Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Rubber Compression Molding
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber compression molding
In today’s global manufacturing landscape, rubber compression molding stands out as a pivotal process for producing high-quality rubber components across various industries. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding this method is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and compliance with diverse regional standards. The ability to source effective rubber molded products can significantly impact product performance and overall business success.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of rubber compression molding, covering critical areas that influence procurement decisions. Buyers will explore the different types of rubber products, including gaskets and seals, and evaluate various materials tailored to specific applications. Additionally, the guide addresses essential manufacturing processes and quality control standards that underpin product reliability, ensuring consistent performance across industries.
Furthermore, insights on supplier evaluation and sourcing strategies are provided to help mitigate risks and enhance supply chain resilience. Buyers will also gain a thorough understanding of cost factors and market trends, equipping them with the knowledge needed to navigate pricing dynamics effectively. By leveraging the insights offered in this guide, B2B buyers will be empowered to make informed sourcing decisions that foster long-term success in the competitive rubber compression molding market.
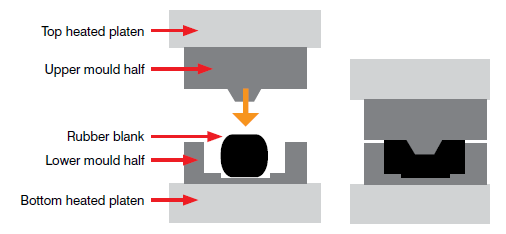
Understanding rubber compression molding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flash Type Mold | Allows excess material to escape as “flash” during molding | Flat parts, gaskets, seals | Pros: Lower tooling cost; Cons: Requires careful control to avoid defects. |
| Positive Type Mold | Fully fills the mold cavity with pre-measured compound | High-performance applications | Pros: Excellent control and minimal waste; Cons: High tooling costs. |
| Semi-Positive Mold | Combines features of flash and positive molds | Complex geometries, custom parts | Pros: Better quality for intricate designs; Cons: Highest tooling costs. |
| Multi-Cavity Mold | Contains multiple cavities for simultaneous production | High-volume runs | Pros: Increased production efficiency; Cons: More complex design and setup. |
| Insert Mold | Accommodates additional materials (e.g., metal inserts) | Automotive, industrial components | Pros: Versatile for hybrid products; Cons: May complicate the curing process. |
Flash Type Mold
The Flash Type Mold is characterized by its ability to allow excess rubber material to escape during the molding process. This type is particularly suited for producing flat parts and components like gaskets and seals. For B2B buyers, the low tooling cost is an attractive feature, especially for companies looking to minimize initial investments. However, it is crucial to manage the mold closing speed carefully to prevent defects such as excess flash or compromised part density.
Positive Type Mold
The Positive Type Mold ensures that the mold cavity is completely filled with a pre-measured amount of rubber compound, which is beneficial for high-performance applications. This method is ideal for producing precision parts where material waste needs to be minimized. B2B buyers should consider the higher tooling costs associated with this method, as well as the need for accurate preforming to ensure consistency in production. This approach is particularly valuable in sectors that demand high-quality standards.
Semi-Positive Mold
The Semi-Positive Mold offers a hybrid approach, balancing the controlled material use of positive molds with a limited allowance for flash. This mold type is particularly advantageous for complex geometries and custom parts, providing better quality compared to flash molds. However, B2B buyers must be aware that this method typically incurs the highest tooling costs. It is best suited for applications where precision and intricate designs are paramount, making it a worthwhile investment for specialized manufacturers.
Multi-Cavity Mold
The Multi-Cavity Mold is designed to produce multiple parts simultaneously, significantly enhancing production efficiency. This type is particularly advantageous for high-volume runs, allowing manufacturers to meet demand without sacrificing quality. Buyers should consider the complexity of the mold design and setup, as well as the potential for increased upfront costs. However, the return on investment can be substantial, especially for businesses anticipating ongoing production needs.
Insert Mold
The Insert Mold accommodates additional materials, such as metal or fabric inserts, during the compression molding process. This versatility makes it suitable for applications in the automotive and industrial sectors where hybrid components are required. B2B buyers should evaluate the potential complications that may arise during the curing process, as integrating different materials can affect the overall quality of the final product. This method allows for innovative designs, making it a valuable option for companies looking to differentiate their offerings.
Related Video: The Silicone Rubber Compression Molding Process Explained
Key Industrial Applications of rubber compression molding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Rubber Compression Molding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing of gaskets and seals | Ensures durability and reliability in vehicle performance | Material compatibility, compliance with automotive standards, and lead times for custom parts |
| Electrical | Production of insulators and connectors | Enhances safety and efficiency in electrical systems | Certification requirements, material properties, and production volume capabilities |
| Consumer Goods | Production of handles and buttons | Improves user experience and product functionality | Design flexibility, material selection, and cost-effectiveness |
| Construction | Vibration dampeners and structural components | Increases longevity and performance of construction materials | Material sourcing, compliance with building codes, and custom design capabilities |
| Sporting Goods | Manufacturing of equipment components (e.g., grips) | Enhances performance and user comfort | Material performance under stress, design specifications, and market trends |
Automotive Industry
Rubber compression molding is extensively used in the automotive sector for producing gaskets and seals, which are critical for maintaining vehicle integrity and preventing leaks. This method allows for the creation of thick, durable parts that can withstand harsh environments. International buyers should focus on sourcing materials that meet regional automotive standards and ensure compatibility with various vehicle types. Additionally, lead times for custom parts should be evaluated to meet production schedules effectively.
Electrical Industry
In the electrical sector, rubber compression molding is vital for creating insulators and connectors that ensure safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. The molded rubber components must comply with safety regulations and withstand environmental factors such as moisture and temperature fluctuations. B2B buyers should consider the certification requirements for materials and the performance characteristics necessary for their specific applications. Reliability in sourcing high-quality components can significantly reduce operational risks.
Consumer Goods
Rubber compression molding is employed in the consumer goods industry for manufacturing items like handles and buttons, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. The flexibility of this molding process allows for the creation of intricate designs that improve user experience. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer a range of materials and customization options to meet market demands. Cost-effectiveness is also a critical consideration, especially for high-volume production runs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Construction Industry
In construction, rubber compression molding is used to produce vibration dampeners and other structural components that enhance the performance and longevity of buildings and infrastructure. These components help mitigate noise and vibration, contributing to overall structural integrity. Buyers must ensure that sourced materials comply with local building codes and standards. Custom design capabilities are also essential for meeting specific project requirements and optimizing performance.
Sporting Goods
The sporting goods industry benefits from rubber compression molding through the production of equipment components such as grips and pads that improve user comfort and performance. The ability to mold rubber into complex shapes allows manufacturers to create innovative designs that appeal to consumers. B2B buyers should focus on material performance under stress and the latest market trends to ensure their products meet customer expectations and enhance competitive advantage.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber compression molding
When selecting materials for rubber compression molding, international B2B buyers must consider the specific properties and applications of various rubber types. This analysis highlights four common materials used in rubber compression molding, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for different markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Natural Rubber (NR)
Key Properties:
Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity, resilience, and tensile strength. It performs well under moderate temperature ranges (up to 80°C) and is resistant to wear and abrasion. However, it has limited resistance to ozone and UV light, which can affect its longevity in outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of NR is its superior mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. It is widely available and offers good performance in applications requiring flexibility and durability. However, its susceptibility to environmental factors can limit its use in harsh conditions, leading to potential failures.
Impact on Application:
NR is commonly used in automotive components, such as tires and seals, where flexibility and resilience are crucial. Buyers should consider the environmental conditions of their applications, particularly in regions with high UV exposure or ozone levels.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM D2000 in the U.S. or EN 681 in Europe, to guarantee product quality. Additionally, sourcing NR from sustainable sources is increasingly important for compliance with environmental regulations.
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Key Properties:
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C and has good mechanical strength.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of NBR is its ability to maintain performance in oil-rich environments, which is critical for seals and gaskets. However, it is less flexible than NR and can become brittle over time, particularly in extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application:
NBR is often used in fuel hoses, seals, and gaskets, particularly in automotive applications. Buyers should assess the chemical compatibility of NBR with the media it will contact, ensuring it meets the specific requirements of their applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards like ASTM D1418 is crucial for ensuring that NBR products meet performance expectations. Buyers in regions with stringent oil and chemical regulations should prioritize suppliers who can provide certification and testing data.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
Key Properties:
EPDM is known for its excellent weather resistance, UV stability, and ozone resistance. It can operate in temperature ranges from -50°C to 150°C, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of EPDM is its durability in harsh environmental conditions, making it ideal for roofing membranes and automotive weather seals. However, it has limited resistance to oils and fuels, which can restrict its use in certain applications.
Impact on Application:
EPDM is widely used in automotive parts, roofing, and electrical insulation. Buyers should evaluate the environmental conditions and media exposure to ensure EPDM is suitable for their specific needs.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with local standards such as ASTM D1056 and EN 681 to ensure product reliability. Additionally, sourcing EPDM from reputable manufacturers who adhere to environmental regulations is essential for maintaining compliance.
Silicone Rubber (VMQ)
Key Properties:
Silicone rubber exhibits excellent temperature resistance (from -60°C to 230°C), flexibility, and chemical resistance. It is also non-toxic and has low compression set, making it ideal for sealing applications.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of silicone is its versatility and performance in extreme conditions, which is beneficial for applications in the food and medical industries. However, it tends to be more expensive than other rubber types and may require specialized processing techniques.
Impact on Application:
Silicone is commonly used in the food industry for seals and gaskets, as well as in medical devices. Buyers must ensure that silicone products meet food safety standards (e.g., FDA compliance) and are suitable for their specific applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with strict health and safety regulations, such as the EU, should prioritize suppliers who can provide certifications for silicone products. Understanding local compliance requirements is crucial for successful procurement.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber compression molding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber (NR) | Automotive tires and seals | Superior elasticity and cost-effective | Limited UV and ozone resistance | Medium |
| Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Fuel hoses and gaskets | Excellent oil and chemical resistance | Less flexible and can become brittle | Medium |
| Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) | Automotive weather seals and roofing | Exceptional weather and UV resistance | Limited oil and fuel resistance | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber (VMQ) | Food industry seals and medical devices | High temperature and chemical resistance | Higher cost and specialized processing | High |
This strategic material selection guide equips B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties and applications of various rubber materials, enabling informed decision-making in the procurement process.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber compression molding
The manufacturing process of rubber compression molding is pivotal for producing high-quality rubber components that meet the diverse needs of various industries. For international B2B buyers, understanding these processes and the associated quality assurance measures is crucial in ensuring reliable sourcing and compliance with regional standards.
Manufacturing Process Overview
Rubber compression molding consists of several key stages, each contributing to the final quality of the product. Here’s a detailed breakdown of these stages:
1. Material Preparation
The initial step involves mixing and preparing the rubber compound. The raw materials, which may include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, and additives, are blended to achieve the desired properties. This stage is critical as the quality of the rubber compound directly impacts the performance of the final product.
- Key Techniques:
- Batch Mixing: Ensures uniformity in the compound, which is vital for consistent product quality.
- Quality Control: Conduct tests on the compound, such as viscosity and tensile strength, to ensure it meets specifications before proceeding.
2. Preforming
In this stage, the mixed rubber compound is shaped into a preform or charge. This process can involve cutting or pressing the compound into precise shapes and weights to ensure it fits well in the mold.
- Key Considerations:
- Accurate preforming is essential for minimizing waste and ensuring proper filling of the mold.
- Use of automated systems can enhance precision and reduce labor costs.
3. Mold Loading
Once the preform is prepared, it is placed into the heated mold cavity. Care must be taken to ensure the mold is clean and free from defects, as any contamination can affect the curing process.
4. Mold Closing and Heating
The mold is then closed, and heat and pressure are applied. This is where the rubber compound begins to cure or vulcanize, taking on the shape of the mold.
- Key Techniques:
- Controlled Heating: Maintaining the right temperature is crucial for achieving the desired properties in the final product.
- Pressure Regulation: Adequate pressure ensures complete filling of the mold and proper curing.
5. Curing/Crosslinking
This phase involves holding the mold at a specific temperature and pressure for a predetermined time to allow the rubber to cure fully. The vulcanization process is critical as it enhances the rubber’s durability and elasticity.
6. Cooling and Demolding
After curing, the mold is cooled, and the finished part is demolded. Proper cooling techniques are essential to prevent warping or distortion of the final product.
7. Post-processing
This final stage includes trimming excess material, deburring edges, and conducting inspections. Post-processing is vital to ensure the product meets all specifications and is free from defects.
Quality Assurance (QA) Standards
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, adhering to quality assurance standards is crucial. Here are the relevant aspects of quality assurance in rubber compression molding:
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant in Europe, this certification indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For buyers in industries such as oil and gas, adherence to API standards ensures that products meet stringent safety and performance requirements.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control should be integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspect incoming materials for compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitor production processes to identify and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conduct thorough inspections and testing of finished products before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of rubber components:
- Mechanical Testing: Assess properties such as tensile strength, elongation, and hardness.
- Dimensional Inspection: Verify that products meet specified dimensions and tolerances using precision measuring tools.
- Visual Inspection: Identify surface defects, such as bubbles or discoloration.
Supplier Verification for Quality Assurance
B2B buyers must implement robust verification processes to ensure their suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
- Audits: Regularly conduct audits of suppliers’ facilities to assess compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes.
- Reports: Request detailed quality reports from suppliers, including testing results and production metrics.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage third-party inspectors to conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing process and final products.
Regional Considerations for International Buyers
Buyers from different regions should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Africa: Focus on local certifications and standards compliance, as well as logistics considerations for timely delivery.
- South America: Ensure that suppliers understand and comply with local regulations, especially in industries like automotive and healthcare.
- Middle East: Emphasize the importance of certifications like ISO and API, given the region’s stringent quality expectations in oil and gas.
- Europe (e.g., Spain, UAE): Buyers should prioritize CE compliance and ensure that suppliers can demonstrate adherence to EU regulations.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in rubber compression molding is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable and high-quality rubber products. By familiarizing themselves with these processes, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements, ultimately driving value in their procurement strategies.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber compression molding Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of rubber compression molding is essential for international B2B buyers. This section offers a comprehensive analysis of the key cost components, price influencers, and practical tips to optimize procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of rubber compound significantly impacts costs. Common materials include Natural Rubber (NR), Nitrile Rubber (NBR), and Silicone Rubber (VMQ). Each material has different pricing, influenced by market demand and availability. Buyers should assess their specific application needs to select the most cost-effective material without compromising quality.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, can provide a competitive advantage. However, consider the skill level required for complex molding processes, as skilled labor may command higher wages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Efficient operational practices can mitigate overhead costs, making it essential for buyers to evaluate suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom molds. Buyers should expect to invest in mold design and fabrication, which can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars. Understanding the mold type (flash, positive, or semi-positive) can help buyers optimize tooling expenses based on their production volume and part complexity.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is crucial to ensure product consistency and compliance with industry standards. While this adds to the initial cost, it can prevent expensive recalls or failures in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, tariffs, and import duties can significantly affect the total cost of ownership. Consider the proximity of suppliers and the chosen Incoterms, as these factors will influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on supplier reputation, market conditions, and the complexity of the parts being produced.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger order volumes often lead to discounted pricing. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) with suppliers can help negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom parts with unique specifications generally incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may increase costs but are essential for applications with stringent safety and performance standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Engaging with multiple suppliers and conducting due diligence can yield favorable terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for cost management in international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, impacting shipping costs and risk management.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms and pricing with suppliers. Building long-term relationships can lead to better deals and service.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront costs. This includes evaluating lifecycle costs, maintenance, and potential savings from quality assurance.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and regional economic conditions that may impact pricing. Engage local experts or consultants who understand the market dynamics in your target regions.
-
Market Research: Regularly analyze market trends and competitor pricing. Staying informed can provide leverage during negotiations and help identify the best sourcing opportunities.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing dynamics of rubber compression molding is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and drive long-term value. Always consider that prices may vary based on numerous factors, and it is advisable to obtain indicative quotes tailored to specific requirements.
Spotlight on Potential rubber compression molding Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘rubber compression molding’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber compression molding
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with rubber compression molding is essential for international B2B buyers. This knowledge ensures that procurement decisions align with quality requirements, production capabilities, and market standards.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the specific type of rubber compound used in the molding process, such as Natural Rubber (NR), Nitrile Rubber (NBR), or Silicone Rubber (VMQ).
– B2B Importance: Different grades possess unique properties such as temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and mechanical strength. Selecting the right material grade is crucial for ensuring product performance in its intended application. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the molded part. It is usually expressed as a range (e.g., ±0.01 mm).
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances are essential for parts that must fit precisely within assemblies. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can meet the required tolerances to avoid costly rework or production delays. -
Durometer Hardness
– Definition: This measures the hardness of rubber, typically on the Shore A scale, ranging from soft (10) to hard (100).
– B2B Importance: The durometer value affects the elasticity, strength, and wear resistance of the final product. Buyers must consider the durometer when selecting materials to ensure functionality in applications like seals or gaskets. -
Cure Time
– Definition: The time required for the rubber to vulcanize or cure under heat and pressure.
– B2B Importance: Understanding cure times helps buyers anticipate lead times for production. Shorter cure times can improve efficiency and reduce costs, making it a key factor in high-volume applications. -
Compression Set
– Definition: This property indicates the material’s ability to return to its original shape after being compressed.
– B2B Importance: A lower compression set means better resilience and longer service life for molded parts. Buyers in industries like automotive and aerospace should prioritize this property for reliability in critical applications.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is vital for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers must assess whether the MOQ aligns with their production needs and financial capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms. This process is crucial for making informed procurement decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms used to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in transactions.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms helps buyers comprehend shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and costs associated with logistics. This knowledge is essential for effective supply chain management. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The total time from the initiation of a process to its completion, including production and shipping.
– Importance: Awareness of lead times allows buyers to plan effectively for inventory and production schedules. It is particularly important in industries where timely delivery is critical.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their rubber compression molding needs. This knowledge ultimately supports operational efficiency and product quality across various applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the rubber compression molding Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The rubber compression molding sector is experiencing robust growth driven by various global factors. Key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing increased demand for high-quality molded rubber products across diverse industries, including automotive, healthcare, and construction. The growing emphasis on lightweight materials and energy efficiency is steering innovations in rubber formulations and molding processes, enhancing product performance while reducing costs.
Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0 and advanced automation are reshaping sourcing trends. B2B buyers are increasingly turning to suppliers who utilize smart manufacturing techniques, enabling real-time monitoring and quality control. This shift not only improves production efficiency but also fosters greater transparency in supply chains. Additionally, the integration of digital platforms for procurement is gaining traction, allowing buyers to compare suppliers easily and manage inventory effectively.
For international buyers, understanding regional market dynamics is crucial. For instance, the EU’s strict regulatory framework encourages the adoption of sustainable practices, compelling suppliers to demonstrate compliance with environmental standards. In contrast, markets in Africa and South America may present opportunities for cost-effective sourcing, albeit with varying levels of quality assurance. Thus, B2B buyers must balance cost, quality, and compliance when navigating this evolving landscape.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of rubber compression molding is a growing concern among international buyers. As industries face increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, the importance of sustainable sourcing practices cannot be overstated. Ethical supply chains not only contribute to environmental stewardship but also enhance brand reputation, making them a critical consideration for B2B buyers.
Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who prioritize sustainability by utilizing eco-friendly materials and processes. For instance, sourcing from manufacturers that use recycled rubber or bio-based elastomers can significantly reduce environmental impact. Furthermore, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) can help buyers identify suppliers committed to sustainable practices.
Implementing these sourcing strategies not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also meets the increasing consumer demand for green products. As regulatory landscapes evolve, companies that invest in sustainable practices will likely gain a competitive edge in the marketplace, positioning themselves favorably among environmentally conscious buyers.
Brief Evolution/History
The origins of rubber compression molding can be traced back to the late 19th century, coinciding with the industrial revolution and the rise of rubber as a key material in manufacturing. Initially, the process was rudimentary, relying heavily on manual labor and basic tools. However, advancements in material science and engineering have transformed it into a sophisticated and efficient method for producing high-quality rubber components.
Over the decades, the introduction of synthetic rubber and technological innovations, such as automated presses and computer-aided design (CAD), have significantly improved the capabilities of compression molding. Today, the process is integral to various industries, providing a cost-effective solution for producing durable and precise rubber parts. As the market continues to evolve, ongoing investments in research and development are expected to further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of rubber compression molding.
Related Video: Chapter 9: International Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber compression molding
-
What key factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for rubber compression molding?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their manufacturing capabilities, experience in your industry, and quality assurance processes. Request samples of previous work to assess their product quality. Additionally, inquire about their compliance with international standards, certifications, and their ability to meet specific material requirements. Don’t overlook their communication responsiveness and logistics capabilities, as these can significantly impact your supply chain efficiency. -
Can rubber compression molded products be customized to meet specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for rubber compression molded products. You can request specific shapes, sizes, and material types based on your application requirements. It’s essential to communicate your specifications clearly and work closely with the supplier during the design phase. Keep in mind that highly customized products may have longer lead times and higher costs, so plan accordingly. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for rubber compression molding?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers, often ranging from 100 to several thousand units depending on the complexity of the part and the supplier’s capacity. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by factors such as mold creation, material availability, and production schedules. It’s crucial to discuss these parameters upfront to align your expectations with the supplier’s capabilities. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for my rubber compression molded products?
Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards relevant to your application. Establish a quality control plan that includes regular inspections and testing of materials and finished products. Ask for documentation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and consider conducting audits to verify their adherence to these standards. This proactive approach can help mitigate risks associated with product quality. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing rubber compression molded products internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping costs, customs regulations, and import/export duties that can impact your overall budget. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in international logistics and can provide insight into shipping timelines and costs. Additionally, ensure that the supplier can accommodate your preferred shipping methods and is prepared to handle any potential delays in the supply chain. -
How can I handle disputes or issues with my rubber compression molding supplier?
Establish clear communication channels and maintain documentation of all agreements and transactions to help resolve disputes efficiently. If issues arise, approach your supplier with a solution-oriented mindset, discussing the problem openly. If necessary, refer to any contracts or agreements outlining dispute resolution processes. In extreme cases, consider mediation or legal avenues, but strive to maintain a collaborative relationship for future transactions. -
What are the common payment terms and methods for international B2B transactions in rubber compression molding?
Payment terms vary by supplier but typically include options like advance payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers accept bank transfers, credit cards, or payment platforms like PayPal. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect your interests, such as escrow services for large orders. Ensure you understand the implications of currency fluctuations on pricing and payments if dealing with international suppliers. -
How can I stay informed about market trends and innovations in rubber compression molding?
Subscribe to industry publications, attend trade shows, and participate in webinars focused on rubber manufacturing and molding. Engaging with industry associations can provide access to valuable resources and networking opportunities. Additionally, following relevant online forums and social media groups can help you stay updated on new technologies, materials, and market shifts that may impact your sourcing strategies.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber compression molding
In summary, strategic sourcing in rubber compression molding is critical for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains and enhance product quality. By understanding the nuances of the compression molding process, including material selection and mold design considerations, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key takeaways include the advantages of compression molding—such as low tooling costs and minimal material waste—making it particularly suitable for industries like automotive and consumer goods. Buyers should also be mindful of potential challenges, such as slower cycle times and the need for precise specifications, which can be mitigated through careful supplier selection and process optimization.
As the global market evolves, the demand for high-quality rubber components will only grow. Therefore, it is essential for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to stay ahead of industry trends and innovations. Investing in strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers will not only enhance product quality but also foster resilience in supply chains.
Embrace the opportunities in rubber compression molding and take proactive steps today to secure your competitive edge for tomorrow.