Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Lost Wax Casting Materials
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lost wax casting materials
Navigating the global market for lost wax casting materials is essential for businesses aiming to produce high-quality, precision-engineered components. This advanced manufacturing technique, renowned for its ability to deliver intricate designs and tight tolerances, is pivotal across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors. With the increasing demand for customized parts and the rising complexity of modern applications, selecting the right casting materials becomes a critical decision that influences product performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide serves as an invaluable resource for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Mexico and Turkey. It delves into various types of lost wax casting materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous alloys, and explores their specific applications. Additionally, the guide covers essential aspects such as manufacturing processes, quality control standards, supplier selection, cost considerations, and market trends.
By providing actionable insights and detailed information, this guide empowers buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. Understanding the nuances of lost wax casting materials enables companies to enhance their supply chain strategies, optimize production processes, and ultimately achieve superior product outcomes. Whether you are a seasoned industry player or new to the field, this guide will equip you with the knowledge necessary to thrive in a competitive global market.
Understanding lost wax casting materials Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal | Marine, medical, food-grade industries | Pros: Durable, versatile; Cons: Higher cost compared to carbon steel. |
| Carbon Steel | High strength, impact resistance | Automotive, industrial machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, strong; Cons: Prone to corrosion without treatment. |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, excellent thermal conductivity | Aerospace, automotive, consumer products | Pros: Lightweight, good corrosion resistance; Cons: Lower strength than steel. |
| Ductile Iron | Excellent ductility and wear resistance | Pump housings, automotive components | Pros: Cost-effective, strong; Cons: Heavier than aluminum, limited high-temperature applications. |
| Nickel Alloys | Exceptional high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, chemical processing | Pros: High performance in extreme conditions; Cons: Expensive and complex to machine. |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a popular choice in lost wax casting due to its remarkable corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. The most common types used are austenitic and martensitic stainless steels, each offering unique properties. B2B buyers should consider the specific application, such as marine or medical uses, as these industries often demand strict compliance with corrosion standards. While stainless steel parts provide long-lasting performance, they come at a higher price point compared to other alloys, making cost analysis critical for budget-conscious buyers.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is favored for its high strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications in the automotive and industrial sectors. This material is more cost-effective than stainless steel, providing a good balance between performance and price. However, buyers must factor in the need for protective coatings to prevent corrosion, especially in environments exposed to moisture. Understanding the specific grades and their mechanical properties is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right carbon steel for their projects.
Aluminum
Aluminum casting is known for its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications in aerospace and automotive industries. Its resistance to corrosion adds to its appeal, especially for outdoor and high-humidity applications. However, B2B buyers should be aware that aluminum typically has lower strength compared to steel, which might limit its use in heavy-duty applications. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their projects to determine if aluminum is the right choice.
Ductile Iron
Ductile iron is characterized by its excellent ductility and wear resistance, making it a reliable option for components like pump housings and automotive parts. It offers a strong combination of performance and cost-effectiveness, appealing to industries looking to balance quality with budget constraints. However, ductile iron is heavier than aluminum, which may be a disadvantage in weight-sensitive applications. Buyers should assess the trade-offs between strength, weight, and cost when considering ductile iron for their casting needs.
Nickel Alloys
Nickel alloys are distinguished by their high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for demanding environments such as aerospace and chemical processing. These alloys perform exceptionally well under extreme conditions, but they come with a higher price tag and can be challenging to machine. B2B buyers must weigh the benefits of performance against the costs and machining complexities when selecting nickel alloys for their applications. Understanding the specific needs of the end-use environment is crucial for making an informed purchasing decision.
Related Video: Lost Wax Casting Process from START to FINISH! EVERYTHING You Need to Know to Cast Jewelry At Home
Key Industrial Applications of lost wax casting materials
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lost wax casting materials | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of turbine blades | High precision and performance in extreme conditions | Certification standards (e.g., NADCAP), material traceability |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of engine components | Enhanced durability and weight reduction | Supplier reliability, lead times, and material certifications |
| Medical Devices | Creation of surgical instruments | Biocompatibility and precision for patient safety | Compliance with medical regulations, custom design capabilities |
| Oil & Gas | Production of valve bodies and fittings | High resistance to corrosion and pressure | Material specifications, sourcing from certified foundries |
| Jewelry | Crafting intricate designs | Ability to achieve fine detail and unique aesthetics | Quality of wax patterns, design flexibility, and turnaround time |
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, lost wax casting materials are critical for producing turbine blades that require high precision and performance under extreme conditions. This process allows manufacturers to create complex geometries that are lightweight yet robust, essential for fuel efficiency and safety. International buyers must consider certification standards such as NADCAP and ensure material traceability to meet stringent industry regulations.
Automotive
Lost wax casting is widely used in the automotive sector for manufacturing engine components, such as cylinder heads and exhaust manifolds. The method provides enhanced durability and allows for significant weight reduction, which can improve vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Buyers should prioritize supplier reliability, lead times, and material certifications to ensure consistent quality and compliance with automotive standards.
Medical Devices
In the medical device industry, lost wax casting is employed to create surgical instruments that require high precision and biocompatibility. The ability to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances ensures patient safety and instrument efficacy. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should focus on compliance with medical regulations and the supplier’s custom design capabilities to meet specific needs.
Oil & Gas
The oil and gas industry utilizes lost wax casting for producing valve bodies and fittings that must withstand high pressures and corrosive environments. This casting method offers superior mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy, critical for operational reliability. Buyers should be attentive to material specifications and seek suppliers that are certified foundries to ensure the integrity and performance of these components.
Jewelry
Lost wax casting is a preferred method in the jewelry industry for crafting intricate designs and fine details. This process allows artisans to create unique pieces with complex shapes that would be difficult to achieve through traditional methods. When sourcing materials, buyers should assess the quality of wax patterns, design flexibility, and turnaround time to ensure timely delivery of custom pieces.
Related Video: Lost Wax Casting Process
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lost wax casting materials
When selecting materials for lost wax casting, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence product performance, manufacturing complexity, and regulatory compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in lost wax casting, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly the austenitic (300 series) and martensitic (400 series) types, offers excellent corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and durability. These alloys can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, which extends the lifespan of components. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process may require specialized equipment and techniques, increasing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications in the food, medical, and marine industries due to its hygienic properties and resistance to harsh environments. Buyers should ensure compatibility with specific media, especially in food-grade applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific grades in their regions, as sourcing can vary significantly.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and offers excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It is suitable for applications requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its low weight, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. However, it has lower strength compared to steel and may not perform well under extreme temperatures, which can limit its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in automotive parts and structural components. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, but buyers should assess its limitations in high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the different aluminum alloys available and their respective properties. Compliance with standards like JIS and ASTM is essential, especially for aerospace applications.
Ductile Iron
Key Properties: Ductile iron exhibits excellent ductility and strength, making it a preferred choice for components subjected to high stress and impact. It also offers good wear resistance and machinability.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of ductile iron is its cost-effectiveness combined with mechanical performance, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. However, it may not offer the same level of corrosion resistance as stainless steel, which could limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Ductile iron is often used in automotive parts, agricultural equipment, and construction components. Its performance in various media should be evaluated, especially in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that ductile iron components meet local and international standards. Understanding the specific grades and their properties is vital for ensuring suitability for intended applications.
Bronze
Key Properties: Bronze alloys, primarily composed of copper and tin, are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and wear properties. They also exhibit good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of bronze is its resistance to corrosion, especially in marine environments, making it ideal for shipbuilding and underwater applications. However, bronze can be more expensive than other materials, and its mechanical strength may not match that of steel.
Impact on Application: Bronze is commonly used in marine hardware, valves, and bearings due to its durability and resistance to seawater. Buyers should consider its compatibility with other metals to avoid galvanic corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with marine industry standards is essential for buyers in coastal regions. Understanding the specific bronze alloy grades and their properties will help in making informed decisions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for lost wax casting materials | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive parts, aerospace components | Lightweight and good conductivity | Lower strength in extreme temperatures | Medium |
| Ductile Iron | Automotive components, agricultural equipment | Cost-effective with good strength | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Bronze | Marine hardware, valves | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and lower mechanical strength | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection process for lost wax casting, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lost wax casting materials
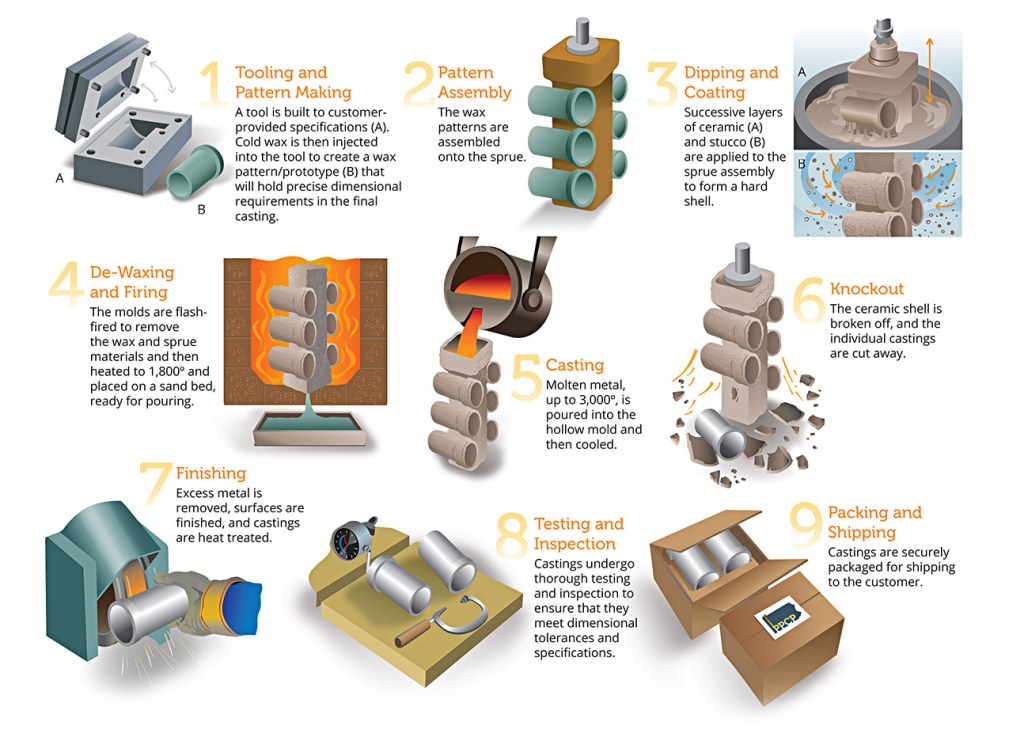
Manufacturing Process for Lost Wax Casting Materials
The manufacturing process for lost wax casting materials involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and quality in the final product. Below is a detailed overview of these stages, key techniques employed, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the lost wax casting process is the selection and preparation of the materials. Typically, this involves:
- Choosing the Right Alloy: Selecting an appropriate metal alloy is crucial, as it affects the mechanical properties of the final product. Common choices include stainless steel, aluminum, and various non-ferrous alloys, each offering distinct advantages such as corrosion resistance or lightweight characteristics.
- Wax Pattern Creation: A precise wax pattern is created using injection molding techniques. This pattern serves as a replica of the final component, and its accuracy is vital for achieving the desired quality in the casting.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming the wax patterns into a mold:
- Wax Tree Assembly: Multiple wax patterns are assembled onto a central runner or gate to form a tree-like structure. This enables the simultaneous casting of several parts, enhancing production efficiency.
- Shell Building: The assembled wax tree is repeatedly dipped into a ceramic slurry and then coated with fine sand. This process builds a robust ceramic shell that will withstand the molten metal during pouring.
3. Dewaxing
After the shell is formed, the wax must be removed to leave a hollow mold:
- High-Temperature Dewaxing: The ceramic shell is subjected to high temperatures in an autoclave or furnace, which melts the wax and allows it to drain away. This step is critical to ensure that the shell is ready to accept molten metal.
4. Pouring
With the wax removed, the next step is to pour the molten metal into the mold:
- Preheating the Mold: The ceramic shell is preheated to prevent thermal shock and ensure that the molten metal flows smoothly into the cavities.
- Metal Pouring: The selected alloy is poured into the mold, filling all intricate details created by the wax patterns. The cooling and solidification of the metal is closely monitored to ensure uniformity.
5. Finishing
After the metal has cooled and solidified, the final steps involve finishing the cast components:
- Shell Removal: The ceramic shell is broken away to reveal the cast parts. This process may involve mechanical methods or chemical treatments to ensure complete shell removal.
- Post-Casting Operations: The parts are cut from the runner and undergo various finishing processes, including sandblasting, CNC machining, and surface treatments. These steps are essential to achieve the final specifications and surface quality required by the customer.
Quality Assurance in Lost Wax Casting
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of lost wax casting materials. It ensures that the final products meet international standards and specific customer requirements.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the following international quality standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is widely recognized across industries. Compliance indicates that a supplier has established processes to ensure consistent quality.
- CE Marking: In the European market, CE marking demonstrates that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For buyers in the oil and gas industry, American Petroleum Institute (API) standards are crucial for components used in these applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) during the manufacturing process typically involves several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections are conducted throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, the finished products undergo thorough testing and inspection to verify that they meet all specifications.
Common Testing Methods
To ensure the integrity and performance of casting materials, various testing methods can be employed:
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing, X-ray inspection, and dye penetrant testing are used to detect internal and surface defects without damaging the components.
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, hardness, and fatigue tests are performed to evaluate the physical properties of the materials.
- Chemical Composition Analysis: Spectrometry is often used to confirm that the alloy composition matches the specifications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify supplier QC practices:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality systems, and compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports from suppliers can help assess their adherence to specified quality standards and identify any potential issues.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and manufacturing capabilities.
Navigating QC Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing lost wax casting materials internationally, buyers should consider:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality perceptions can help navigate supplier relationships more effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers comply with the specific regulatory requirements of the target market to avoid legal or logistical issues.
- Language Barriers: Clear communication is essential; consider working with suppliers who can provide documentation and support in a language that is comfortable for your team.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with lost wax casting materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensure product quality, and foster strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lost wax casting materials Sourcing
In the realm of lost wax casting materials, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. The cost components involved are multifaceted and can significantly influence the final price of the materials sourced.
Cost Components
- Materials: The choice of alloy (ferrous or non-ferrous) greatly impacts the cost. For instance, stainless steel tends to be more expensive than carbon steel due to its corrosion-resistant properties. Non-ferrous alloys like aluminum are typically lighter and may offer performance advantages but can also be pricier.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes compromise quality. Skilled labor is essential for the precision required in the lost wax casting process, which can lead to higher costs in regions with stringent labor regulations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help in minimizing overhead, but buyers should ensure that quality is not sacrificed for cost savings.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. Buyers should consider the amortization of these costs over the expected production volume to assess the impact on unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the final products meet specifications. However, enhanced QC measures can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate the balance between necessary quality assurance and cost-effectiveness.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are particularly critical for international buyers. Factors such as distance, mode of transportation, and customs duties can add to the overall cost. Incoterms also play a vital role in determining which party is responsible for various shipping costs, influencing pricing strategies.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin that reflects their operating costs and desired profit. Buyers should be aware of the typical margins in the industry to negotiate effectively.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence pricing for lost wax casting materials:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their production needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized components can incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality/Certifications: Materials with specific certifications (e.g., ISO) may command higher prices. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications against their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better quality assurance and service.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation is key to securing favorable pricing. Buyers should be prepared to discuss volume commitments and payment terms to achieve better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Opting for slightly higher-priced materials that offer greater durability may yield long-term savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and tariffs that may affect overall pricing. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can also mitigate some of these costs.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Pricing in the casting materials market can be volatile and subject to change based on market conditions, availability, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should approach pricing discussions with flexibility and an understanding of the broader market dynamics.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic negotiation tactics can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions in sourcing lost wax casting materials. By considering these factors, buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and optimize their supply chain efficiency.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential lost wax casting materials Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘lost wax casting materials’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lost wax casting materials
Key Technical Properties of Lost Wax Casting Materials
When engaging in the lost wax casting process, understanding the technical properties of the materials involved is critical for ensuring quality and performance in the final products. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade: The classification of the metal alloy used in casting, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or bronze. Different grades offer varying properties, including strength, corrosion resistance, and ductility. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital as it directly influences the product’s durability and suitability for specific applications.
-
Tolerance: This refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the final product. In lost wax casting, achieving tight tolerances is essential for components that fit into complex assemblies. Tighter tolerances often lead to higher production costs but can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of the final parts.
-
Surface Finish: The texture and quality of the part’s surface after casting. A finer surface finish may be required for aesthetic purposes or to reduce friction in moving parts. Understanding the required surface finish is crucial for determining the post-processing steps and costs involved in the production.
-
Yield Strength: This is the maximum stress that a material can withstand without permanent deformation. Knowing the yield strength is essential for applications where the components will be subjected to heavy loads or extreme conditions, ensuring that they maintain their structural integrity over time.
-
Corrosion Resistance: The ability of the material to withstand deterioration due to environmental factors. For industries such as marine or chemical processing, selecting materials with high corrosion resistance can prevent premature failure and reduce maintenance costs.
Common Trade Terminology in Lost Wax Casting
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are several terms commonly used in the lost wax casting sector:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can be crucial for buyers looking to source components that meet specific design and performance criteria.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for international buyers to know, as it can affect inventory management and overall costs, especially for smaller businesses.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): A document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and other relevant details for a specific quantity of products. Sending an RFQ is a critical step for buyers to ensure they receive competitive pricing and availability information from potential suppliers.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): A series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that are widely used in international commercial transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk, and costs associated with the delivery of goods.
-
Lead Time: The total time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the final product. This is a crucial factor for B2B buyers, especially in industries with tight deadlines, as it affects project timelines and inventory planning.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions, optimize sourcing strategies, and foster successful partnerships in the lost wax casting market.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the lost wax casting materials Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The lost wax casting materials sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. Key among these is the increasing demand for precision-engineered components across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. As manufacturers strive for higher quality and efficiency, the need for advanced casting techniques, like lost wax casting, is becoming more prominent. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping sourcing strategies. Automation and data analytics are enhancing production processes, allowing for greater customization and faster turnaround times.
Emerging trends include the integration of additive manufacturing (AM) with traditional casting methods. This hybrid approach enables the production of complex geometries and optimizes material usage, thus reducing waste. Furthermore, international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly prioritizing local sourcing to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains. This shift is partly a response to the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, prompting businesses to develop more resilient sourcing strategies.
In terms of market dynamics, buyers are advised to stay informed about fluctuations in raw material prices and geopolitical factors that can impact supply chains. Establishing partnerships with local suppliers not only enhances responsiveness but also fosters collaboration on innovation, allowing companies to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the lost wax casting materials sector. The environmental impact of traditional casting methods has led to a growing demand for sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking materials that minimize ecological footprints, such as those certified with green credentials. This includes sourcing from suppliers that adhere to environmentally friendly practices and utilize recycled materials in their casting processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as stakeholders are more aware of the social implications of their supply chains. Companies are encouraged to prioritize suppliers that demonstrate commitment to fair labor practices and transparency. This not only enhances brand reputation but also attracts customers who value corporate social responsibility.
To support sustainability efforts, international B2B buyers should look for suppliers offering certified green materials and adhere to standards such as ISO 14001. Engaging in partnerships with manufacturers who invest in sustainable technologies, like energy-efficient furnaces or waste-reduction systems, can significantly contribute to a more sustainable supply chain.
Brief Evolution/History
The lost wax casting technique, also known as investment casting, dates back over 5,000 years, with origins traced to ancient civilizations in China, India, and Egypt. Initially used for creating intricate jewelry and religious artifacts, the method has evolved significantly over the centuries. The introduction of modern materials and technologies has enhanced its application across various industries.
In the 20th century, the technique gained prominence in industrial applications, particularly for producing high-precision components in sectors such as aerospace and automotive. The advent of computer-aided design (CAD) and advanced materials has further transformed the landscape, allowing for the production of complex geometries and high-performance alloys. Today, lost wax casting stands at the forefront of manufacturing innovation, combining traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technology to meet the demands of a global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lost wax casting materials
-
How do I effectively vet suppliers for lost wax casting materials?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, certifications, and customer reviews. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their materials and production capabilities. It’s also essential to assess their financial stability and production capacity to ensure they can meet your demands. Consider suppliers that have a proven track record in international markets, particularly in your region, to ensure smooth communication and compliance with local regulations. -
Can I customize my lost wax casting orders?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for lost wax casting materials, including specific alloy compositions and part designs. Communicate your requirements clearly, including dimensions and tolerances, to ensure that the supplier can accommodate your needs. Customization may impact lead times and costs, so discuss these factors upfront to align expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for lost wax casting materials?
MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers, often influenced by the complexity of the parts and the materials used. It’s common to encounter MOQs ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the supplier’s capacity and your customization requirements. Always confirm these details during negotiations to avoid unexpected delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing lost wax casting materials?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and may include options such as upfront deposits, net 30/60/90 days, or payment upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that reflect the risk and trust level between your company and the supplier. Ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in the contract to prevent disputes later on. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for casting materials?
Request documentation for quality assurance processes, including ISO certifications and material test reports. A reputable supplier should be transparent about their quality control measures and provide certifications that verify the materials’ compliance with international standards. Consider conducting third-party audits if necessary to ensure the supplier adheres to required quality benchmarks. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing casting materials?
Logistical considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and potential tariffs or duties. Choose a supplier experienced in international shipping to avoid complications. Work with logistics partners familiar with your region to streamline the import process. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides all necessary shipping documents to facilitate smooth customs clearance. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding lost wax casting materials?
Establish a clear communication channel and escalation process for disputes before they arise. If issues occur, document all communications and agreements related to the problem. Many suppliers will have defined dispute resolution procedures, so familiarize yourself with these. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as a less confrontational approach before resorting to legal action. -
What are the risks associated with sourcing lost wax casting materials internationally?
International sourcing carries risks such as fluctuating exchange rates, political instability, and varying quality standards. To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough market research and choose suppliers with a stable reputation in your region. Diversifying your supplier base can also reduce dependency and potential disruptions. Consider insurance options for shipments to protect against loss or damage during transit.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lost wax casting materials
In summary, the strategic sourcing of lost wax casting materials is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance product quality and operational efficiency. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting the right alloys—such as stainless steel for corrosion resistance or aluminum for lightweight applications—as these choices directly influence performance and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, leveraging innovative manufacturing techniques like AM-assisted investment casting can expand material options and improve the mechanical properties of components.
Strategic sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also fosters partnerships that can lead to long-term success. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, prioritizing relationships with reputable suppliers will facilitate access to high-quality materials and advanced technologies.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing lost wax casting materials, consider the evolving market dynamics and emerging technologies that promise to reshape the industry. Engage with suppliers who understand your unique needs and can offer tailored solutions. The future of your manufacturing capabilities depends on the strategic decisions you make today—ensure they are informed, deliberate, and aligned with your long-term goals.