Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Perforated Aluminum
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for perforated aluminum
Aluminium perforated panels have emerged as a cornerstone material in modern architecture and industrial applications, offering a unique blend of functionality and aesthetic appeal. From the bustling urban landscapes of Europe to the growing infrastructure in Africa and South America, these panels cater to diverse needs, including ventilation, noise reduction, and decorative features. The lightweight and corrosion-resistant nature of perforated aluminum makes it a preferred choice for international B2B buyers seeking reliable, long-lasting solutions.
As procurement teams navigate the complexities of global sourcing, understanding the various types, materials, and manufacturing standards is essential. This guide equips decision-makers with actionable insights into the aluminium perforated panel market, covering critical areas such as panel types and materials, manufacturing and quality control, and supplier evaluation. Additionally, buyers will gain clarity on cost factors, pricing trends, and regional market considerations, ensuring they make informed choices tailored to their specific contexts.
By delving into this comprehensive resource, B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe will be empowered to minimize sourcing risks, optimize supplier relationships, and select products that meet both technical specifications and budgetary constraints. Ultimately, this guide serves as a roadmap for leveraging the potential of aluminium perforated panels in a competitive global marketplace, facilitating successful projects that resonate with local demands and standards.
Understanding perforated aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Round Hole Panel | Uniform, circular perforations; most common pattern | Facades, sunscreens, ventilation | Versatile, cost-effective; limited in decorative appeal |
| Slotted/Oblong Hole Panel | Long, narrow slots; aligned or staggered | Acoustic panels, screens, filtration | Enhanced airflow; may reduce panel strength |
| Decorative/Custom Pattern Panel | Complex or graphic patterns | Architectural cladding, branding | High visual impact; longer production lead time |
| Micro-Perforated Panel | Extremely small holes (<2 mm diameter) | Acoustic control, building interiors | Superior sound absorption; reduced structural strength |
| Corrugated/3D Perforated Panel | Perforations on a shaped or contoured panel | Exterior walls, shading, barriers | Higher rigidity, modern aesthetics; challenging to fabricate |
Standard Round Hole Panel
The standard round hole panel is characterized by its uniform circular perforations, making it a popular choice in various applications. Its design provides an optimal balance between open area and structural integrity, making it suitable for facades, ventilation systems, and sunshades. Buyers should consider the panel’s thickness and the percentage of open area to ensure compliance with local building codes, particularly in regions facing extreme weather conditions.
Slotted/Oblong Hole Panel
Featuring elongated slots, the slotted or oblong hole panel is engineered to enhance airflow and light passage. This design is ideal for acoustic panels and filtration systems, often used in commercial or industrial settings. While these panels offer better directional functionality, buyers should assess their mechanical strength, especially for high-traffic areas, as they may require additional reinforcement to prevent deformation.
Decorative/Custom Pattern Panel
Decorative panels allow for intricate designs, making them perfect for architectural branding and aesthetic applications. These panels can be customized to reflect cultural motifs or corporate identities, providing significant visual impact for projects such as corporate offices and retail spaces. However, buyers must account for longer production times and higher costs, necessitating close collaboration with manufacturers on design specifications.
Micro-Perforated Panel
Micro-perforated panels are renowned for their acoustic properties, making them suitable for interiors where sound absorption is crucial, such as auditoriums and public transport facilities. While their fine perforations enhance sound control, they also compromise structural integrity, limiting their use in load-bearing applications. Buyers should ensure that these panels meet international noise control standards while balancing aesthetic considerations.
Corrugated/3D Perforated Panel
The corrugated or 3D perforated panel features perforations on contoured surfaces, providing modern aesthetics and higher rigidity. These panels are frequently used in exterior applications, such as shading and architectural barriers. However, the complexity of their design may pose challenges in fabrication and transportation, which buyers need to consider when planning project timelines and logistics.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of perforated aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Perforated Aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Exterior cladding and facades | Enhances aesthetic appeal while providing durability and ventilation | Assess local climate requirements, panel thickness, and finishes |
| Automotive | Grilles and interior components | Lightweight design improves fuel efficiency and performance | Ensure compliance with industry standards and material specifications |
| Aerospace | Structural components and panels | High strength-to-weight ratio supports safety and efficiency | Verify supplier certifications and quality control measures |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Acoustic panels and filtration systems | Reduces noise pollution and enhances air quality in workspaces | Consider customization options for specific acoustic or filtration needs |
| Art and Design | Decorative installations and architectural features | Creates unique visual elements that enhance branding and identity | Collaborate closely with suppliers for custom designs and lead times |
Construction
In the construction sector, perforated aluminum is widely used for exterior cladding and facades. These panels not only contribute to the building’s aesthetic appeal but also provide essential ventilation and protection against the elements. For international buyers, especially in regions with diverse climates like Europe and Africa, it is crucial to evaluate local weather conditions when selecting the panel thickness and finishes. Understanding local building codes and regulations will ensure compliance and durability, ultimately affecting project success.
Automotive
Perforated aluminum is increasingly utilized in the automotive industry for components such as grilles and interior fittings. Its lightweight properties contribute to improved fuel efficiency, making vehicles more competitive in the market. When sourcing these materials, buyers should ensure that suppliers meet stringent industry standards for safety and quality. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for corrosion resistance and aesthetic finishes can significantly enhance the performance and appeal of automotive products.
Aerospace
In the aerospace sector, perforated aluminum is employed for various structural components due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This characteristic is vital for maintaining safety and efficiency in aircraft design. Buyers in this industry must prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international aerospace standards and quality control certifications. Engaging with reliable suppliers who understand the unique demands of aerospace applications can mitigate risks associated with sourcing critical components.
Industrial Manufacturing
Perforated aluminum plays a crucial role in industrial manufacturing, particularly for acoustic panels and filtration systems. These panels effectively reduce noise pollution and improve air quality, creating a safer and more comfortable working environment. Buyers should consider customization options to meet specific acoustic or filtration requirements, ensuring that the panels function optimally in their intended applications. Collaborating with manufacturers who specialize in industrial solutions can enhance the overall effectiveness of the sourced materials.
Art and Design
In the realm of art and design, perforated aluminum is used to create striking decorative installations and architectural features. This application allows businesses to enhance branding and identity through unique visual elements. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to explore customization options, as bespoke designs can significantly elevate a project’s aesthetic. Additionally, understanding lead times for production and delivery is essential to ensure that timelines are met without compromising quality.
Related Video: Advanced Aluminum Alloys for Aerospace Applications
Strategic Material Selection Guide for perforated aluminum
Aluminum perforated panels are available in various materials, each offering unique properties and suitability for different applications. Understanding these materials is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially when considering factors like durability, cost, and compliance with regional standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in perforated aluminum products.
1. Standard Aluminum Alloy (e.g., 3003, 5052)
Key Properties:
Standard aluminum alloys like 3003 and 5052 are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and good formability. These alloys can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of these alloys is their lightweight nature and ease of fabrication, which reduces manufacturing complexity. However, they may not be as strong as other materials, which can limit their use in load-bearing applications.
Impact on Application:
These alloys are ideal for architectural applications such as facades and sunshades, where aesthetic appeal and moderate structural integrity are required. They are compatible with various environmental conditions, though extreme climates may necessitate additional treatments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or ISO certifications, to guarantee product quality. Understanding the local climate can also influence the choice of alloy, as some may require protective coatings in humid environments.
2. Marine Grade Aluminum (e.g., 5083, 5086)
Key Properties:
Marine grade aluminum alloys, such as 5083 and 5086, offer superior corrosion resistance, particularly against saltwater environments. They maintain structural integrity under high-pressure conditions, making them suitable for marine applications.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of marine-grade aluminum is its durability and resistance to pitting corrosion, which extends the lifespan of products used in harsh environments. However, these alloys can be more expensive than standard grades and may require specialized fabrication techniques.
Impact on Application:
These materials are particularly suited for applications in coastal areas or industries involving water exposure, such as marine construction. Their enhanced properties ensure longevity and reliability in challenging conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in the Middle East and coastal regions of Africa should prioritize marine-grade aluminum for projects exposed to saltwater. Compliance with maritime standards is essential, and buyers should verify that suppliers can meet these specifications.
3. Anodized Aluminum
Key Properties:
Anodized aluminum undergoes an electrochemical process that enhances its corrosion resistance and surface hardness. This treatment allows for a variety of colors and finishes, making it aesthetically versatile.
Pros & Cons:
The major advantage of anodized aluminum is its enhanced surface durability and resistance to wear, making it suitable for high-traffic areas. However, the anodizing process can increase production costs and lead times.
Impact on Application:
Anodized panels are ideal for decorative applications in commercial and residential buildings, where visual appeal is paramount. They are also suitable for environments that require frequent cleaning, as the anodized surface is easier to maintain.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe and urban areas of South America should consider local aesthetic preferences and regulatory requirements for building materials. Ensuring that suppliers comply with relevant standards, such as DIN or EN, can help mitigate risks.
4. Powder-Coated Aluminum
Key Properties:
Powder-coated aluminum is coated with a dry powder that is cured under heat, resulting in a hard finish that is tougher than conventional paint. This process enhances corrosion resistance and allows for a wide range of colors.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of powder coating is its ability to provide a durable, uniform finish that resists chipping and fading. However, the process can be more costly and may require longer lead times compared to standard finishes.
Impact on Application:
This material is particularly effective for architectural applications, including facades and outdoor installations, where both aesthetics and durability are critical. It can withstand various environmental conditions, making it suitable for diverse climates.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in regions with extreme weather conditions, such as the Middle East, should ensure that the powder coating is suitable for their specific climate. Compliance with local environmental regulations regarding coatings is also essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for perforated aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Aluminum Alloy | Architectural facades, sunshades | Lightweight and easy to fabricate | Limited strength for load-bearing | Medium |
| Marine Grade Aluminum | Marine construction, coastal applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and specialized fabrication | High |
| Anodized Aluminum | Decorative applications, high-traffic areas | Enhanced durability and aesthetics | Increased production costs | Medium |
| Powder-Coated Aluminum | Outdoor installations, architectural facades | Durable, uniform finish | Higher costs and longer lead times | Medium |
This guide equips international B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for perforated aluminum, ensuring informed decision-making that aligns with project requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for perforated aluminum
Manufacturing Processes for Perforated Aluminum
Manufacturing perforated aluminum involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets the desired specifications for quality, performance, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers, as it enables informed decisions when sourcing from international suppliers.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process involves selecting the right aluminum alloy, typically 3003 or 5052, known for their excellent corrosion resistance and formability. Once the alloy is chosen, the aluminum sheets are cut to the required dimensions. The sheets are often pre-treated to enhance surface quality, which may include processes like cleaning, degreasing, and surface etching to remove impurities and improve adhesion for subsequent finishes.
Forming
The core of the manufacturing process is the perforation stage, where holes are created in the aluminum sheets. This is achieved through various methods:
- Mechanical Punching: A common technique where a punch presses through the sheet, creating holes. This method is efficient for high-volume production and allows for precise control over hole size and spacing.
- Laser Cutting: Offers high precision and flexibility in creating intricate patterns. This technique is especially useful for decorative panels where custom designs are required.
- Water Jet Cutting: Utilizes high-pressure water jets to cut through aluminum. This method is beneficial for thicker materials and can create complex shapes without generating heat that may alter the material properties.
After perforation, the sheets are often subjected to forming techniques such as bending or rolling to achieve the desired panel shape.
Assembly and Finishing
Once the perforated sheets are formed, they may undergo various finishing processes to enhance durability and aesthetics:
- Anodizing: An electrochemical process that increases corrosion resistance and allows for color finishes. Anodized surfaces are also easier to clean and maintain.
- Powder Coating: A dry finishing process that provides a durable finish available in a wide range of colors and textures. This is often used for architectural applications to meet specific design requirements.
- Painting: Involves applying liquid paint to the surface, suitable for projects requiring specific color matching.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of perforated aluminum to ensure that the products meet international standards and specific customer requirements.
International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of relevant international standards that govern the quality of aluminum products. The most pertinent include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system and is essential for suppliers aiming to demonstrate consistent product quality and improvement processes.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For applications in industries such as oil and gas, suppliers may need to comply with API standards, ensuring safety and reliability.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Throughout the manufacturing process, several quality control checkpoints help maintain product integrity:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Initial inspection of raw materials to ensure compliance with specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to detect and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection of the finished product against specifications, including dimensional checks, visual inspections, and testing of mechanical properties.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to validate the quality of perforated aluminum:
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensures that the perforated patterns and panel dimensions meet specified tolerances.
- Mechanical Testing: Involves tensile tests, hardness tests, and impact tests to verify the material’s strength and durability.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Assesses the material’s performance under various environmental conditions, crucial for applications in humid or coastal regions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital to mitigate risks associated with sourcing. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier reliability:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct thorough audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing capabilities, quality management systems, and compliance with international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing methods, results, and any certifications held by the supplier.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to conduct independent assessments of the supplier’s facilities and product quality before shipment.
Regional Considerations for International Buyers
When sourcing perforated aluminum, regional factors may influence quality assurance practices and supplier selection:
- Africa: Buyers should be vigilant about local standards and regulations, as compliance may vary significantly between countries. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who understand local compliance is essential.
- South America: Import regulations can be stringent; therefore, ensure suppliers can navigate local customs and provide necessary documentation for smooth imports.
- Middle East: The harsh climate necessitates specific testing for corrosion resistance. Ensure suppliers have experience with environmental conditions typical in the region.
- Europe: High standards for environmental sustainability and product safety mean that European buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust certifications and quality management systems.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with perforated aluminum, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their project requirements and regional standards.
Related Video: Mercedes C-Class CAR FACTORY – HOW IT’S MADE Assembly Production Line Manufacturing Making of
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for perforated aluminum Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing of perforated aluminum is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The overall pricing of perforated aluminum panels is influenced by several key components, including raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, and logistics.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of aluminum fluctuates based on global market trends, with factors such as availability, demand, and geopolitical events impacting prices. Buyers should keep an eye on market reports and consider hedging strategies for large orders.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly across regions. For instance, manufacturing facilities in South America may have lower labor costs compared to Europe. Understanding local wage standards can help buyers assess the total cost of labor involved in production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. High overhead can be an indicator of a well-maintained facility, which may lead to better quality products.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for custom perforation designs can be substantial. Tooling costs are amortized over the quantity produced, meaning larger orders can reduce the per-unit cost significantly.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in stringent QC processes ensures compliance with international standards and reduces the risk of defects. While this may increase upfront costs, it can lead to savings by minimizing returns and replacements.
-
Logistics: Freight and shipping costs are critical, especially for international transactions. These costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and local regulations. Understanding Incoterms is essential to clarify who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can differ based on market conditions, competition, and brand reputation. Buyers should evaluate suppliers not only on price but also on the value they bring in terms of quality and service.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Higher volumes often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific material specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications may charge more but can offer peace of mind regarding product reliability and compliance with industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their proven track record and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms can affect the total landed cost of products. Buyers should understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs to avoid unexpected expenses.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always engage in negotiations with suppliers. Understanding the cost structure allows buyers to identify areas where they can negotiate better terms or prices.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs over the product’s lifecycle. This perspective can lead to smarter purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of regional pricing variances influenced by local market dynamics, currency fluctuations, and regulatory environments.
Disclaimer
Prices for perforated aluminum can fluctuate due to market conditions and are subject to change. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and engage with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate and competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential perforated aluminum Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘perforated aluminum’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for perforated aluminum
Key Technical Properties of Perforated Aluminum
Understanding the essential technical properties of perforated aluminum is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed decisions. Here are some of the most critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
Aluminum is categorized into various grades, typically identified by the 1000 to 7000 series. The most common grades for perforated aluminum are 3003 and 5052, known for their excellent corrosion resistance and formability. Choosing the right material grade is vital as it affects the panel’s strength, weight, and suitability for specific applications. For instance, 3003 is often used for architectural applications, while 5052 is preferred for marine environments. -
Thickness
The thickness of the aluminum sheet directly impacts its durability and structural integrity. Common thicknesses range from 0.5 mm to 6 mm. Thicker sheets provide greater strength and resistance to deformation, making them ideal for high-traffic or load-bearing applications. Buyers should consider local building codes and the environmental conditions of their project site when selecting thickness. -
Hole Size and Pattern
The size and arrangement of perforations determine airflow, light transmission, and aesthetic appeal. Hole sizes typically range from 1 mm to 20 mm, and patterns can vary from standard round holes to intricate custom designs. Understanding how these factors affect functionality and design is crucial for buyers looking to achieve specific performance and aesthetic outcomes. -
Open Area Percentage
This term refers to the proportion of the panel that is open (i.e., perforated) compared to the total area. A higher open area allows for better airflow and light penetration, which is essential for applications like ventilation and acoustic panels. Buyers need to balance open area with structural strength to meet their project’s functional requirements.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Tolerance
Tolerance specifies the allowable variation in dimensions and hole sizes during manufacturing. Industry standards usually dictate tolerances, which can vary based on the application. Understanding tolerance is critical for ensuring that the panels fit accurately within the intended design and function, particularly in precision applications.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms related to perforated aluminum:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of perforated aluminum, buyers often work with OEMs to source custom panels that meet specific design and functional requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to ensure they can meet their project needs without incurring excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process wherein a buyer requests a quote from suppliers for specific products or services. It is crucial for buyers to provide detailed specifications when submitting an RFQ to receive accurate pricing and lead times. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost implications, ensuring smooth cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This is particularly important for project planning and scheduling. Buyers should factor in lead times when sourcing perforated aluminum to ensure timely project completion.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the perforated aluminum market more effectively, ensuring their projects are executed with precision and efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the perforated aluminum Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for perforated aluminum is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across various industries including construction, automotive, and aerospace. Key trends shaping this sector include increasing customization, where buyers seek tailored solutions to meet specific design and functional requirements. Additionally, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, such as CNC machining and laser cutting, are enabling suppliers to offer more intricate designs with enhanced precision.
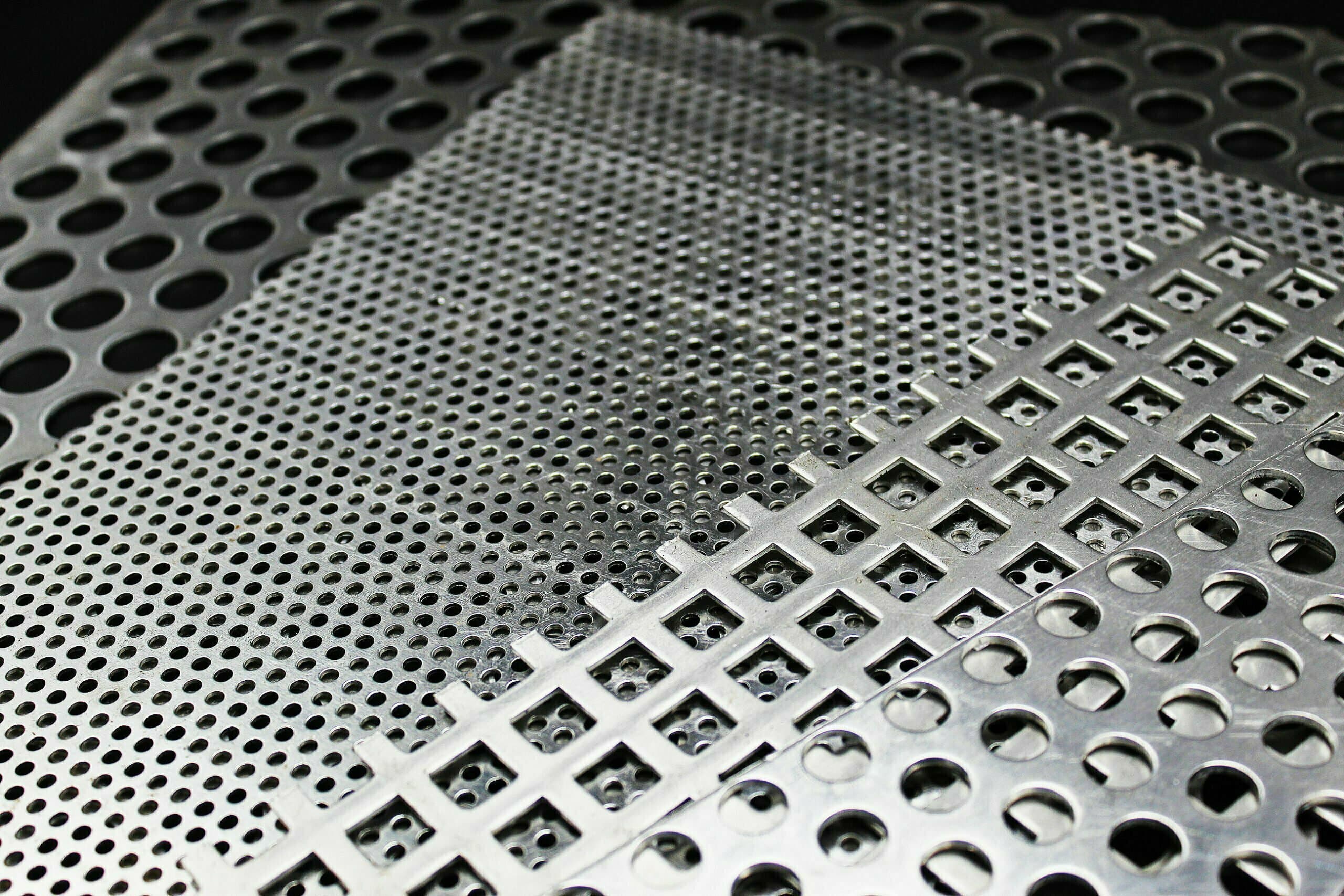
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must stay informed about regional market dynamics. For instance, in Africa, the expansion of urban infrastructure is driving demand for perforated aluminum in building facades and ventilation systems. In contrast, Europe emphasizes aesthetic appeal and sustainability, leading to a preference for high-quality decorative panels. Understanding these regional preferences can facilitate better sourcing decisions.
Moreover, supply chain transparency is becoming increasingly important. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that provide detailed information on their sourcing practices, production methods, and compliance with international standards. This trend is indicative of a larger shift towards responsible sourcing, where ethical considerations are influencing procurement strategies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is a significant concern for B2B buyers in the perforated aluminum sector. The environmental impact of aluminum production is substantial, particularly concerning energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that utilize recycled aluminum and possess certifications indicating responsible sourcing practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design).
In addition, companies are increasingly adopting ‘green’ materials and processes to minimize their carbon footprint. Choosing perforated aluminum products that are manufactured using sustainable practices can contribute to overall project sustainability and compliance with local regulations. Furthermore, engaging with suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and provide transparency in their supply chain can enhance corporate social responsibility (CSR) efforts.
B2B buyers are encouraged to ask suppliers about their sustainability initiatives and the lifecycle analysis of their products, which can help in making informed purchasing decisions that align with both business goals and environmental values.
Brief Evolution/History
The use of perforated aluminum can be traced back to the early 20th century when it began to gain traction in architectural and industrial applications. Initially favored for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, the material became increasingly popular as design trends evolved to favor aesthetic versatility.
In recent decades, the advent of advanced manufacturing technologies has transformed the perforated aluminum sector, allowing for more complex designs and tailored solutions. This evolution has positioned perforated aluminum as a key player in modern architecture and sustainable design, catering to the evolving needs of international B2B buyers who are now seeking both functionality and style in their projects.
As the market continues to grow, understanding these historical contexts and current trends will empower buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their long-term business objectives.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of perforated aluminum
-
How do I effectively vet suppliers for perforated aluminum?
When sourcing perforated aluminum, it’s essential to assess suppliers based on their reputation, experience, and product offerings. Start by reviewing their portfolio for past projects and client testimonials. Check for industry certifications such as ISO or other quality assurance standards, which indicate adherence to production norms. Additionally, consider requesting samples to evaluate the quality and customization options. Engage in direct communication to gauge their responsiveness and customer service capabilities, which are crucial for long-term partnerships. -
What customization options are typically available for perforated aluminum?
Most suppliers offer a range of customization options, including hole sizes, shapes, and patterns, as well as panel thickness and finishes. Depending on your project requirements, you can specify unique designs, such as decorative patterns or micro-perforations for acoustic applications. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your specific needs by discussing your design files and expectations upfront. Collaborating closely with the manufacturer during the design process can help achieve the desired aesthetic and functional outcomes. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities for perforated aluminum panels can vary significantly by supplier and project specifications. Generally, MOQs range from a few hundred to several thousand square meters, depending on the complexity of the order and supplier capabilities. Lead times typically range from 2 to 8 weeks, influenced by factors such as customization, supplier location, and current production schedules. It’s advisable to clarify these details before finalizing your order to avoid delays in your project timeline. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and compliance with industry standards?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing protocols for strength, durability, and aesthetic compliance. Verify that the supplier has relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which demonstrates commitment to quality management. Conducting audits or site visits can provide additional assurance. Additionally, consider including quality clauses in your purchase agreement to outline expectations for product specifications and compliance with local regulations. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing internationally?
When sourcing perforated aluminum internationally, it’s crucial to consider shipping methods, costs, and import regulations. Evaluate logistics options such as air freight for speed versus sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Familiarize yourself with customs duties, tariffs, and any required documentation for importation into your country. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the shipping process and help navigate complex logistics, ensuring timely delivery to your project site. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers?
In the event of a dispute with a supplier, start by addressing the issue directly and professionally. Clearly outline the problem and provide any supporting documentation, such as contracts or correspondence. If resolution is not achieved, consult the terms outlined in your purchase agreement regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Maintaining clear communication and documentation throughout the procurement process can help mitigate disputes and support your position if legal intervention becomes necessary. -
What payment terms are commonly used in international B2B transactions?
Payment terms in international transactions often vary based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the order. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect your interests while ensuring supplier confidence. Consider using escrow services for large transactions to safeguard both parties. Establishing a clear payment schedule and understanding any currency exchange implications can also facilitate smoother transactions. -
What are the key regional market considerations when sourcing perforated aluminum?
Regional market considerations include local regulations, material standards, and climatic factors that may influence material selection. In Africa and South America, for example, prioritize corrosion-resistant finishes due to harsher environmental conditions. In Europe and the Middle East, compliance with stricter building codes and sustainability practices is vital. Understanding these regional nuances can guide your procurement strategy, ensuring that the perforated aluminum panels you source are suitable for your specific application and locale.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for perforated aluminum
Navigating the global market for aluminum perforated panels offers substantial opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Strategic sourcing is essential, enabling procurement teams to select the right materials that align with project specifications, budget constraints, and regional regulations. By understanding the various panel types, manufacturing standards, and supplier capabilities, buyers can mitigate risks and enhance project outcomes.
Key takeaways include the importance of thorough supplier evaluation, including their experience, product variety, and customization options. Furthermore, recognizing the significance of local market conditions can influence sourcing decisions, ensuring compliance and sustainability in diverse environments.
As the demand for aluminum perforated panels continues to grow, the outlook remains positive. Buyers should remain proactive, leveraging innovative designs and functional applications that elevate their projects. Engage with reputable suppliers, explore emerging trends, and embrace the versatility of aluminum perforated panels to drive efficiency and creativity in your upcoming ventures. The future is bright for those who make informed, strategic sourcing decisions in this dynamic market.