Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Plastic Fabrication
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic fabrication
Plastic fabrication is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, essential for producing a wide array of products across various industries, including automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods. For international B2B buyers from dynamic markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of plastic fabrication is not merely beneficial; it is critical for maintaining a competitive edge. The ability to source high-quality, cost-effective plastic components can significantly impact operational efficiency and product innovation.
This comprehensive guide serves as your strategic resource for navigating the complexities of the global plastic fabrication market. It delves into various fabrication methods such as injection molding, thermoforming, and extrusion, highlighting the unique advantages and limitations of each. You will also find detailed insights on material selection, manufacturing workflows, and quality control standards, ensuring you can evaluate suppliers effectively and mitigate risks associated with international sourcing.
Additionally, the guide addresses key considerations like cost optimization strategies and market dynamics, empowering procurement leaders and technical managers to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives. With this knowledge, you can confidently engage with suppliers and enhance your sourcing strategies, ultimately driving innovation and growth in your operations across regions like Egypt, Brazil, the UAE, and beyond.
Understanding plastic fabrication Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | High-pressure injection of molten plastic into molds | Automotive parts, consumer electronics, medical devices | Pros: High repeatability, low per-unit cost at scale; Cons: High upfront tooling cost, long lead time. |
| Blow Molding | Air pressure inflates heated plastic into hollow forms | Bottles, containers, tanks | Pros: Ideal for seamless, hollow products; fast cycles; Cons: Limited shape complexity, not suitable for high precision. |
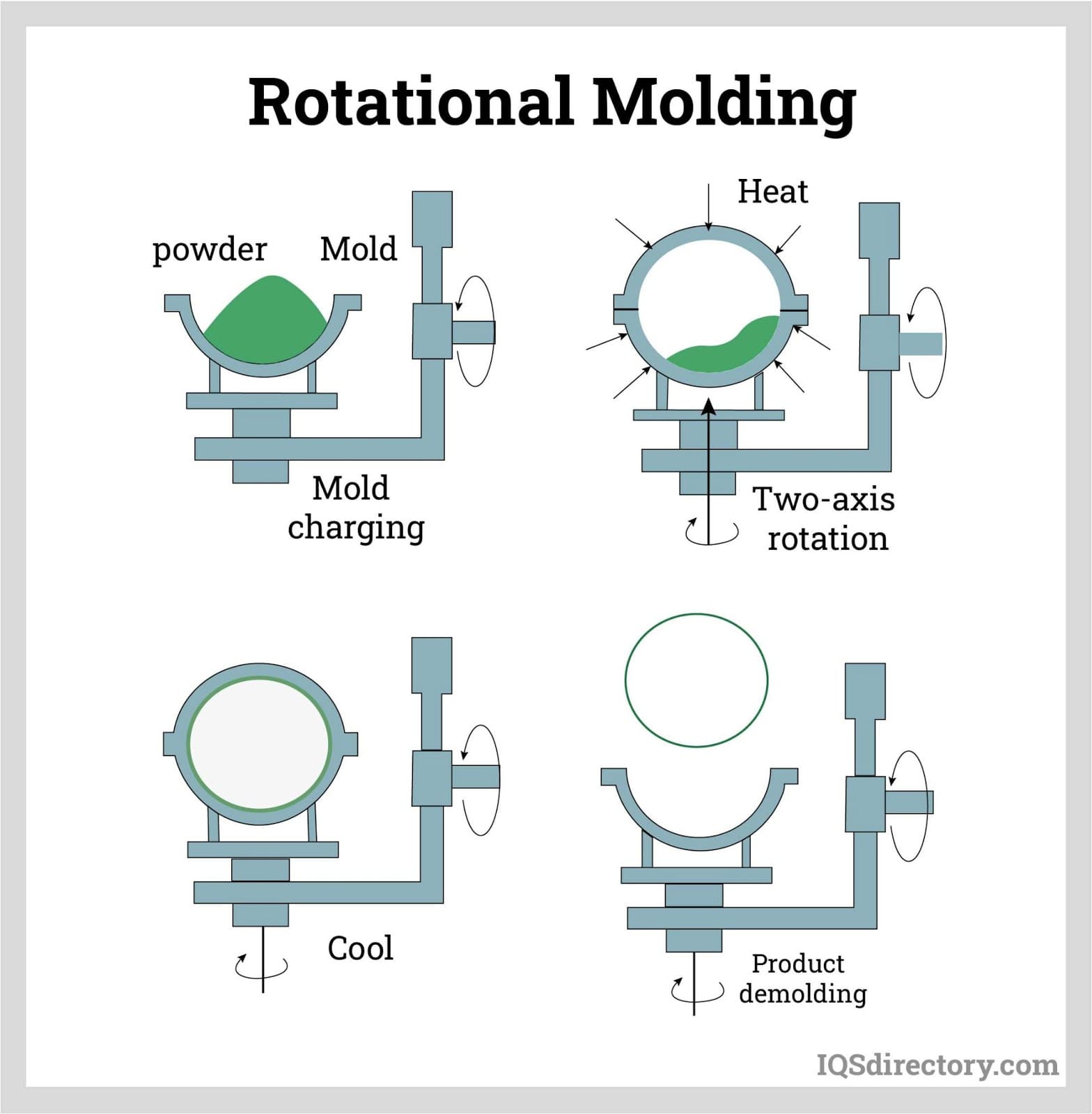
| Rotational Molding | Rotating molds distribute powdered plastic evenly | Water tanks, playground equipment, large containers | Pros: Low tooling costs, minimal waste; Cons: Slower cycle times, limited detail and tolerances. |
| Thermoforming | Heated plastic sheets shaped over molds under vacuum or pressure | Packaging, automotive panels, industrial trays | Pros: Low tooling costs, fast prototyping; Cons: Limited to moderate production volumes, typically single-sided parts. |
| 3D Printing | Layer-by-layer plastic build, no tooling required | Rapid prototyping, custom components, low-volume specialty parts | Pros: Fast and versatile; Cons: Not ideal for large-scale or high-strength needs. |
Injection Molding
Injection molding is the cornerstone of high-volume plastic production, favored for its ability to create complex, high-precision parts. This method is particularly suitable for industries requiring consistent quality and scalability, such as automotive and consumer electronics. B2B buyers should consider the initial tooling costs and lead times against their production forecasts, as the investment is justified by reduced per-unit costs at scale. Quality control and supplier reliability are crucial factors in this method.
Blow Molding
Blow molding is ideal for manufacturing hollow plastic products, such as bottles and containers. This process is characterized by its ability to produce seamless structures quickly, making it suitable for medium to large production runs. Buyers should assess the complexity of the product shapes required, as blow molding is less effective for intricate designs. Partnering with suppliers who have robust mold design capabilities can enhance flexibility in production sizes and reduce costs.
Rotational Molding
Rotational molding is particularly advantageous for creating large, hollow parts that do not require fine detail. This method allows for lower tooling costs and minimal material waste, making it attractive for infrastructure projects in regions like Africa and the Middle East. B2B buyers should weigh the longer cycle times and lower precision against the functional requirements of their products, particularly for applications like water tanks or playground equipment.
Thermoforming
Thermoforming uses heat to shape plastic sheets into three-dimensional forms, making it suitable for packaging and automotive applications. This method is valued for its low tooling costs and rapid prototyping capabilities, allowing for quick adjustments in production. However, B2B buyers should note that thermoforming typically results in single-sided parts with moderate detail. Ensuring a reliable supplier that can handle varying material thicknesses is essential for maintaining quality standards.
3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, offers unparalleled flexibility for rapid prototyping and low-volume production of custom components. This method is particularly useful for creating specialized parts without the need for extensive tooling. B2B buyers should consider the material properties and strength requirements of their products, as 3D printing may not be suitable for large-scale production where durability is paramount. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in advanced materials can enhance the effectiveness of this approach.
Related Video: Plastic Processing Overview
Key Industrial Applications of plastic fabrication
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of plastic fabrication | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of dashboards and interior components | Enhanced durability, lightweight design, and cost savings | Material compatibility, lead times, and quality certifications |
| Healthcare | Manufacturing of medical devices and components | High precision, compliance with safety standards | Regulatory compliance, material biocompatibility, and traceability |
| Packaging | Creation of custom packaging solutions | Improved product protection, reduced waste, and branding | Customization capabilities, material options, and sustainability practices |
| Construction | Fabrication of piping and fittings | Cost-effective solutions with high resistance to corrosion | Supplier reliability, material certifications, and local regulations |
| Consumer Electronics | Production of housings and electronic enclosures | Aesthetic appeal, functional protection, and lightweight | Precision manufacturing capabilities, design flexibility, and scalability |
Automotive
In the automotive sector, plastic fabrication plays a crucial role in producing dashboards, interior components, and body panels. The lightweight nature of plastics helps improve fuel efficiency while enhancing durability against wear and tear. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing from suppliers with advanced manufacturing techniques and quality certifications is essential to ensure compliance with stringent automotive standards. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding materials used in automotive applications can impact sourcing decisions.
Healthcare
Plastic fabrication is pivotal in the healthcare industry for manufacturing medical devices and components such as syringes, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment. The need for high precision and adherence to safety standards is paramount, as these products often come into direct contact with patients. B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing suppliers that comply with international regulations and ensure material biocompatibility. In regions like Africa and South America, where healthcare infrastructure is rapidly evolving, establishing relationships with reliable suppliers can facilitate access to innovative medical solutions.
Packaging
The packaging industry leverages plastic fabrication to create custom packaging solutions that enhance product protection and branding. This includes everything from food containers to protective casings for electronics. The ability to customize shapes and sizes while minimizing waste is a significant advantage for businesses looking to differentiate their products in competitive markets. International buyers should consider the sustainability practices of suppliers, as there is a growing demand for eco-friendly materials. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for packaging in different regions can aid in effective sourcing.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Construction
In construction, plastic fabrication is widely used for producing piping, fittings, and other components that are resistant to corrosion and lightweight. These attributes make plastics an ideal choice for both residential and commercial applications, particularly in regions with challenging environmental conditions. For B2B buyers, reliability and supplier reputation are crucial when sourcing these materials, as they directly impact project timelines and costs. Understanding local regulations and standards for construction materials is also essential to ensure compliance and avoid potential project delays.
Consumer Electronics
Plastic fabrication is integral to the consumer electronics sector, where it is used for creating housings and enclosures for devices such as smartphones, laptops, and appliances. The aesthetic appeal and lightweight characteristics of plastics are essential for product design, while also providing protection against environmental factors. International B2B buyers should focus on suppliers that offer precision manufacturing capabilities and design flexibility to accommodate rapid technological advancements. Scalability is also vital, as the demand for electronic products can fluctuate significantly in different markets.
Related Video: 30 Amazing Uses for Plastic 55 Gallon Drums
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic fabrication
When selecting materials for plastic fabrication, understanding the unique properties, advantages, and limitations of each option is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section analyzes four common materials used in plastic fabrication, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, and specific considerations for buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is known for its excellent chemical resistance, low density, and high melting point (around 160°C). It exhibits good fatigue resistance and can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
The material is lightweight and cost-effective, which makes it a popular choice for packaging and automotive parts. However, it has lower impact resistance compared to other plastics and can become brittle at low temperatures, limiting its use in certain climates.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is compatible with a variety of media, including water and many chemicals, making it ideal for containers and automotive components. Buyers should consider its limitations in high-impact environments or extreme temperatures.
Considerations for Buyers:
International buyers must ensure compliance with local regulations regarding food safety and chemical resistance, particularly in sectors like packaging. Standards such as ASTM and ISO are commonly referenced in quality assurance processes.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Key Properties:
PVC is recognized for its durability, chemical resistance, and excellent dimensional stability. It has a relatively high temperature resistance (up to 60°C) and can be rigid or flexible depending on the formulation.
Pros & Cons:
PVC is robust and resistant to environmental degradation, making it suitable for pipes, fittings, and construction materials. However, its production can involve toxic additives, raising environmental concerns. Additionally, it may require additional processing to achieve desired flexibility.
Impact on Application:
PVC is widely used in construction, plumbing, and electrical applications due to its compatibility with water and various chemicals. Buyers should evaluate the specific formulation to ensure it meets application requirements.
Considerations for Buyers:
B2B buyers must be aware of the varying regulations regarding PVC use, especially in Europe where stricter environmental standards apply. Compliance with standards like DIN and EN is essential for market acceptance.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Key Properties:
ABS is a strong and impact-resistant thermoplastic with a high melting point (around 105°C). It offers good chemical resistance and excellent surface finish, making it suitable for aesthetic applications.
Pros & Cons:
The material is easy to process and can be molded into complex shapes, making it ideal for consumer products and automotive parts. However, it can be more expensive than other plastics and may not perform well in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application:
ABS is commonly used in applications requiring high strength and durability, such as electronic housings and automotive interiors. Its aesthetic qualities also make it a favorite for consumer goods.
Considerations for Buyers:
International buyers should consider the availability of ABS in their region and the associated costs. Compliance with safety standards, such as UL for electrical components, is crucial for market entry.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is known for its exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity. It can withstand temperatures up to 135°C and is often used in applications requiring transparency and strength.
Pros & Cons:
The material is highly durable and resistant to UV radiation, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, it can be more expensive than other plastics and may be prone to scratching unless treated.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is widely used in safety equipment, automotive parts, and transparent enclosures. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, but buyers must consider its susceptibility to scratching in high-wear applications.
Considerations for Buyers:
B2B buyers should ensure that polycarbonate products meet relevant safety and performance standards, particularly in industries like automotive and construction. Compliance with ASTM and ISO standards is often necessary.
| Material | Typical Use Case for plastic fabrication | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Packaging, automotive components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower impact resistance, brittle in low temperatures | Low |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Pipes, construction materials | Durable and chemically resistant | Environmental concerns, requires processing for flexibility | Medium |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer products, automotive parts | Strong and impact-resistant | Higher cost, not suitable for high temperatures | Medium |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Safety equipment, transparent enclosures | Exceptional impact resistance | More expensive, prone to scratching | High |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a foundational resource for B2B buyers to make informed decisions in their sourcing strategies, ensuring alignment with both product requirements and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic fabrication
In the landscape of plastic fabrication, understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance (QA) is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to source high-quality products. This section delves into the main stages of the manufacturing process, key techniques employed, and the quality control measures necessary to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards.
Manufacturing Processes
The plastic fabrication process typically consists of four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in determining the overall quality and suitability of the final product.
1. Material Preparation
Material preparation involves selecting the appropriate type of plastic resin based on the desired properties of the end product. Common resins include:
- Polyethylene (PE): Known for its durability and chemical resistance, ideal for packaging and containers.
- Polypropylene (PP): Offers excellent fatigue resistance and is used in automotive and consumer goods.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Highly versatile, often used in construction and medical applications.
During this phase, the resins may be compounded with additives to enhance specific characteristics, such as UV resistance or color. Proper handling and storage of materials are critical to prevent contamination and degradation.
2. Forming Techniques
The forming stage encompasses various methods tailored to specific applications and product designs. Key techniques include:
-
Injection Molding: This method involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create complex shapes. It is highly efficient for high-volume production and offers excellent precision.
-
Thermoforming: In this process, heated plastic sheets are molded over forms using vacuum or pressure. It is suitable for larger items like trays and panels.
-
Blow Molding: Ideal for hollow products like bottles, this method uses air pressure to shape the plastic within a mold.
-
Rotational Molding: This technique is employed for creating large, hollow parts and is particularly popular for outdoor products and tanks.
-
3D Printing: An emerging technology for rapid prototyping, it allows for the creation of complex geometries without the need for molds.
Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages based on factors such as production volume, part complexity, and cost considerations.
3. Assembly
In the assembly phase, components are joined together if the product consists of multiple parts. This may involve:
- Adhesive Bonding: Using specialized adhesives to ensure strong connections.
- Mechanical Fastening: Employing screws, bolts, or clips for assembly, which allows for easier disassembly.
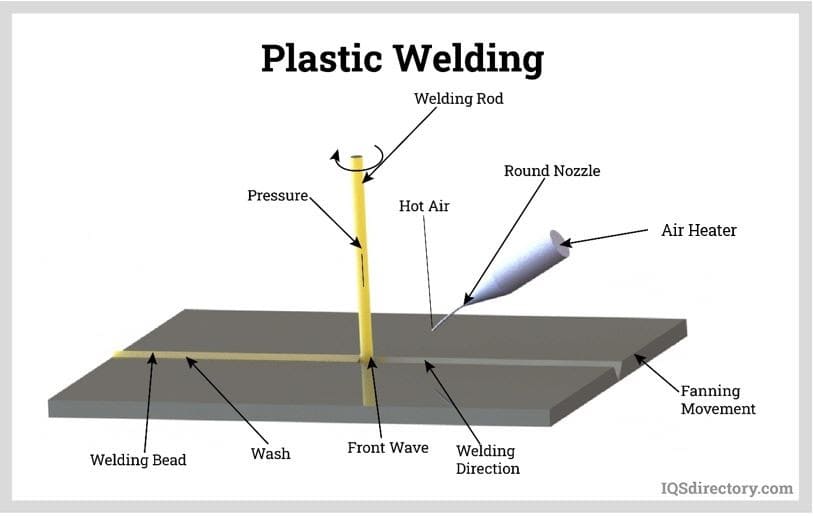
- Welding: Techniques such as ultrasonic welding or heat staking may be used for certain thermoplastics.
Choosing the right assembly method is critical to ensure product integrity and durability, especially for applications in demanding environments.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of the product. Common finishing techniques include:
- Trimming and CNC Machining: Providing precision cuts and adjustments to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finishes.
- Surface Treatments: Such as painting, coating, or texturing to improve appearance and resistance to wear or chemicals.
- Quality Checks: Incorporating inspection points to assess conformity to specifications before final packaging.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in the plastic fabrication process, ensuring that products meet both customer expectations and regulatory standards. International standards such as ISO 9001 are widely recognized, focusing on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications may apply, such as:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety and health requirements.
- API Standards: Relevant for products used in the oil and gas industry.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Ensures that raw materials meet specified criteria before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during manufacturing to monitor processes and identify deviations early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive review of the finished products to verify compliance with specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods vary based on the application but may include:
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility.
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers and gauges to ensure parts meet design specifications.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Evaluating how materials respond to exposure to various chemicals.
Supplier Verification
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Key methods include:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site inspections to review manufacturing capabilities, quality systems, and compliance with standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting documentation that outlines testing results, production processes, and corrective actions taken for any issues identified.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent agencies to conduct inspections and audits, providing an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s operations.
Nuances for International B2B Buyers
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of specific nuances:
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding local regulations and standards is essential, as they may vary significantly by region.
- Cultural Considerations: Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance communication and collaboration, which is particularly important in regions with different business practices.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Risks: Buyers should evaluate logistics capabilities and potential risks associated with shipping, customs, and lead times to ensure timely delivery.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in plastic fabrication, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands. This knowledge empowers businesses to select the right suppliers, optimize production costs, and maintain the quality standards essential for success in today’s competitive environment.
Related Video: Plastic Bag Mass Production Factory in Korea. Plastic Bag Manufacturing Process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic fabrication Sourcing
Cost Structure in Plastic Fabrication
Understanding the cost structure of plastic fabrication is crucial for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of plastic resin significantly influences pricing. Commodity plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene are generally less expensive than engineered polymers such as polycarbonate or nylon. Price fluctuations in raw materials can impact overall costs, making it essential to stay informed on market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, influenced by local wage standards and the complexity of the fabrication process. Automated processes can reduce labor costs but require higher initial investments.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility operation, utilities, and maintenance of equipment. Overhead can vary widely based on location, impacting the overall pricing strategy.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are particularly significant in processes like injection molding, where high-quality molds can be expensive to produce. Buyers should weigh the upfront tooling investment against the projected production volume to determine cost-effectiveness.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality assurance processes adds to costs but is essential for ensuring product reliability. Certifications, such as ISO standards, may require additional investment but can enhance product credibility in international markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can significantly affect the final price, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and import duties must be considered when calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin on top of their costs to ensure profitability. Understanding supplier pricing strategies can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence pricing in the plastic fabrication market:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should evaluate their demand patterns to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs and specifications typically increase costs. Buyers should balance their need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The type of plastic selected can dramatically alter costs. Buyers should consider material performance characteristics in relation to pricing.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality standards and necessary certifications can increase costs but are essential for compliance in regulated industries, such as healthcare or automotive.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms is crucial for managing costs effectively. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can impact the final price, especially for buyers in diverse regions.
Buyer Tips for Cost Management
To ensure cost efficiency in sourcing plastic fabrication, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices, especially for larger volumes. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes initial costs, maintenance, and potential waste or defects. This broader perspective can lead to more informed sourcing decisions.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly monitor material prices and industry developments. This knowledge enables buyers to anticipate shifts that could affect pricing and availability.
-
Evaluate Local vs. International Suppliers: Consider both local and international suppliers. While international suppliers may offer competitive pricing, local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Familiarize yourself with regional pricing dynamics. Factors such as currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and local economic conditions can influence pricing for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Disclaimer
Prices for plastic fabrication can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions and supplier specifics. The insights provided here are indicative and should be validated through direct supplier engagement and market research.
Spotlight on Potential plastic fabrication Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘plastic fabrication’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic fabrication
When engaging in plastic fabrication procurement, understanding essential technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for making informed decisions. Below are key specifications and common trade terms that B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with to navigate the complexities of this sector effectively.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the classification of plastics based on their chemical composition and performance characteristics.
– Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade is critical for ensuring the final product meets specific performance requirements, such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to heat or chemicals. For instance, choosing a high-grade polyethylene for packaging applications can enhance durability and shelf life. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance is the allowable deviation from a specified dimension or measurement in the manufacturing process.
– Importance: In precision industries, such as automotive and medical devices, maintaining tight tolerances is essential for product functionality and safety. Buyers must communicate clear tolerance requirements to ensure parts fit correctly and perform as intended. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: Surface finish describes the texture and quality of a product’s outer layer, which can range from smooth to textured.
– Importance: The surface finish impacts both aesthetic appeal and functionality, such as adhesion for coatings or ease of cleaning. B2B buyers should specify surface finish requirements to align with industry standards and customer expectations. -
Impact Resistance
– Definition: Impact resistance measures a material’s ability to withstand sudden force or shock without breaking.
– Importance: Products used in harsh environments, such as construction or automotive applications, require materials with high impact resistance to ensure safety and longevity. Understanding impact resistance helps buyers choose materials that meet operational demands. -
Chemical Resistance
– Definition: Chemical resistance indicates a material’s ability to withstand exposure to various chemicals without degrading.
– Importance: For industries such as pharmaceuticals and food packaging, selecting plastics with suitable chemical resistance is vital to prevent contamination and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company under its brand name.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is critical for buyers looking to source components that meet specific branding or quality standards, ensuring that they are purchasing from reputable suppliers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to avoid excess inventory or increased costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making and fostering competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and liability, which is crucial when dealing with international suppliers. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and inventory management. Buyers should factor in lead times when evaluating supplier reliability and capability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the landscape of plastic fabrication more effectively, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers to meet their business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the plastic fabrication Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global plastic fabrication market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand across various industries, and a focus on efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Key drivers include the rise of automation and Industry 4.0, which enhance production capabilities and reduce lead times. In regions like Africa and South America, the growing infrastructure projects and consumer markets are pushing demand for fabricated plastics in construction, packaging, and automotive applications.
Emerging technologies, such as 3D printing and advanced composites, are reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging additive manufacturing for rapid prototyping and low-volume production, allowing for greater design flexibility and reduced material waste. Additionally, the integration of data analytics and AI into supply chain management is helping companies optimize sourcing decisions, improve quality control, and anticipate market trends.
International buyers must navigate a complex landscape marked by varying regulatory environments and standards. For instance, European buyers often face stringent compliance requirements, while Middle Eastern buyers might focus on durability and performance in extreme conditions. Understanding these regional dynamics is essential for effective sourcing and supplier evaluation. Moreover, the growing emphasis on local sourcing in Africa and South America presents opportunities for buyers to engage with regional suppliers, fostering partnerships that can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce lead times.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the plastic fabrication sector. The environmental impact of plastic production and waste has prompted industries to seek sustainable practices and materials. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint, utilizing recycled materials, and implementing waste management strategies.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies strive to ensure that their supply chains are not only environmentally responsible but also socially conscious. This includes vetting suppliers for fair labor practices and compliance with local laws. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Global Recycle Standard (GRS) for recycled materials can serve as valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Investing in “green” materials—such as bioplastics or plastics derived from renewable resources—can also enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers. As regulations around plastic usage become stricter globally, aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals will be essential for long-term viability and market competitiveness.
Brief Evolution/History
The plastic fabrication industry has witnessed significant evolution since the mid-20th century, transitioning from basic manufacturing methods to advanced, automated processes. Initially dominated by simple techniques like extrusion and molding, the sector has embraced technological innovations, including CNC machining and 3D printing.
This evolution has been propelled by the growing demand for versatile, high-performance materials across various sectors, including automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods. The introduction of engineered plastics has expanded application possibilities, while global supply chains have facilitated access to diverse materials and expertise. As a result, today’s plastic fabrication landscape is characterized by rapid adaptation to market needs, technological integration, and a strong focus on sustainability, shaping the future of B2B sourcing in this dynamic industry.
Related Video: Made in the world: Better understanding global trade flows
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic fabrication
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers for plastic fabrication?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with proven industry experience and positive client testimonials. Request references and case studies to gauge their capability in meeting your specific needs. Assess their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and certifications such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider suppliers’ compliance with international standards relevant to your industry, such as FDA or REACH regulations. Conducting site visits or virtual audits can also provide insight into their operational practices and culture. -
Can I customize my plastic fabrication order?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options based on your project requirements. Discuss material selection, design specifications, and production methods to ensure your needs are met. Be clear about your desired features, such as color, texture, or functional attributes. Keep in mind that more complex customizations may impact lead times and costs. Collaborating with suppliers early in the design phase can help optimize production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities vary by supplier and manufacturing method. For injection molding, MOQs can be high due to tooling costs, while processes like thermoforming may offer lower MOQs. Lead times generally range from a few weeks to several months, influenced by factors such as production capacity, material availability, and complexity of the design. Always discuss these factors upfront with your supplier to align expectations and ensure timely delivery. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Reputable suppliers implement stringent quality assurance protocols, including regular inspections and testing throughout the production process. Look for suppliers that utilize advanced quality control systems, such as Statistical Process Control (SPC), to monitor and maintain standards. Certifications like ISO 9001 or industry-specific qualifications indicate a commitment to quality. Request documentation of quality assurance processes and results to ensure that the products meet your specifications and industry regulations. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping when sourcing internationally?
Logistics can be complex when sourcing internationally. Engage suppliers who have experience with global shipping and can manage customs clearance and documentation efficiently. Discuss shipping options, costs, and estimated delivery times upfront. It may be beneficial to partner with a freight forwarder who can provide expertise in international logistics, ensuring that your products arrive safely and on time. Always factor in potential delays due to customs or transportation issues when planning your supply chain.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What should I do if there’s a dispute with my supplier?
In the event of a dispute, maintaining open communication with your supplier is essential. Document all interactions and agreements to have a clear record. Try to resolve issues amicably through discussion or negotiation. If necessary, refer to the contractual terms agreed upon at the outset, which may include dispute resolution clauses. If resolution proves difficult, consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, especially in international contexts where legal frameworks may differ. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for plastic fabrication?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common practices include upfront deposits (typically 30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer payment through letters of credit, which can protect both parties. Always clarify payment terms during negotiations and ensure they are documented in the contract. Be aware of the potential for currency fluctuations and consider using stable currencies for transactions to mitigate financial risks. -
What certifications or compliance should I look for in plastic fabrication suppliers?
Depending on your industry, certain certifications may be essential. Look for ISO certifications, which indicate adherence to international quality management standards. For products in healthcare or food sectors, certifications like FDA compliance or GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) may be necessary. Additionally, check for environmental certifications such as ISO 14001, which reflect a commitment to sustainable practices. Ensure your suppliers can provide documentation for these certifications to verify compliance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic fabrication
In the fast-evolving landscape of plastic fabrication, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical driver of competitive advantage for B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse fabrication methods—such as injection molding, blow molding, and thermoforming—enables companies to select the most suitable process for their specific needs, balancing factors like cost, quality, and production volume. Leveraging insights into material properties and manufacturing workflows can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced product performance.
As procurement leaders and technical managers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate these complexities, establishing strong partnerships with reliable suppliers is essential. Evaluating suppliers based on their capabilities, compliance with international standards, and ability to innovate will mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
Looking ahead, the plastic fabrication industry is poised for transformation driven by advancements in technology and sustainability initiatives. B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace these changes, exploring innovative materials and processes that align with their long-term strategies. By proactively engaging in strategic sourcing, businesses can not only optimize their supply chains but also position themselves as leaders in their respective markets. Seize the opportunity to enhance your sourcing strategy today, ensuring your business remains resilient and competitive in the global arena.