Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Linear Guide Rail System
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for linear guide rail system
In today’s global marketplace, the demand for precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes has made linear guide rail systems an essential component across various industries. These systems provide smooth, reliable motion for a wide range of applications, from automation and robotics to medical technology and aerospace. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of linear guide rail systems is critical for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of linear guide rail systems, including ball rail systems, roller guides, and miniature options. We will explore the materials used in their construction, highlighting the advantages of carbon steel versus stainless steel. Additionally, the guide will cover manufacturing and quality control processes that ensure the durability and reliability of these systems.
B2B buyers will also gain insights into the pricing landscape, enabling them to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of different options. We will address common FAQs to clarify any uncertainties regarding maintenance, lubrication, and expected lifespan. By equipping buyers with this knowledge, we aim to empower them to source the most suitable linear guide rail systems that meet their operational needs while optimizing performance and reducing downtime. With this guide, buyers can confidently navigate the global market, making choices that support their strategic objectives and enhance their competitive edge.
Understanding linear guide rail system Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Rail Systems | High precision, low friction, optional position measuring function | Automation, handling, machine tools | Pros: High accuracy, low maintenance. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Roller Rail Systems | Enhanced load capacity, rigidity, suitable for heavy loads | Machine tools, measuring machines | Pros: Excellent stability, long service life. Cons: Heavier and more expensive. |
| Miniature Ball Rail Systems | Compact design, suitable for tight spaces | Microelectronics, medical technology | Pros: Space-efficient, precise. Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Linear Bushings and Shafts | Self-supporting, flexible mounting options | Automation, food industry | Pros: Versatile, easy installation. Cons: May require more frequent maintenance. |
| Cam Roller Guides | Designed for high-speed applications, simple construction | High-speed conveyors, packaging machines | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to replace. Cons: Lower precision compared to other types. |
Ball Rail Systems
Ball rail systems utilize precision-engineered ball bearings to minimize friction, ensuring smooth and accurate linear motion. These systems are ideal for applications requiring high precision, such as automation and machine tools. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the initial investment against the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and operational efficiency. While they may have a higher upfront cost, their durability and low maintenance requirements often justify the expense.
Roller Rail Systems
Roller rail systems are distinguished by their robust design, making them suitable for applications with heavy loads. They provide enhanced rigidity and stability, which is crucial for machine tools and measuring equipment. Buyers should consider their specific load requirements and operational environment, as these systems tend to be heavier and more expensive than other options. However, their long service life and ability to handle significant weight can make them a worthwhile investment for demanding applications.
Miniature Ball Rail Systems
Miniature ball rail systems are designed for applications where space is at a premium, such as in microelectronics and medical devices. These compact systems offer high precision in a small footprint, making them ideal for intricate operations. Buyers should assess the load capacity and environmental conditions, as these systems may not be suitable for heavy loads. While they excel in precision, their limited capacity can be a drawback in certain applications.
Linear Bushings and Shafts
Linear bushings and shafts provide a self-supporting mechanism with flexible mounting options, making them versatile for various applications, including automation and the food industry. They are relatively easy to install, which can reduce setup time and costs. However, buyers should be aware that these systems may require more frequent maintenance compared to other types. Evaluating the operational environment and expected maintenance intervals is crucial for ensuring long-term performance.
Cam Roller Guides
Cam roller guides are designed for high-speed applications and feature a simple construction that allows for easy replacement. They are commonly used in packaging machines and high-speed conveyors. While they are generally more cost-effective, buyers should be cautious about their lower precision levels compared to other linear guide types. Understanding the specific speed and precision requirements of the application will help in making an informed purchasing decision.
Related Video: How to install Linear Guides – NSK Installation Tutorial
Key Industrial Applications of linear guide rail system
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of linear guide rail system | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision assembly lines in automotive production | Enhances efficiency and accuracy in high-speed operations | Load capacity, environmental resistance, and lubrication options |
| Medical Technology | Automated laboratory equipment for diagnostics | Ensures precise movements for accurate test results | Cleanroom compatibility, material choice, and maintenance requirements |
| Food & Beverage | Packaging and bottling machinery | Increases throughput and reduces downtime | Hygiene standards, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning |
| Electronics | PCB manufacturing and testing machinery | Supports high-precision assembly and testing processes | Size constraints, load ratings, and compatibility with existing systems |
| Robotics | Robotic arms in automation systems | Provides smooth and reliable motion for complex tasks | Weight capacity, speed requirements, and integration capabilities |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, linear guide rail systems are pivotal in precision assembly lines, particularly in automotive production. These systems facilitate high-speed operations while maintaining accuracy, which is critical for assembling complex components. For international buyers, especially in regions like Europe and South America, sourcing guides that can handle specific load capacities and environmental conditions is essential. Additionally, considering lubrication options can enhance the longevity and efficiency of the system, reducing maintenance costs.
Medical Technology
In the medical technology field, linear guide rail systems are employed in automated laboratory equipment for diagnostics. These systems ensure precise movements, which are vital for accurate test results. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing guides that comply with cleanroom standards, as contamination can lead to erroneous outcomes. Furthermore, the choice of materials is critical; stainless steel options are preferred for their durability and ease of sterilization.
Food & Beverage
Linear guide rail systems are extensively used in the food and beverage industry for packaging and bottling machinery. By providing reliable motion control, these systems can significantly increase throughput and minimize downtime, essential for meeting production demands. Buyers should focus on sourcing guides that meet hygiene standards and offer corrosion resistance, as these factors are crucial in maintaining product quality. Additionally, ease of cleaning should be a priority to ensure compliance with health regulations.
Electronics
In electronics, linear guide rail systems are integral to PCB manufacturing and testing machinery. They support high-precision assembly and testing processes, which are essential in producing reliable electronic components. International B2B buyers must consider size constraints and load ratings when sourcing these systems, ensuring they fit within existing production lines. Compatibility with current machinery can also be a deciding factor, as retrofitting can incur additional costs.
Robotics
Linear guide rail systems play a vital role in robotics, particularly in automation systems where robotic arms require smooth and reliable motion. This is essential for executing complex tasks with precision. Buyers in emerging markets, such as those in Africa and South America, should focus on weight capacity and speed requirements when sourcing these systems. Integration capabilities with existing technologies are also crucial to ensure seamless operation and maximize productivity.
Related Video: An introduction to Linear Guide Rail Systems and their benefits
Strategic Material Selection Guide for linear guide rail system
When selecting materials for linear guide rail systems, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in linear guide rail systems: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, and Plastic. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can affect the suitability for specific applications.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and rigidity, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°C and can withstand moderate pressure. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Pros & Cons: The durability of carbon steel makes it an excellent choice for high-load applications, but its susceptibility to rust can lead to increased maintenance costs. Additionally, while carbon steel is generally cost-effective, the need for protective coatings can add to the overall expense.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is particularly effective in environments where high load-bearing capacity is required, such as in manufacturing and heavy machinery. However, its corrosion vulnerability limits its use in humid or corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local corrosion protection standards. In Europe, adherence to DIN standards is crucial for ensuring product quality.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can operate effectively in temperatures up to 800°C. Its mechanical properties make it suitable for dynamic loads, providing smooth motion.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and staining, making it ideal for environments where hygiene is critical, such as food processing and medical applications. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be harder to machine, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is well-suited for applications involving exposure to chemicals or moisture. Its durability and strength make it a preferred choice for high-precision machines.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of compliance with ASTM and JIS standards, especially in the Middle East and Europe. The higher cost may also necessitate a thorough cost-benefit analysis for budget-conscious buyers.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, with a temperature rating of approximately 150°C. It is resistant to corrosion and provides good thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which facilitates easier installation and reduced energy costs in dynamic applications. However, it is less rigid than steel, which may limit its use in heavy-load scenarios.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as robotics and automation systems. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe often prefer aluminum for its sustainability and recyclability. Compliance with EU regulations on materials can be a deciding factor, especially in environmentally conscious markets.
Plastic
Key Properties: Plastics, such as polyamide or POM (Polyoxymethylene), are lightweight and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They typically operate effectively in temperatures up to 100°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its low weight and cost, making it an economical choice for low-load applications. However, plastics may not provide the same level of durability and rigidity as metals, limiting their use in high-load scenarios.
Impact on Application: Plastic linear guides are suitable for applications in the electronics and medical industries, where weight and corrosion resistance are critical. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic complies with relevant standards, such as FDA regulations for medical applications in the U.S. and EU.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for linear guide rail system | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Heavy machinery, manufacturing | High strength and load capacity | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Robotics, automation systems | Lightweight and easy to install | Less rigid compared to steel | Medium |
| Plastic | Electronics, medical applications | Low weight and cost | Limited durability and load capacity | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the materials used in linear guide rail systems, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on application requirements, cost considerations, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for linear guide rail system
Understanding Manufacturing Processes for Linear Guide Rail Systems
The manufacturing of linear guide rail systems involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the precise specifications required for various applications. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes is essential for selecting reliable suppliers and ensuring product quality.
Key Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Materials: The primary materials used in linear guide rail systems are carbon steel and stainless steel, chosen for their durability and resistance to wear and corrosion.
– Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into specified lengths using precision cutting tools. This step may also involve heat treatment processes to enhance material strength. -
Forming
– Machining: Components undergo machining processes, including milling and turning, to achieve the required dimensions and surface finishes. This ensures smooth operation and compatibility with other system parts.
– Heat Treatment: For components subjected to high loads, heat treatment is performed to improve hardness and wear resistance, which is crucial for the longevity of the guide systems. -
Assembly
– Component Integration: The linear rail and blocks are assembled, often incorporating ball bearings or roller elements that facilitate smooth movement. This step requires precise alignment to ensure optimal performance.
– Lubrication Application: Proper lubrication is applied to minimize friction and wear during operation. Advanced lubrication systems may be integrated for low-maintenance requirements. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Coatings such as anodizing or galvanizing may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. This is particularly important for systems used in harsh environments.
– Final Inspection: Each assembled unit undergoes a thorough inspection to verify that it meets design specifications and performance criteria.
Quality Assurance Standards
Quality assurance is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for linear guide rail systems. B2B buyers should be familiar with the relevant international standards that ensure product reliability and performance.
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is crucial for manufacturers aiming to enhance customer satisfaction through effective process management.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: In certain industries, particularly oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary for ensuring product quality and safety.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure compliance with standards.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This includes checking for material integrity and dimensional accuracy. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– During manufacturing, critical checkpoints are established where measurements and tests are conducted to ensure that components remain within tolerances. This can include dimensional checks and surface finish evaluations. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– After assembly, each guide rail system undergoes comprehensive testing, including load testing and functionality assessments. This step is vital for verifying that the system performs as expected under operational conditions.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to guarantee the quality and performance of linear guide rail systems:
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing calipers and micrometers to measure critical dimensions and tolerances.
- Load Testing: Assessing the system’s performance under maximum load conditions to ensure it meets required specifications.
- Lubrication Tests: Evaluating the effectiveness of lubrication systems to ensure they minimize friction and wear.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are actionable steps to take:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can reveal adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can include on-site visits to assess facilities and practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports that document testing methods, results, and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide unbiased evaluations of the manufacturing processes and product quality before shipment.
Navigating QC/CERT Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing linear guide rail systems, international buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regional Compliance: Different regions may have unique certification requirements. For instance, products exported to the EU must comply with CE marking, while those destined for the U.S. may need to meet ANSI standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can aid in effective communication with suppliers, ensuring that quality expectations are clearly articulated and met.
- Documentation: Ensure that all quality-related documentation, including certifications, inspection reports, and compliance statements, is available and accurately reflects the product’s quality.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for linear guide rail systems, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations.
Related Video: Product Design & Manufacturing Collection workflows: Factory
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for linear guide rail system Sourcing
In the realm of linear guide rail systems, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will break down the key cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable tips for buyers to enhance their purchasing strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary material components for linear guide rail systems include carbon steel and stainless steel. The choice of material directly affects the cost; stainless steel is typically more expensive due to its corrosion resistance and durability, making it suitable for high-load or harsh environments.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce required for manufacturing and assembly. Skilled labor is essential for precision engineering, especially for high-quality systems. Geographic location can influence labor costs significantly; for instance, production in Europe may incur higher labor costs compared to South America or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes and advanced machinery can reduce overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Tooling expenses are incurred for creating molds and other specialized equipment necessary for manufacturing linear guide components. Custom tooling for specific applications can increase initial costs but may lead to better long-term pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are crucial to ensure the reliability and safety of linear guide systems. The costs associated with testing and certification can vary based on the complexity of the product and industry standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, shipping method, and volume. Buyers must consider local tariffs, taxes, and transportation costs when assessing total expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely based on the supplier’s positioning in the market, brand reputation, and service offerings. Established brands may command higher prices due to perceived quality and reliability.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically yield better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchasing to lower unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific features may increase costs. Buyers should clearly define requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can increase costs but are essential for applications in sensitive industries such as aerospace or medical technology.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation and reliability can affect pricing. Long-term partnerships may lead to better pricing structures due to trust and established order history.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms is crucial for international transactions to avoid unexpected fees.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Leverage potential long-term relationships to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower lifetime costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and international shipping costs that may impact the final price. Additionally, consider local suppliers to minimize logistics costs and lead times.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Prices for linear guide rail systems can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. Buyers should obtain formal quotes from suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs and conditions.
By understanding these cost components and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints, ultimately leading to more effective sourcing strategies for linear guide rail systems.
Spotlight on Potential linear guide rail system Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘linear guide rail system’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for linear guide rail system
Key Technical Properties of Linear Guide Rail Systems
Understanding the essential technical properties of linear guide rail systems is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially when evaluating options for automation and machinery applications. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
Linear guide rails are typically made from carbon steel or stainless steel. Carbon steel is cost-effective and suitable for standard applications, while stainless steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance, making it ideal for environments exposed to moisture or chemicals. Buyers should consider the environmental conditions of their applications when selecting materials to ensure longevity and performance. -
Load Rating
The load rating indicates the maximum load a linear guide can support while maintaining performance. It is vital for buyers to choose a guide rail with a load rating that exceeds their application requirements to prevent premature wear or failure. For instance, applications in heavy manufacturing may require guides with higher load ratings to ensure reliability. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in the dimensions of the linear guide components. Precise tolerances are essential for ensuring smooth operation and accuracy in motion applications. Buyers should assess the tolerance levels based on the precision requirements of their machinery to achieve optimal performance. -
Service Life
The estimated service life of a linear guide system depends on factors such as load, speed, and maintenance practices. Buyers should evaluate the expected service life to ensure it aligns with their operational needs and maintenance capabilities. Regular monitoring and lubrication can significantly extend the life of the guides, reducing total operational costs. -
Lubrication Mechanism
The lubrication mechanism can influence the maintenance frequency and overall efficiency of the linear guide. Some systems are designed with extended lubrication intervals, which can reduce downtime and maintenance costs. Understanding the lubrication requirements and options available is crucial for maintaining optimal performance in various environments.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is critical for buyers looking for quality components that meet specific standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their purchases effectively and avoid excess inventory costs. It’s particularly relevant for international buyers who may need to manage shipping costs and logistics. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products. This process helps buyers compare costs and terms from different suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal for their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for determining who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thereby minimizing potential disputes and ensuring smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. It is an essential factor for B2B buyers to consider, as it impacts project timelines and inventory management. Buyers should communicate their lead time expectations to suppliers to ensure timely delivery. -
Compatibility
This term indicates whether a linear guide rail system can function effectively with other components in a machinery setup. Compatibility is crucial for seamless integration and performance, making it an essential consideration for buyers when selecting components for their applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers from diverse regions can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and enhance their procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the linear guide rail system Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The linear guide rail system sector is experiencing dynamic growth driven by several global factors. Increasing automation across manufacturing industries, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, is propelling demand for precise and reliable linear motion systems. International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly adopting advanced technologies such as Industry 4.0 and IoT, which require high-performance linear guide systems for enhanced operational efficiency.
Emerging trends in sourcing include a shift towards modular systems that offer flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to adapt to changing production needs without extensive reconfiguration. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has prompted manufacturers to invest in automated logistics solutions, further driving the demand for linear guide systems. Buyers are also leaning towards suppliers that provide comprehensive product support, including CAD files and configurators, enabling them to customize solutions that meet specific application requirements.
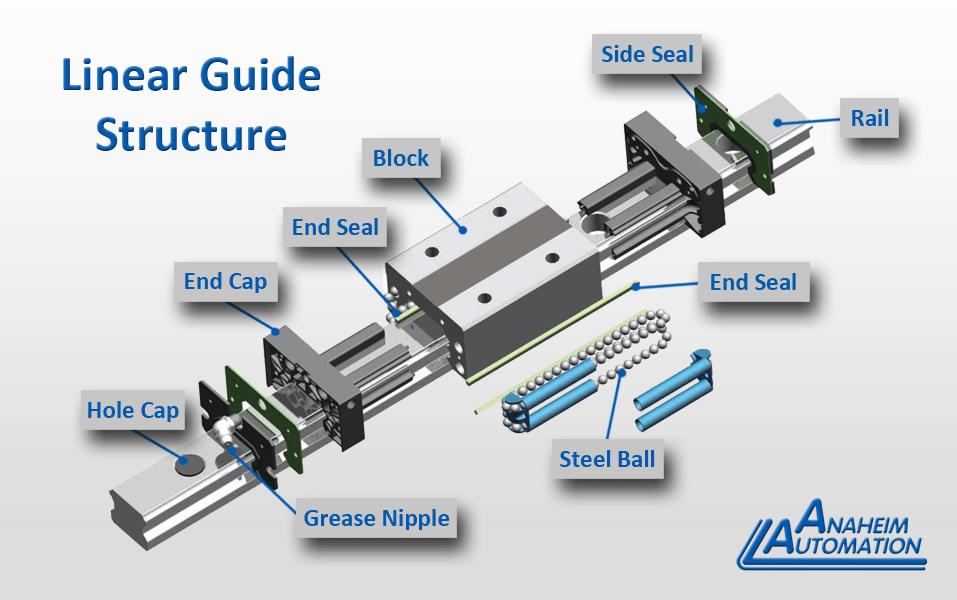
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Moreover, manufacturers are focusing on developing low-maintenance products with extended lubrication intervals, such as Bosch Rexroth’s ball rail systems that can operate for up to 20,000 km without relubrication. This trend not only reduces operational downtime but also lowers long-term costs, making such solutions attractive to B2B buyers across diverse markets.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the linear guide rail system sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including resource consumption and waste generation, is prompting companies to adopt greener practices. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through responsible sourcing and production methods.
Ethical supply chains are essential for ensuring that materials used in linear guide systems are sourced responsibly. Buyers should seek suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials and adhere to sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001, which indicates effective environmental management systems. The integration of recycled materials into product offerings is also gaining traction, allowing buyers to contribute to circular economy initiatives.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Furthermore, suppliers are developing products that minimize energy consumption and reduce carbon footprints. For instance, linear guide systems designed for high efficiency can lead to lower energy costs over their operational lifetimes. By choosing suppliers that align with sustainable practices, B2B buyers not only enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles but also position themselves competitively in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
Brief Evolution/History
The linear guide rail system has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, these systems were simple sliding contact bearings, but advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies have transformed them into sophisticated, high-precision components that cater to various industrial applications. The introduction of ball bearings improved friction reduction and load capacity, leading to the development of rolling element linear motion systems.
As automation technologies progressed, the demand for linear guide systems surged, particularly in high-speed and high-accuracy applications. Today, the market features a diverse array of products, including miniature systems for precision instruments and robust solutions for heavy machinery. This evolution reflects the sector’s responsiveness to the growing needs of global industries, positioning linear guide systems as essential components in modern manufacturing and automation landscapes.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of linear guide rail system
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of linear guide rail systems?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with a proven track record and industry certifications such as ISO 9001. Look for customer reviews and case studies that demonstrate reliability and quality. It’s also beneficial to request samples to assess product quality firsthand. Check if the supplier offers comprehensive technical support and after-sales service. Additionally, verify their production capabilities and lead times to ensure they can meet your demand. -
Can I customize linear guide rail systems to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for linear guide rail systems. This can include modifications in length, material, load capacity, and additional features such as integrated sensors or lubrication systems. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and application requirements to the supplier. Be prepared for potential changes in lead times and pricing based on the complexity of the customization. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for linear guide rail systems?
MOQs can vary significantly by supplier and product type, often ranging from 10 to 100 units. For specialized or customized products, MOQs may be higher. Lead times generally depend on the supplier’s stock levels and production capabilities, typically ranging from 2 to 6 weeks. Always confirm these details during your initial discussions to ensure they align with your project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing linear guide rail systems?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common arrangements include 30% upfront payment with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer credit terms, especially for established customers. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring the supplier feels secure. Explore options like letters of credit for larger orders to mitigate risks. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification of linear guide rail systems?
Request certifications from suppliers to verify compliance with international quality standards, such as CE marking or ISO certifications. It’s also prudent to ask about their quality control processes, including testing procedures for durability and performance. Some suppliers may offer third-party inspection services, which can provide additional assurance of product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing linear guide rail systems?
When importing, factor in shipping costs, potential tariffs, and delivery timelines. Choose a logistics partner experienced in handling industrial machinery to navigate customs regulations effectively. Ensure that the supplier provides proper documentation, such as commercial invoices and packing lists, to streamline the import process. Consider using Incoterms like FOB or CIF to clarify responsibilities for shipping and insurance. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding linear guide rail systems?
Establish clear terms in your purchase agreement regarding product specifications, delivery, and payment to minimize disputes. In case of issues, start with open communication to resolve the matter amicably. If necessary, involve a mediator or refer to the dispute resolution clause in your contract. It’s beneficial to document all communications and agreements to protect your interests. -
What are the best practices for maintaining linear guide rail systems?
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity of linear guide rail systems. Implement a schedule for cleaning rails and blocks to remove debris and dust, which can affect performance. Lubrication should be monitored and replenished according to manufacturer recommendations. Additionally, conduct periodic inspections for wear and tear, and replace components as needed to ensure consistent operation and prevent costly downtime.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for linear guide rail system
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of linear guide rail systems is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By understanding the various types of linear guides available—such as ball rail systems and roller rail systems—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs. Considerations such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and required maintenance will significantly impact the longevity and performance of these systems.
For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local suppliers while also exploring global options can lead to competitive pricing and better service support. Establishing strong partnerships with manufacturers ensures access to quality products and innovation, which is crucial in today’s fast-paced industrial landscape.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing linear guide rail systems, remain proactive in evaluating market trends and technological advancements. This approach will not only keep your operations running smoothly but also position your business for future growth. Engage with suppliers and industry experts to optimize your sourcing strategy—your next step could redefine your operational capabilities.