Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Size Reduction Equipment
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for size reduction equipment
Size reduction equipment plays a pivotal role in numerous industries, from food processing and pharmaceuticals to mining and recycling. These specialized machines are essential for breaking down solid materials into smaller, more manageable particles, enhancing product quality, and facilitating efficient processing. For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of size reduction equipment is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with specific operational needs and market demands.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the size reduction equipment landscape. It delves into various types of machinery, including crushers, grinders, pulverizers, and mills, each tailored for unique applications. Buyers will gain insights into the materials these machines can process, the manufacturing and quality control standards to consider, and the factors influencing supplier selection. Furthermore, the guide examines cost considerations and provides an overview of the current market trends, empowering buyers to navigate their purchasing journey with confidence.
Additionally, a dedicated FAQ section addresses common queries, ensuring that buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as France and the UAE—can overcome potential hurdles in their procurement process. By equipping themselves with this knowledge, international B2B buyers can optimize their operations, enhance productivity, and achieve superior outcomes in their respective industries.
Understanding size reduction equipment Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Crushers | Utilize high-speed impact to fracture materials. | Mining, construction, recycling. | Pros: Efficient for hard materials; versatile. Cons: Limited to specific material types. |
| Industrial Grinders | Achieve finer particle sizes; suitable for softer materials. | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals. | Pros: Produces uniform particle sizes; adaptable. Cons: May require more maintenance. |
| Pulverizers | Encompass various mechanisms, often for fine grinding. | Coal, plastics, rubber processing. | Pros: Versatile; can handle diverse materials. Cons: Initial costs can be high. |
| Ball Mills | Employ rotating cylinders filled with grinding media. | Mining, ceramics, pharmaceuticals. | Pros: Effective for large batches; consistent output. Cons: Energy-intensive operation. |
| Disc Mills | Use two discs to shear materials into fine particles. | Food, plastics, pharmaceuticals. | Pros: High efficiency; precise control over particle size. Cons: Limited to dry materials. |
Impact Crushers
Impact crushers are designed to break down hard materials through high-speed impacts. They are particularly useful in mining and construction industries for reducing large rocks into manageable sizes. When considering an impact crusher, B2B buyers should evaluate the material hardness and the desired output size, as these machines excel with specific materials like limestone and gypsum but may not perform well with softer substances.
Industrial Grinders
Industrial grinders are capable of producing finer, more uniform particles compared to crushers. They are widely used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries where consistent particle size is crucial. Buyers should consider the grinder’s capacity, the nature of the material being processed, and maintenance requirements, as these machines may require more upkeep to maintain optimal performance.
Pulverizers
Pulverizers serve as a broad category of size reduction equipment that can handle a variety of materials, including coal and plastics. They employ different mechanisms to achieve fine grinding, making them suitable for diverse applications. For B2B buyers, the versatility of pulverizers can be a significant advantage, but initial investment costs and energy consumption should be weighed against the expected throughput and material types.
Ball Mills
Ball mills are effective for grinding large quantities of materials using rotating cylinders filled with balls or other grinding media. They are commonly used in mining, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals. Buyers should assess the energy efficiency of the mill, the size of the batches they need to process, and the material compatibility, as ball mills can be energy-intensive and may require significant power for operation.
Disc Mills
Disc mills utilize two horizontally positioned discs to shear materials into fine particles, making them ideal for processing dry materials in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals. B2B buyers should focus on the mill’s capacity, the desired particle size, and the type of material being processed, as disc mills may not be suitable for wet materials. Their high efficiency and precise control over particle size can significantly enhance production processes.
Related Video: Size reduction equipment-1
Key Industrial Applications of size reduction equipment
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of size reduction equipment | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Grinding grains and spices | Enhances flavor extraction and product consistency | Equipment must meet food safety standards and hygiene regulations. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Milling active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) | Improves bioavailability and product uniformity | Compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., FDA) is critical. |
| Mining and Minerals | Crushing ores for extraction | Increases recovery rates and reduces processing costs | Durability and maintenance support are essential for heavy-duty applications. |
| Recycling | Size reduction of plastics and metals | Facilitates easier sorting and processing | Equipment should be versatile to handle various materials. |
| Construction Materials | Crushing concrete and asphalt | Reduces waste and allows for re-use of materials | Consideration for equipment mobility and power supply requirements. |
Food Processing
In the food industry, size reduction equipment is crucial for grinding grains, spices, and other ingredients. This process enhances flavor extraction and ensures product consistency, which is vital for maintaining quality in food products. International buyers must ensure that the equipment adheres to strict food safety standards and hygiene regulations, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where compliance is heavily monitored. Choosing equipment that is easy to clean and maintain can significantly reduce downtime and improve operational efficiency.
Pharmaceuticals
In pharmaceuticals, size reduction is critical for milling active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to improve their bioavailability and ensure uniformity in dosage forms. This is especially important in regions like South America and Africa, where regulatory compliance can vary. Buyers in this sector should prioritize equipment that meets stringent regulatory standards, such as those set by the FDA or EMA. Additionally, considerations for contamination control and batch consistency are paramount, making the choice of machinery a critical factor in the manufacturing process.
Mining and Minerals
Size reduction equipment in the mining sector is primarily used for crushing ores, which is essential for extracting valuable minerals. By reducing particle size, businesses can increase recovery rates and lower processing costs. International buyers, especially in Africa and South America, should focus on sourcing durable machinery that can withstand harsh operational environments. Maintenance support and availability of spare parts are also crucial considerations, as they directly impact the longevity and efficiency of the equipment.
Recycling
In the recycling industry, size reduction equipment plays a vital role in processing plastics and metals. By breaking down materials into smaller pieces, the equipment facilitates easier sorting and processing, ultimately enhancing recycling efficiency. Buyers must consider the versatility of the machinery to handle various types of materials, which is particularly important in regions with diverse waste streams. Additionally, energy efficiency and operational costs are key factors that can affect the overall profitability of recycling operations.
Construction Materials
Size reduction equipment is widely used in the construction sector for crushing concrete and asphalt, enabling the re-use of materials and reducing waste. This not only contributes to sustainability efforts but also lowers material costs for construction projects. Buyers in this industry should consider the mobility of the equipment, especially in regions like the UAE where construction sites can be expansive. Furthermore, power supply requirements and ease of operation are critical to ensure that equipment can be effectively utilized on-site.
Related Video: Size Reduction by different milling machines and their principles
Strategic Material Selection Guide for size reduction equipment
When selecting materials for size reduction equipment, international B2B buyers must consider a variety of factors that affect performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in size reduction equipment, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers in diverse global markets.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating up to 1,500°F (815°C) and is resistant to a wide range of chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is durable and easy to clean, making it suitable for industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including abrasive materials, which makes it ideal for grinding and pulverizing applications.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for quality assurance. In regions like Europe and the UAE, certifications regarding food safety and hygiene are critical.
2. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel offers high strength and toughness, with a temperature rating that can exceed 1,200°F (650°C). It is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel but can be treated for enhanced durability.
Pros & Cons:
Carbon steel is generally less expensive than stainless steel and easier to machine, which can reduce manufacturing complexity. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can limit its lifespan in certain applications, requiring regular maintenance.
Impact on Application:
It is often used in applications involving non-corrosive materials, making it suitable for mining and recycling industries.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the local environmental regulations regarding material disposal, especially in regions like South America and Africa, where compliance can vary significantly.
3. Ceramic Materials
Key Properties:
Ceramic materials are known for their hardness and high-temperature resistance, often exceeding 2,000°F (1,093°C). They exhibit excellent chemical resistance, making them suitable for aggressive environments.
Pros & Cons:
Ceramics are incredibly durable and resistant to wear, making them ideal for high-abrasion applications. However, they can be brittle and may require careful handling during manufacturing and operation, leading to higher costs in certain scenarios.
Impact on Application:
Ceramics are particularly effective in grinding applications where extreme hardness is required, such as in the production of fine powders in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of ceramic materials in their region and any import tariffs that may apply. Compliance with international quality standards is also essential, especially in Europe.
4. Bronze Alloys
Key Properties:
Bronze alloys, primarily composed of copper and tin, offer excellent corrosion resistance and good machinability. They can withstand moderate temperatures, typically up to 600°F (315°C).
Pros & Cons:
Bronze is known for its low friction properties, making it suitable for applications requiring reduced wear. However, it can be more expensive than carbon steel and may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application:
Bronze is often used in size reduction equipment that processes softer materials, such as plastics and food products, where corrosion resistance is a priority.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers:
Understanding the specific alloy composition is crucial for compliance with local standards, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, where material specifications can be stringent.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for size reduction equipment | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | Mining, recycling | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Susceptible to rust and corrosion | Medium |
| Ceramic Materials | Chemical and pharmaceutical grinding | Extremely durable and wear-resistant | Brittle and requires careful handling | High |
| Bronze Alloys | Processing softer materials like plastics | Low friction and good corrosion resistance | Higher cost and limited high-temperature use | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for size reduction equipment
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for size reduction equipment are critical for ensuring that the machinery meets the rigorous demands of various industries. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can aid in making informed purchasing decisions. This section delves into the typical manufacturing stages, key techniques used, and quality control measures relevant to size reduction equipment.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of size reduction equipment generally involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is essential to ensure that the final product meets specified performance and durability standards.
Material Preparation
- Material Selection: The first step involves selecting appropriate materials based on the equipment’s intended use. Common materials include high-strength steel, stainless steel, and ceramics for their durability and resistance to wear.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into manageable sizes using saws or lasers. This is crucial for ensuring precision in subsequent manufacturing steps.
-
Surface Treatment: Before forming, materials often undergo surface treatments to enhance properties such as corrosion resistance and wearability. Techniques include galvanizing, anodizing, and coating with wear-resistant materials.
Forming
-
Casting and Forging: Components like frames and housings may be produced through casting or forging, which allows for complex shapes and improved structural integrity.
-
Machining: Precision machining processes, including turning, milling, and grinding, are employed to achieve the exact dimensions required for various components like rotors and blades.
-
Welding and Fabrication: For larger assemblies, welding techniques (TIG, MIG, etc.) are used to join parts. This is critical in ensuring that the equipment can withstand operational stresses.
Assembly
-
Component Assembly: After individual parts are fabricated, they are assembled into larger units. This may include installing motors, bearings, and other mechanical components essential for operation.
-
Alignment and Calibration: Proper alignment of moving parts is crucial for functionality and longevity. Calibration ensures that the equipment performs to specifications.
-
Testing during Assembly: Initial testing is often conducted during the assembly phase to catch any issues early in the process.
Finishing
-
Surface Finishing: Final surface treatments may be applied to improve aesthetics and performance, including polishing and painting.
-
Final Assembly and Inspection: The last step involves final assembly, followed by a thorough inspection to ensure that all components meet quality standards before shipping.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of size reduction equipment to ensure safety, reliability, and performance. International B2B buyers should be aware of the standards and checkpoints involved in the quality control process.
International Standards
-
ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems. Compliance indicates that a manufacturer adheres to consistent quality practices across all operations.
-
CE Marking: For equipment sold in the European market, CE marking signifies compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is crucial for B2B buyers in Europe to ensure that suppliers have this certification.
-
API Standards: For manufacturers producing size reduction equipment for the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before being used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to monitor critical parameters and maintain quality. This may include dimensional checks, material properties testing, and performance evaluations.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the equipment is shipped, a comprehensive final inspection is performed. This includes functional testing and ensuring compliance with all relevant standards.
Common Testing Methods
- Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile tests, hardness tests, and impact tests to evaluate the strength and durability of materials.
- Performance Testing: Equipment is often run under simulated operational conditions to assess efficiency, throughput, and particle size reduction capabilities.
- Fatigue Testing: This is crucial for components subjected to repetitive stress, ensuring they can withstand operational demands over time.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to review the manufacturing process, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards firsthand.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for documentation of quality control processes, including inspection reports, testing results, and certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality assurance practices and compliance with industry standards.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances when it comes to quality control and certification. For instance:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and compliance requirements.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers from different regions (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe) can affect communication and expectations regarding quality.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer transparency in their supply chain practices, as this can impact the quality and reliability of the equipment.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships for sourcing size reduction equipment.
Related Video: Exploring 5 Intriguing Factory Mass Production Processes in China.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for size reduction equipment Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of size reduction equipment is critical for B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis outlines the various components of cost, factors influencing pricing, and strategic tips for negotiating the best deals.
Cost Components
- Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing size reduction equipment, such as steel, ceramics, and specialized alloys, significantly influence the overall cost. High-quality materials enhance durability and efficiency but may also increase the initial investment.
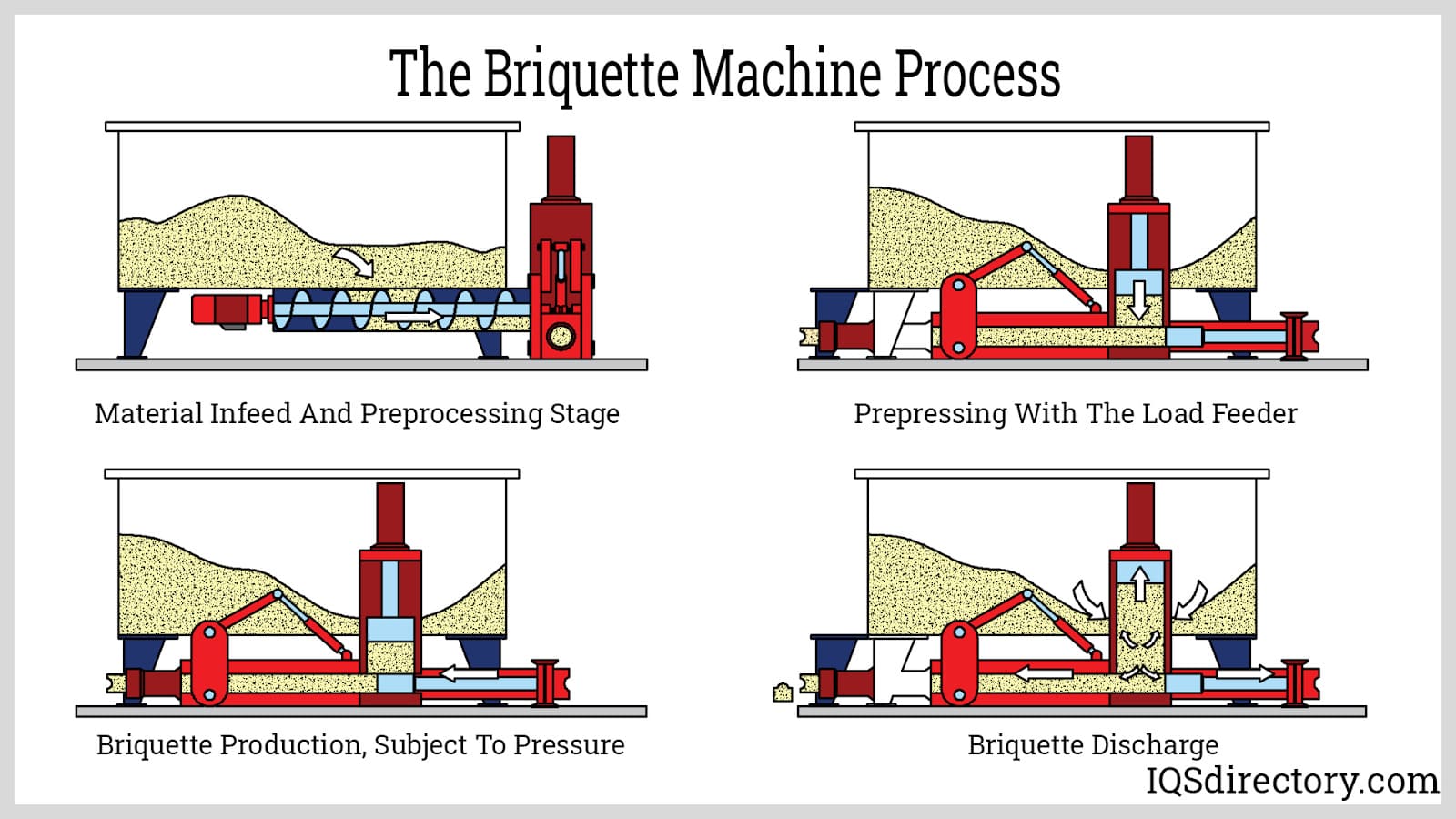
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with higher labor costs may lead to increased prices for equipment, whereas countries with lower labor costs might provide more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs, which can be reflected in the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized equipment can add to the initial costs. Standardized tooling can reduce expenses, but may limit customization options.
-
Quality Control (QC): Stringent quality control measures ensure that the equipment meets industry standards, particularly in critical applications such as pharmaceuticals or food processing. Enhanced QC processes can lead to higher costs but are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the equipment’s size, weight, and destination. International shipping can introduce additional complexities, including customs fees and tariffs, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. Understanding the average margins in the industry can provide insight into fair pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should consider their needs and negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom equipment tailored to specific applications usually incurs higher costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with available off-the-shelf solutions that may offer cost savings.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. High-performance materials may be more expensive but can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer equipment lifespans.
-
Quality/Certifications: Equipment that meets international quality standards or certifications will typically command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are necessary for their operations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, while newer entrants may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms agreed upon in international contracts is vital. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total cost.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions to negotiate pricing, especially for bulk purchases or long-term contracts. Building a strong relationship can lead to better terms and discounts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs over the equipment’s lifespan. A lower upfront cost may not always result in the best long-term investment.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, equipment costs may vary significantly between Europe and Africa due to labor costs, import tariffs, and local demand. Buyers should research local market conditions and pricing trends.
Disclaimer
Prices for size reduction equipment can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential size reduction equipment Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘size reduction equipment’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for size reduction equipment
Key Technical Properties of Size Reduction Equipment
When selecting size reduction equipment, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring it meets your operational needs. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
This refers to the quality of materials used in the equipment’s construction, such as stainless steel or carbon steel. High-grade materials enhance durability and resistance to wear, which is vital for maintaining productivity and minimizing downtime. For industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals, compliance with health and safety regulations also necessitates the use of food-grade or corrosion-resistant materials. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the acceptable deviation from a specified dimension. In size reduction, maintaining precise tolerances is critical for ensuring uniform particle sizes and quality of output. This is particularly important in applications like pharmaceuticals, where the efficacy of active ingredients can be affected by particle size variations. -
Throughput Capacity
This specification indicates the volume of material that can be processed by the equipment in a given time frame, typically measured in tons per hour. Understanding throughput capacity is essential for aligning production capabilities with demand. Buyers must ensure that the equipment’s capacity matches their operational requirements to avoid bottlenecks. -
Energy Efficiency
This property measures the amount of energy consumed during the size reduction process relative to the output produced. Energy-efficient machines not only reduce operational costs but also minimize environmental impact, a growing concern for many industries. Buyers should inquire about energy ratings and operational costs to assess long-term viability. -
Particle Size Distribution
This specification indicates the range of particle sizes produced by the equipment. Consistency in particle size is crucial for applications that require specific characteristics, such as flowability or reactivity. Understanding the equipment’s capabilities in this regard helps buyers select machines that meet their specific application needs.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some key terms relevant to size reduction equipment:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce equipment that is marketed by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they are purchasing high-quality, tested equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for international buyers who may want to balance inventory costs with their production needs. Knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and planning procurement strategies. -
RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ is a crucial step in the procurement process, enabling them to compare options and negotiate better terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
HGI (Hardgrove Grindability Index)
This index measures the ease with which a material can be ground. Understanding HGI is crucial for selecting the right size reduction equipment, as it directly impacts throughput and efficiency. Equipment performance can vary significantly based on the material’s grindability, making this a key factor in procurement decisions.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their operations and enhance product quality in their respective industries.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the size reduction equipment Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The size reduction equipment market is experiencing substantial growth, driven by the increasing demand across various industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and construction. Key global drivers include the rising need for efficient processing methods to enhance product quality and minimize waste. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective sourcing and investment decisions.
Current and emerging trends in technology include the integration of automation and IoT within size reduction equipment. These advancements enable real-time monitoring and data analytics, optimizing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. Moreover, the trend towards modular machinery allows for tailored solutions that meet specific processing needs while reducing capital expenditure.
The market dynamics are also influenced by regional variations. In Africa and South America, the growing mining and agricultural sectors necessitate robust size reduction solutions, while in Europe and the Middle East, the emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency drives innovation. Buyers should consider local supplier capabilities and technological advancements when sourcing equipment to ensure compatibility with their operational goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the procurement of size reduction equipment. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of machinery must be evaluated. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing carbon footprints and implementing eco-friendly practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as it encompasses the responsible procurement of materials and adherence to labor standards throughout the supply chain. Buyers should seek out manufacturers who provide transparency regarding their sourcing practices and can demonstrate compliance with international labor rights.
Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and the use of recyclable materials in equipment production can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By opting for ‘green’ certified suppliers, companies can not only reduce their environmental impact but also enhance their brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers and stakeholders.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of size reduction equipment can be traced back to ancient milling techniques, where manual grinding was employed to process grains. As industrialization progressed in the 19th and 20th centuries, the introduction of mechanical crushers and grinders revolutionized the industry, significantly increasing efficiency and capacity.
Today, the sector has transformed with advancements in materials science and engineering, leading to more sophisticated machinery capable of handling diverse materials with precision. The focus has shifted towards automation and energy-efficient designs, reflecting the changing demands of global markets and the increasing importance of sustainability. This historical context highlights the necessity for B2B buyers to stay abreast of technological advancements and evolving industry standards to make informed purchasing decisions.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of size reduction equipment
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of size reduction equipment?
When sourcing size reduction equipment, consider several key factors: reputation, experience, and certifications. Research suppliers’ histories and client reviews to gauge reliability. Check if they possess relevant certifications (ISO, CE, etc.) that indicate compliance with international standards. Additionally, assess their technical expertise in customizing equipment to meet your specific needs, as well as their capacity to provide after-sales support and maintenance services. -
Can I customize size reduction equipment to meet my specific production needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for size reduction equipment. Discuss your specific requirements regarding particle size, throughput, and material types with potential suppliers. This may include adjustments in design, materials, or technology used. Ensure that the supplier provides clear documentation and specifications for any modifications to avoid miscommunication and ensure optimal performance. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for size reduction equipment?
MOQs and lead times can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the equipment. Generally, MOQs can range from one unit for standard models to larger quantities for customized solutions. Lead times often range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the manufacturing process and the supplier’s current workload. Always confirm these details upfront to align with your project timelines. -
What payment terms and methods are commonly accepted by suppliers?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include 50% upfront and 50% upon delivery. Ensure to clarify accepted payment methods, which often include bank transfers, letters of credit, or payment platforms like PayPal. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect your investment, particularly if you’re dealing with international suppliers. Consider using escrow services for significant transactions to mitigate risk. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and compliance with international standards?
Request detailed documentation of quality assurance processes from your supplier, including test certificates and compliance with relevant industry standards. Inquire about their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and any third-party inspections they may conduct. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility or requesting samples to verify the quality of the equipment before making a large commitment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing size reduction equipment?
Logistics can significantly impact your procurement process. Ensure the supplier can handle international shipping and understand your local import regulations. Discuss packaging methods to prevent damage during transit and clarify who is responsible for shipping costs and customs duties. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can streamline this process and mitigate potential delays. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers?
To effectively manage disputes, establish clear communication channels from the outset. Include dispute resolution clauses in your contracts, specifying methods such as mediation or arbitration. Keep detailed records of all transactions and communications for reference. If a dispute arises, address it promptly and professionally, aiming for a solution that maintains the relationship while protecting your interests. -
What certifications should I look for to ensure the equipment meets industry standards?
When evaluating suppliers, look for certifications relevant to your industry, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and CE marking for compliance with European safety standards. For specific industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals, additional certifications such as FDA or HACCP may be necessary. These certifications indicate that the equipment adheres to rigorous safety and quality standards, ensuring reliability in your production processes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for size reduction equipment
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of size reduction equipment is pivotal for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe evolve, the demand for specialized equipment tailored to specific material processing needs becomes increasingly vital. Buyers should prioritize understanding the various types of size reduction machinery—impact crushers, grinders, pulverizers, and mills—while considering factors like throughput capacity, material characteristics, and desired particle sizes.
Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers:
- Assess Application Needs: Evaluate your specific requirements to select the most suitable equipment type.
- Focus on Quality and Efficiency: Invest in high-quality machines that enhance processing efficiency and reduce overall operational costs.
- Supplier Relationships: Build strong partnerships with reputable manufacturers to ensure access to the latest technologies and innovations in size reduction.
As the market continues to advance, international buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging technologies and trends in size reduction equipment. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, companies can position themselves for success, ensuring they meet the evolving demands of their industries. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your operations and drive growth in your business.