Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Power Cord Types
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for power cord types
In today’s interconnected world, the choice of power cord types is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to ensure seamless operations across various markets. Whether you are sourcing for manufacturing plants in Africa, assembling electronics in South America, or equipping offices in Europe, understanding the nuances of power cords can significantly impact your operational efficiency and safety standards. With the rise of global trade, the risks associated with non-compliance or mismatched specifications have never been more pronounced.
This comprehensive guide demystifies the complexities surrounding power cord types, including the key standards—IEC, NEMA, and CEE—that govern their use. You will gain insights into the various materials and configurations that define quality, durability, and performance. Furthermore, we delve into manufacturing and quality control processes that can affect sourcing decisions, ensuring you partner with reputable suppliers.
Additionally, the guide covers essential cost considerations, market trends, and frequently asked questions, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed sourcing decisions. By navigating this critical aspect of your supply chain effectively, you can mitigate risks, optimize your procurement strategies, and ultimately enhance your product offerings. Empower yourself with the insights needed to thrive in the global marketplace, making your power cord sourcing decisions not just informed, but strategic.
Understanding power cord types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEC | Standardized global connectors, flexible designs | Electronics, IT equipment, household appliances | Pros: Wide compatibility, easy interchangeability. Cons: May require adapters for regional variations. |
| NEMA | Specific to North America, polarized designs | Industrial equipment, power tools, household appliances | Pros: High safety standards, reliable for high-power applications. Cons: Limited to North America, can be bulky. |
| CEE | Designed for high-voltage applications, robust build | Industrial machinery, construction sites | Pros: Durable, suitable for harsh environments. Cons: Heavier, less portable. |
| DC Power | Connects devices requiring direct current, compact design | Laptops, cameras, portable electronics | Pros: Lightweight, efficient for battery-operated devices. Cons: Limited range of applications compared to AC. |
| C13/C14 | Common IEC connector type for computers and peripherals | IT and data centers, consumer electronics | Pros: Universally used, easy to source. Cons: Not suitable for high-power devices. |
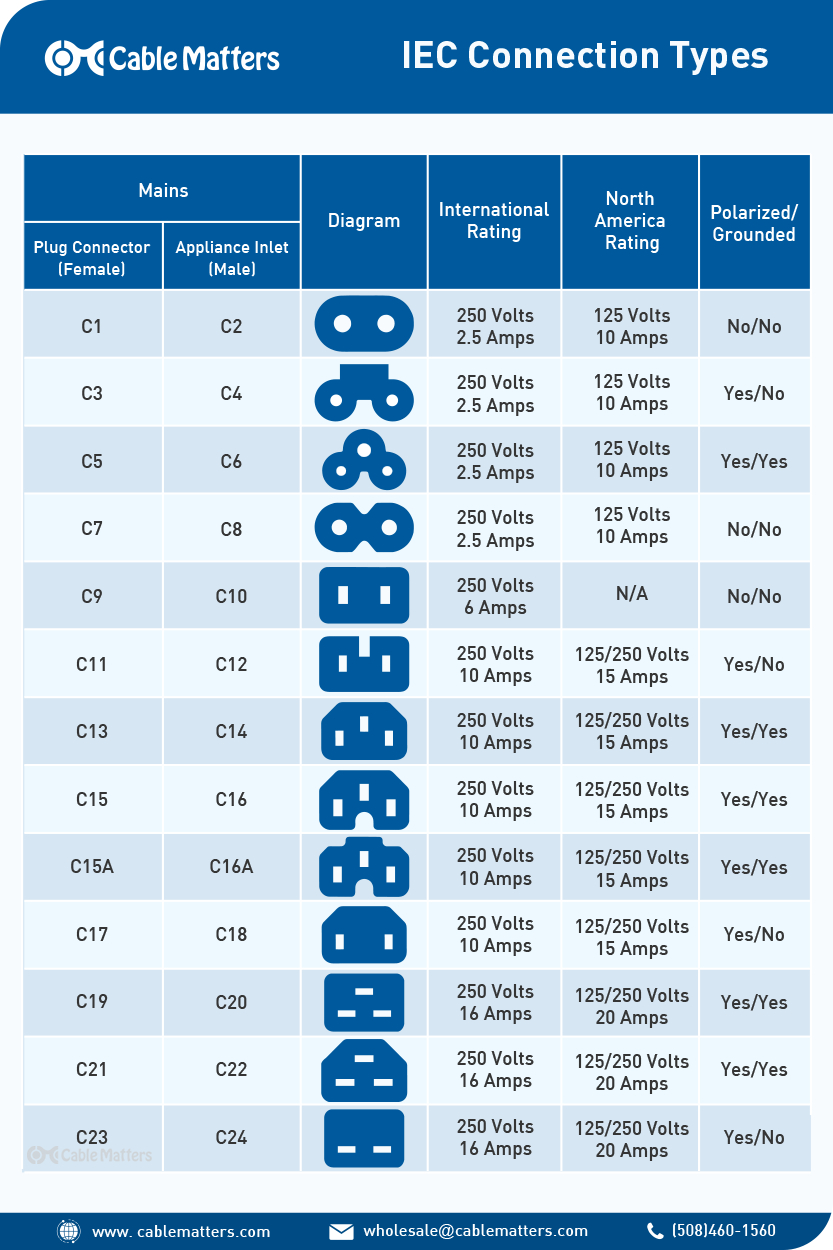
IEC Power Cords
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) power cords are widely recognized for their standardized design, making them a popular choice for international applications. These cords are often used in electronics, IT equipment, and household appliances due to their flexibility and compatibility across different regions. When purchasing IEC power cords, buyers should consider the amperage and voltage ratings to ensure they meet the requirements of their devices. Additionally, while IEC cords can be easily sourced globally, buyers may need adapters for specific regional applications.
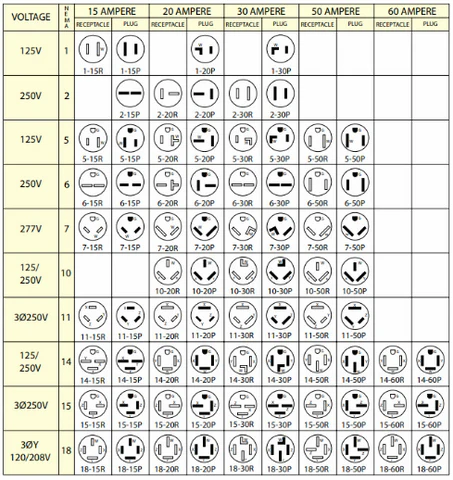
NEMA Power Cords
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) power cords are specifically designed for the North American market. These cords feature polarized designs that enhance safety, making them ideal for industrial equipment, power tools, and household appliances. When considering NEMA power cords, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific NEMA configuration required for their applications, as different configurations cater to varying voltage and amperage needs. While these cords provide high reliability, their geographical limitation to North America and relatively bulky design may pose challenges for international buyers.
CEE Power Cords
CEE (Commission Electrotechnique Européenne) power cords are built to withstand high-voltage applications, making them suitable for industrial machinery and construction sites. Known for their robust construction, CEE cords are designed to perform well in harsh environments. Buyers should focus on the voltage and amperage ratings when selecting CEE connectors, as they are critical for ensuring safe and effective operation. While these cords offer durability, their heavier weight and less portable nature may limit their use in certain applications.
DC Power Cords
DC power cords are essential for devices that operate on direct current, such as laptops, cameras, and other portable electronics. Their compact design makes them ideal for battery-operated devices, providing efficient power delivery. When purchasing DC power cords, buyers should pay attention to connector types and compatibility with AC adapters or batteries. Although DC cords are lightweight and practical for specific applications, their limited range of use compared to AC power cords may restrict their applicability in broader industrial contexts.
C13/C14 Power Cords
The C13/C14 power cords are a common type of IEC connector widely used in computers and peripherals. These connectors are favored in IT and data centers due to their universal application and ease of sourcing. B2B buyers should ensure that the C13/C14 cords meet the necessary specifications for their equipment, particularly regarding voltage and amperage ratings. While they are versatile and readily available, these cords are not suitable for high-power devices, which may necessitate alternative solutions for more demanding applications.
Related Video: All Power Supply Cable Types EXPLAINED
Key Industrial Applications of power cord types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of power cord types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering industrial machinery and tools | Ensures operational efficiency and safety | Compliance with local voltage and amperage standards |
| Healthcare | Connecting medical devices and equipment | Critical for patient safety and device reliability | Certifications for medical-grade cables |
| IT and Telecommunications | Powering servers and network equipment | Supports data integrity and minimizes downtime | Need for high-quality, durable cables with EMI shielding |
| Construction | Temporary power solutions at job sites | Flexibility and safety in powering tools and lights | Weather-resistant materials and compliance with safety standards |
| Consumer Electronics | Powering home appliances and gadgets | Enhances customer satisfaction and product reliability | Variability in plug types and voltage requirements across regions |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, power cords are essential for powering industrial machinery and tools. These cords ensure that equipment runs smoothly, which is vital for maintaining operational efficiency. International buyers must consider local voltage and amperage standards to avoid compatibility issues. Additionally, sourcing durable cords that can withstand heavy use in harsh environments is crucial to prevent downtime and costly repairs.
Healthcare
In healthcare, power cords connect critical medical devices and equipment, such as imaging machines and patient monitors. The reliability of these power connections is paramount for patient safety, as any failure could lead to significant health risks. Buyers in this sector should prioritize certifications for medical-grade cables, ensuring compliance with health regulations and standards. Additionally, the selection of materials that resist wear and tear in clinical environments is essential.
IT and Telecommunications
Power cords in the IT and telecommunications industry are vital for powering servers, routers, and other network equipment. These connections must support high data integrity and minimize downtime, as interruptions can lead to significant financial losses. International buyers should focus on high-quality, durable cables that include electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding to protect sensitive data. Ensuring compatibility with various global standards is also key when sourcing these components.
Construction
In the construction industry, power cords provide temporary power solutions at job sites, facilitating the use of tools and lighting. Flexibility and safety are paramount, as these cords often need to withstand various weather conditions. Buyers should seek cords made from weather-resistant materials and ensure they comply with local safety standards. This consideration is critical to avoid accidents and maintain a safe working environment.
Consumer Electronics
Power cords are integral to powering home appliances and gadgets, ensuring user satisfaction through reliable performance. With a diverse range of products available globally, international buyers must navigate the variability in plug types and voltage requirements across different regions. Sourcing cords that meet local standards while ensuring compatibility with a wide array of devices is essential for maintaining product reliability and customer trust.
Related Video: Why we use Relay in PLC Applications | Relay Wiring Diagram | Types of Relay-SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT
Strategic Material Selection Guide for power cord types
When selecting materials for power cords, it’s crucial for international B2B buyers to understand the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications of each material. This knowledge aids in making informed decisions that align with regional standards and application requirements.
1. Copper
Key Properties: Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, with a conductivity rating of 59.6 x 10^6 S/m. It also has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C), making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which minimizes energy loss and enhances performance. However, copper is relatively expensive and can be prone to corrosion if not properly insulated.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for applications requiring high power transmission and minimal voltage drop, such as industrial machinery and high-performance electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with regional standards such as ASTM and IEC. In regions like Europe, the preference for copper is strong due to its reliability, while buyers in Africa and South America may consider cost implications.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum has a lower conductivity than copper (37.7 x 10^6 S/m) but is lighter and more cost-effective. Its melting point is lower than copper’s at 1,221°F (660°C).
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easier to handle and install, reducing labor costs. However, it has a higher resistance than copper, which can lead to increased energy loss over long distances.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in overhead power lines and applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in transportation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards in their regions, such as DIN in Europe. While aluminum is more affordable, its use may be limited in high-performance applications due to its conductivity limitations.
3. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Key Properties: PVC is a versatile thermoplastic with a temperature rating of up to 176°F (80°C). It is resistant to chemicals and moisture, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, allowing for mass production. However, it may not perform well in high-temperature applications and can become brittle over time.
Impact on Application: PVC is widely used in low-voltage applications, such as household appliances and consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local environmental regulations is crucial, especially in Europe, where there are strict guidelines regarding plastic usage. Buyers should also consider the durability of PVC in their specific application environments.
4. Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
Key Properties: TPE is a flexible material with a temperature rating ranging from -40°F to 221°F (-40°C to 105°C). It offers excellent elasticity and resistance to abrasion and chemicals.
Pros & Cons: TPE provides superior flexibility and durability, making it suitable for dynamic applications. However, it can be more expensive than PVC and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: TPE is ideal for applications requiring flexibility and resilience, such as in robotics and automotive wiring.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure TPE products meet relevant standards like JIS in Japan or ASTM in the U.S. The higher cost may be justified in applications where performance and longevity are critical.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for power cord types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Industrial machinery, high-performance electronics | Superior conductivity | Higher cost, prone to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Overhead power lines, lightweight applications | Lightweight, cost-effective | Higher resistance, energy loss | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Household appliances, consumer electronics | Cost-effective, easy to manufacture | Limited high-temperature performance | Low |
| Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Robotics, automotive wiring | Excellent flexibility and durability | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for power cords, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for power cord types
The manufacturing and quality assurance processes for power cords are critical for ensuring that these essential components meet international safety and performance standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes can lead to better procurement decisions and partnerships with manufacturers. Below is a detailed overview of the main stages involved in manufacturing power cords, key quality assurance practices, and actionable insights for buyers from diverse regions.
Manufacturing Processes for Power Cord Types
Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality materials. Key components include:
- Conductors: Typically made from copper or aluminum, the choice affects conductivity, flexibility, and cost. Copper is preferred for its superior performance, while aluminum is used for lighter, cost-effective solutions.
- Insulation: Materials like PVC, XLPE, and EPR are chosen based on their electrical properties and durability. For harsher environments, advanced materials like TPE or fluoropolymers may be utilized.
- Shielding and Jacket: Shielding materials protect against EMI, while the outer jacket provides environmental protection. The selection here is crucial, especially for applications in industrial or outdoor settings.
Forming
In the forming stage, raw materials are prepared into usable components:
- Cutting: Conductors are cut to length, ensuring precision to prevent waste.
- Stranding: For multi-stranded cables, conductors are twisted together to enhance flexibility and reduce breakage.
- Insulation Application: The insulation is applied using extrusion methods, ensuring a uniform thickness that meets safety standards.
Assembly
The assembly stage involves integrating all components into the final product:
- Termination: Connectors are attached through methods such as crimping or soldering, depending on application requirements. Proper termination is essential for mechanical strength and conductivity.
- Overmolding: This technique involves encapsulating the connector-cable junction to prevent moisture ingress and mechanical stress, which is particularly important for high-performance applications.
Finishing
The final stage includes testing and preparing the product for shipment:
- Marking and Labeling: Cords are labeled with relevant information, including voltage ratings and compliance marks.
- Packaging: Proper packaging is crucial for protecting the product during transport and storage.
Quality Assurance Practices
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the production of power cords. Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications like CE for European markets and UL for North America.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard ensures that manufacturers have a quality management system in place, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- UL Certification: Particularly important for products sold in North America, ensuring they meet rigorous safety standards.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during manufacturing ensure that processes are being followed and that products meet quality criteria.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Completed products undergo rigorous testing to verify performance and compliance with standards.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are essential for verifying the integrity and safety of power cords:
- Electrical Testing: Insulation resistance tests and dielectric strength tests ensure that the cords can handle the required voltage without failure.
- Mechanical Testing: Tests for tensile strength, flexibility, and durability under stress conditions.
- Environmental Testing: Cords may be subjected to temperature extremes, humidity, and chemical exposure to simulate real-world conditions.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and compliance with quality standards.
- Requesting Reports: Buyers should request quality control reports, certifications, and test results to assess the reliability of the supplier’s products.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and product quality.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional compliance requirements is vital:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying requirements for electrical safety and performance. For example, EU buyers need to ensure CE compliance, while buyers in North America should prioritize UL certification.
- Customs and Import Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the import regulations of your region to avoid issues with non-compliant products.
- Cultural and Language Considerations: Effective communication with suppliers can be facilitated by understanding cultural nuances and possibly employing local representatives.
Conclusion
By grasping the intricacies of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for power cords, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Prioritizing suppliers with robust quality control measures and certifications will ensure the procurement of reliable and compliant power cords, ultimately enhancing product performance and safety across various applications.
Related Video: What is Production? Types of Production, Factors of Production
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for power cord types Sourcing
When sourcing power cords, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex cost structure that includes various components influencing the final pricing. Understanding these elements is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost of power cords. High-quality conductors such as copper, which offers superior conductivity, can be more expensive than aluminum. Additionally, insulation materials like PVC or XLPE also vary in price based on their thermal and chemical resistance properties.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the manufacturing location. Regions with higher labor costs will see increased production expenses. For buyers in Africa or South America, sourcing from local manufacturers may reduce logistics costs but could lead to variations in labor efficiency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Buyers should inquire about the overhead rates from suppliers to understand how they affect pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom power cords often require specialized tooling, which can add to the upfront costs. This is especially relevant for OEMs needing specific configurations or features.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality can incur additional costs, particularly when stringent certifications (such as IEC, NEMA, or CEE) are involved. Buyers should consider the impact of QC processes on overall pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and handling, can vary widely depending on the distance, shipping method, and Incoterms used. Understanding these logistics costs is vital for calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s positioning strategy.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders generally attract discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to achieve better pricing, especially when dealing with standard products.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, while necessary for certain applications, can elevate costs. Buyers should assess whether customization is critical or if standard products can suffice.
-
Materials: As noted, the choice of materials directly influences price. Buyers should weigh the benefits of high-quality materials against their budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international standards often carry higher prices. However, investing in certified products can mitigate risks and enhance reliability in the long term.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and history of compliance with standards can affect pricing. Long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), influence the final cost. Buyers should choose Incoterms that balance risk and cost-effectiveness.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders. Leverage competing quotes to secure better terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. Cheaper products may result in higher long-term costs due to failures.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand local market dynamics, including tariffs and currency fluctuations, that can impact final costs. For buyers from Europe, consider the implications of Brexit on sourcing from the UK.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends and pricing fluctuations. Establishing good relationships with suppliers can provide insights into upcoming price changes.
Disclaimer
Prices can vary widely based on numerous factors, and the information provided here is indicative. Buyers should conduct their own market research and consult suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential power cord types Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘power cord types’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for power cord types
Critical Specifications for Power Cord Types
Understanding the essential technical properties of power cords is vital for international B2B buyers to ensure compatibility, safety, and performance. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The quality of materials used in power cords directly affects their performance and longevity. Common materials include copper for conductors and various polymers for insulation. High-grade copper ensures excellent conductivity, while durable insulation materials like PVC or XLPE provide resistance to environmental factors. For buyers, selecting the right material can prevent premature failures and enhance product reliability. -
Current Rating (Amperage)
This specification indicates the maximum current a power cord can safely carry without overheating. It is essential to match the current rating with the intended application to avoid overheating and potential fire hazards. Buyers should assess the current requirements of their devices and ensure that the selected power cord meets or exceeds these specifications. -
Voltage Rating
Voltage rating defines the maximum voltage the cord can handle safely. This specification is crucial for preventing electrical breakdowns that could lead to device damage or safety hazards. Buyers must consider the voltage requirements of their equipment and choose cords that align with their operational environments. -
Temperature Rating
Power cords are often subjected to varying temperatures depending on their application. The temperature rating indicates the maximum operating temperature the cord can withstand. For industries operating in extreme conditions, selecting cords with higher temperature ratings is essential to ensure safe and effective performance. -
Shielding and Insulation Type
Shielding protects against electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can disrupt performance in sensitive electronic applications. The type of insulation also plays a role in protecting the conductors from physical damage and environmental factors. Buyers should evaluate their specific applications to determine the necessary shielding and insulation types for optimal performance. -
Flexibility and Bend Radius
The flexibility of a power cord affects its usability in various settings, especially in applications requiring frequent movement. The bend radius specification indicates the minimum radius the cord can be bent without risking damage. Buyers should ensure that the cords they select can handle the physical demands of their environments.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms used in the power cord market:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of power cords, an OEM may design and produce cords that are then branded and sold by another company. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify potential suppliers and negotiate better deals. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases efficiently and avoid excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare options and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers clarify shipping costs, risk management, and the delivery of goods, ensuring smoother international trade. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the goods are delivered. This specification is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects project timelines and inventory levels. Buyers should consider lead times when planning their procurement strategies. -
Certification Standards
These are regulatory standards that power cords must meet to ensure safety and performance. Common certifications include UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and CE (Conformité Européenne). Buyers should verify that the products they purchase comply with relevant certification standards to ensure quality and safety in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the power cord types Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global power cord market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for electronic devices and the ongoing expansion of renewable energy solutions. With a rise in consumer electronics, industrial automation, and electric vehicles, the demand for reliable and standardized power cords is more critical than ever. In regions such as Africa and South America, burgeoning tech industries and increasing urbanization are propelling the need for efficient power solutions, while the Middle East and Europe are focusing on energy efficiency and sustainable practices.
Current sourcing trends indicate a shift towards modular and customizable power cord solutions. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer flexibility in design and manufacturing to accommodate diverse applications. Additionally, the rise of smart technologies and IoT devices necessitates advanced power connectivity solutions, pushing manufacturers to innovate with high-performance materials and configurations that enhance durability and safety.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Furthermore, international buyers are becoming more discerning about supplier reliability and compliance with global standards such as IEC, NEMA, and CEE. This trend underscores the importance of thorough due diligence during the sourcing process, ensuring that suppliers meet both technical specifications and regulatory requirements. As competition intensifies, establishing strong partnerships with reputable manufacturers can provide strategic advantages in terms of cost, quality, and speed to market.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it has become a critical factor influencing purchasing decisions in the power cord sector. The environmental impact of power cord production, particularly concerning waste and resource use, has prompted B2B buyers to prioritize sustainable practices within their supply chains. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or made from renewable resources, thereby minimizing carbon footprints.
Ethical supply chains are paramount in today’s global marketplace. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS compliance for hazardous substances are essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, the use of green materials in power cord manufacturing, such as halogen-free insulation and biodegradable plastics, is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce environmental harm but also appeal to eco-conscious consumers. Buyers who invest in sustainable sourcing not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute to a larger global movement towards responsible consumption and production.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of power cords can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for safe and reliable electricity transmission became paramount. The introduction of standardized connectors in the 1950s, such as the IEC and NEMA systems, revolutionized the industry by ensuring compatibility across different devices and regions.
As technology advanced, so did the complexity of power cords, leading to the development of various types tailored for specific applications, such as AC and DC power cords. The focus on safety and efficiency has only intensified in recent years, with ongoing innovations in materials and designs aimed at improving performance and reducing environmental impact. Today, the power cord sector stands at the intersection of technology and sustainability, making it an exciting area for B2B buyers looking to align with modern market dynamics.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of power cord types
-
What should I look for when vetting suppliers for power cords?
When vetting suppliers for power cords, prioritize their industry experience and reputation. Check for certifications relevant to your region, such as ISO 9001 or compliance with IEC, NEMA, or CEE standards. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, including quality control processes and testing protocols. Request samples to assess product quality firsthand, and consider visiting their facilities if feasible. Additionally, seek reviews or testimonials from other B2B buyers to gauge reliability and customer service responsiveness. -
Can power cords be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for power cords to meet specific needs. Customizations may include varying lengths, colors, connector types, and insulation materials based on your applications. When discussing customization, be clear about your technical specifications and intended use cases. This ensures that the supplier can meet your requirements effectively. However, keep in mind that extensive customization may affect lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs). -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for power cords?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power cords can vary significantly by supplier, ranging from 100 to several thousand units. Lead times typically range from 2 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s capacity. For customized orders, longer lead times are common due to the additional production processes involved. Always clarify these details upfront to align your procurement planning with supplier capabilities and avoid delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing power cords internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include 30% upfront payment and 70% upon delivery or a letter of credit. For first-time transactions, suppliers may request full payment in advance. Be sure to negotiate terms that protect your interests, such as escrow services or payment upon inspection. Always confirm the accepted payment methods, as international transactions may involve additional fees or currency conversion issues. -
How do I ensure the quality and compliance of the power cords I purchase?
To ensure quality and compliance, request detailed documentation from your suppliers, including test reports and certification evidence. Look for products that adhere to international standards like IEC, NEMA, or CEE. Conduct random inspections or audits during production if feasible, and consider third-party testing for additional assurance. Establish clear quality assurance (QA) protocols in your purchasing agreement to hold suppliers accountable for product standards. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing power cords?
When importing power cords, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling electronics to ensure timely delivery. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes applicable in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Additionally, ensure proper labeling and packaging to comply with local regulations, reducing the risk of delays at customs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How can I resolve disputes with my power cord suppliers?
To resolve disputes with suppliers, first, try to address the issue directly through open communication. Document all correspondence and agreements to support your position. If resolution is not achieved, refer to your purchase agreement for dispute resolution clauses, which may include mediation or arbitration. Consider involving a legal professional with experience in international trade law if necessary. Establishing a clear dispute resolution process upfront can prevent misunderstandings and facilitate smoother negotiations. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with power cord suppliers?
Building a long-term relationship with power cord suppliers requires consistent communication and transparency. Regularly provide feedback on product quality and service, and engage in collaborative discussions about future needs or potential improvements. Honor payment terms and commitments to foster trust and reliability. Consider exploring joint marketing efforts or co-developing products that can benefit both parties. A strong partnership can lead to better pricing, priority service, and enhanced product offerings over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for power cord types
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of power cord types is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their supply chain and ensure compatibility with devices across diverse markets. Understanding the differences among IEC, NEMA, and CEE standards can prevent costly errors and enhance operational efficiency. Key considerations such as material selection, insulation quality, and appropriate connector types are critical to ensuring safety and performance.
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of sourcing power cords, it is vital to partner with reputable manufacturers who prioritize quality and compliance with international standards. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also enhances product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, the demand for versatile and durable power cords will continue to grow as technology evolves. International buyers should remain vigilant about market trends and emerging technologies in power connectivity. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves for success in a competitive landscape. Engage with trusted suppliers today to ensure your power solutions are ready for tomorrow’s challenges.