. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can help buyers negotiate better deals.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit prices. Buyers should evaluate their needs and consider bulk purchases to maximize savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-designed linear guide rails may incur additional costs due to increased complexity in manufacturing. Buyers should weigh the necessity of custom features against their budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality products backed by certifications may command premium prices. However, investing in quality can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer service life.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels are crucial. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and support, justifying a higher price point.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can affect logistics costs and responsibilities. Buyers should select terms that align with their risk tolerance and logistical capabilities.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing and terms. Consider leveraging relationships or long-term contracts for better rates.
-
Cost Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also maintenance, operation, and disposal costs. A lower upfront price may not always equate to lower overall costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade agreements that may impact pricing. For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and market conditions is vital for successful negotiations.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential linear guide rail Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘linear guide rail’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for linear guide rail
Key Technical Properties of Linear Guide Rails
When evaluating linear guide rails for industrial applications, several technical specifications are critical. These properties not only ensure the performance of the linear guide systems but also influence purchasing decisions.
-
Material Grade
Linear guide rails are typically made from carbon steel or stainless steel. The choice of material affects the rail’s strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors like corrosion. For applications in humid or chemically aggressive environments, stainless steel is preferable due to its superior corrosion resistance, which translates to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. -
Load Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum weight that the linear guide can support while maintaining its performance. Understanding the load capacity is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure the selected guide rail can handle the intended application without failure. Overloading can lead to increased wear or catastrophic failure, impacting operational efficiency. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a linear guide’s dimensions. Tight tolerances are vital for applications requiring precision, such as in CNC machinery or robotics. A tighter tolerance generally means higher manufacturing costs, but it is essential for ensuring accurate positioning and smooth operation, which can enhance productivity. -
Rail Length and Pitch
The length of the linear rail determines the distance the guide block can travel, while the pitch refers to the distance between mounting holes. Customizing these specifications allows for flexibility in design and installation. Buyers should consider their application requirements to choose the right lengths and pitches that facilitate seamless integration into their machinery. -
Lubrication Mechanism
Effective lubrication is vital for reducing friction and wear within the linear guide system. Many modern linear guides are equipped with accessible lubrication systems that simplify maintenance. Understanding lubrication requirements can help buyers ensure optimal performance and longevity of the guides.
Common Trade Terms in Linear Guide Rail Procurement
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for B2B buyers to navigate the procurement process effectively. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of linear guide rails, OEMs often supply these components to machinery manufacturers. Buyers should evaluate OEMs based on their reputation for quality and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budget management, especially for smaller companies or those testing new products. Negotiating MOQs can sometimes yield better pricing. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. It typically includes detailed specifications. For B2B buyers, a well-prepared RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure that all potential suppliers provide comparable quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for managing shipping costs and risks. For example, terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) outline who pays for shipping and insurance. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the goods are received. Knowing the lead time is essential for project planning and inventory management, especially for businesses in fast-paced industries.
By grasping these essential properties and terminology, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding linear guide rail procurement, ensuring compatibility with their operational needs and enhancing overall efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the linear guide rail Sector
Global demand for linear guide rails is on the rise, driven by a variety of factors including automation, precision engineering, and the need for enhanced efficiency across industries. The manufacturing sector, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, is experiencing a technological transformation as companies adopt smart manufacturing practices. This shift is resulting in increased investments in linear motion systems, which offer the necessary precision and reliability for modern applications.
Emerging trends such as Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) are reshaping sourcing strategies for linear guide rail systems. Buyers are increasingly looking for integrated solutions that enhance operational efficiency, such as linear guides equipped with sensors for real-time monitoring. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on customization; B2B buyers are seeking suppliers who can provide tailored solutions to meet specific operational needs.
Moreover, the market dynamics are influenced by regional factors. In Europe, for example, stringent regulations around manufacturing processes are prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate compliance with environmental and safety standards. Conversely, in Africa and South America, the focus may lean more toward cost-effective solutions that do not compromise on quality.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the procurement of linear guide rails. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including resource extraction and waste generation, is under scrutiny. International buyers are increasingly demanding transparency in the supply chain, ensuring that their suppliers adhere to ethical practices.
Ethical sourcing is not just a compliance issue; it is a market differentiator. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide materials certified for sustainability, such as recycled metals and environmentally friendly lubricants. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ labels are becoming crucial criteria in supplier selection. Furthermore, companies that adopt sustainable practices are often viewed favorably in the market, enhancing their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Brief Evolution/History
The linear guide rail sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally designed for simple linear motion applications, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of high-performance linear guide systems capable of handling complex tasks in automation and robotics. The introduction of rolling element technology improved load capacity and reduced friction, allowing for smoother operation. Today, the sector is at the forefront of innovation, integrating advanced technologies such as IoT and AI to enhance performance and sustainability in manufacturing processes.
This evolution not only reflects technological advancements but also underscores the growing importance of quality and precision in the global marketplace, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest developments and trends in linear guide rail systems.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of linear guide rail
-
How can I vet potential suppliers of linear guide rails?
Vetting suppliers is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Start by checking their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO or EN. Request references from other clients, particularly those in your industry. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or ThomasNet to read reviews and ratings. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if possible, or arrange virtual tours to assess their operations and quality control processes. -
Are customization options available for linear guide rails?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific application requirements. This may include variations in size, material, or load capacity. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and application context to help suppliers understand your needs. Additionally, inquire about any extra costs associated with custom orders and the impact on lead times, as these can vary significantly. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for linear guide rails?
MOQs can vary widely depending on the supplier and the type of linear guide rail. For standard products, MOQs may start at 10-50 units, while customized solutions might require larger orders. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production schedule. Always clarify these details upfront to avoid unexpected delays. -
What payment methods are commonly accepted by suppliers?
Suppliers often accept a range of payment methods, including wire transfers, credit cards, and PayPal. For larger orders, letters of credit (LC) may be preferred, especially in international transactions. Ensure that you discuss payment terms and conditions, including any advance payments or installment plans, to establish a mutually beneficial agreement. Always verify the supplier’s payment policies before proceeding with an order. -
What quality assurance practices should I expect from suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should have established quality assurance protocols in place. This includes regular inspections during the manufacturing process, as well as final product testing to ensure compliance with specifications. Request documentation of their QA processes, including any certifications or test reports. Additionally, consider asking for samples before placing a large order to evaluate product quality firsthand. -
What certifications should I look for in linear guide rails?
Key certifications to look for include ISO 9001 for quality management systems and CE marking for compliance with European health and safety standards. Depending on your industry, additional certifications like RoHS or REACH may also be relevant. Ensure that the supplier can provide documentation for these certifications, as they are indicative of a commitment to quality and regulatory compliance. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers effectively?
To handle disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels from the outset. Document all agreements, including specifications, delivery dates, and payment terms, in a formal contract. In case of a dispute, approach the supplier with a calm and professional demeanor to discuss the issue. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to legal action, as these methods can be less costly and time-consuming. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing linear guide rails internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping methods, customs duties, and import regulations specific to your country. Discuss logistics with your supplier to understand their shipping options and costs. It’s also wise to work with a freight forwarder who can assist with documentation and ensure compliance with local regulations. Always factor in potential delays at customs, and plan your inventory accordingly to avoid disruptions in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for linear guide rail
As the linear guide rail market continues to evolve, international B2B buyers should prioritize strategic sourcing to optimize their procurement processes. Key takeaways include understanding the environmental considerations and maintenance requirements that affect the performance and longevity of linear guides. By selecting high-quality materials and ensuring proper lubrication, businesses can minimize downtime and maximize productivity.
Moreover, the cost of linear guides varies significantly based on specifications, so it is essential to engage with suppliers for tailored quotes that meet specific application needs. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage regional insights and emerging trends to make informed purchasing decisions.
Looking ahead, the demand for efficient, reliable motion control solutions will likely grow, driven by advancements in automation and manufacturing technologies. As such, maintaining strong supplier relationships and continuously evaluating sourcing strategies will be crucial. Act now to secure your supply chain and gain a competitive edge in the dynamic linear guide rail market. Embrace the opportunity to innovate and enhance operational efficiency through strategic sourcing.