Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Solenoid Coil
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solenoid coil
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation, the solenoid coil stands as a pivotal component, influencing the efficiency and reliability of various systems. From controlling fluid flows in manufacturing to regulating air in HVAC systems, solenoid coils enable precise, rapid responses that drive operational excellence. As a crucial element in solenoid valves, these coils play a significant role in ensuring safety, optimizing costs, and enhancing system performance across diverse sectors.
This comprehensive guide is designed specifically for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. It will delve into the various types of solenoid coils, their materials, and the manufacturing processes that determine quality and performance. Additionally, it will provide insights into evaluating suppliers, understanding cost dynamics, and navigating the global market landscape.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of the key factors influencing their sourcing decisions, this guide empowers them to make informed choices. Whether you are a procurement manager or a technical buyer, the information herein will help you navigate the complexities of the solenoid coil market, ensuring that you select the right products to meet your operational needs effectively.
Understanding solenoid coil Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Solenoid Coil | Simple construction, typically used in general applications | Manufacturing, HVAC, automotive | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited customization options. |
| High-Temperature Solenoid Coil | Designed to operate at elevated temperatures | Oil & gas, aerospace, industrial ovens | Pros: Enhanced durability under heat. Cons: Higher costs, may require specialized sourcing. |
| Waterproof Solenoid Coil | Sealed design to prevent moisture ingress | Marine applications, food processing | Pros: Reliable in wet environments. Cons: Typically more expensive due to sealing. |
| Low Power Solenoid Coil | Requires less energy to operate, often with lower voltage | Robotics, automation, portable devices | Pros: Energy-efficient, suitable for battery-operated devices. Cons: May have lower performance under high load. |
| Custom Solenoid Coil | Tailored specifications for unique applications | Specialized machinery, custom equipment | Pros: Perfect fit for specific needs. Cons: Longer lead times, often higher cost. |
Standard Solenoid Coil
Standard solenoid coils are the most commonly utilized type in various industries. They feature a straightforward design and are suitable for general applications such as manufacturing, HVAC systems, and automotive components. When purchasing, buyers should consider the coil’s voltage and resistance specifications to ensure compatibility with their systems. While they are cost-effective and readily available, options for customization may be limited, which could pose challenges in specialized applications.
High-Temperature Solenoid Coil
High-temperature solenoid coils are engineered to withstand elevated temperatures, making them ideal for industries like oil and gas, aerospace, and industrial ovens. These coils often use advanced materials that enhance durability and performance under heat stress. Buyers should focus on thermal ratings and potential installation environments when sourcing these coils. Although they offer significant benefits in harsh conditions, the increased costs and need for specialized sourcing can be a drawback for some businesses.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Waterproof Solenoid Coil
Waterproof solenoid coils are designed with sealed constructions to prevent moisture ingress, making them suitable for marine applications and food processing environments. These coils provide reliability in wet or humid conditions, ensuring consistent performance. When sourcing waterproof coils, buyers must verify the IP (Ingress Protection) rating and consider potential impacts on pricing due to enhanced sealing technologies. While they offer strong protection against environmental factors, the higher costs associated with these designs may deter some buyers.
Low Power Solenoid Coil
Low power solenoid coils are designed to operate efficiently with reduced energy requirements, often functioning at lower voltages. They are particularly beneficial in applications such as robotics, automation, and portable devices. Buyers should assess the coil’s energy consumption and operational efficiency to ensure it meets their specific needs. While these coils promote energy savings, they may exhibit lower performance under heavy loads, which can limit their applicability in more demanding environments.
Custom Solenoid Coil
Custom solenoid coils are tailored to meet unique specifications, making them ideal for specialized machinery and custom equipment applications. These coils allow for precise adjustments in parameters such as size, voltage, and materials, ensuring they fit specific operational needs perfectly. When considering custom coils, buyers should be prepared for longer lead times and potentially higher costs. However, the ability to achieve a perfect fit for unique requirements often justifies these trade-offs, making them a valuable option for businesses with specialized demands.
Related Video: Solenoid Valve Explained | Types and Application
Key Industrial Applications of solenoid coil
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solenoid coil | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Pneumatic Actuation Systems | Enhances automation efficiency and reduces downtime | Look for coils with high response times and durability ratings. |
| Food & Beverage | Automated Dosing Systems | Ensures precision in ingredient mixing, maintaining quality | Ensure compliance with food safety standards and material certifications. |
| HVAC | Temperature Control Valves | Improves energy efficiency and system reliability | Select coils suitable for varying environmental conditions. |
| Medical Equipment | Fluid Control in Devices like Dialysis Machines | Guarantees patient safety through reliable fluid management | Prioritize coils with stringent quality control and certifications. |
| Petrochemical | Valve Control in Chemical Processing | Enhances safety and efficiency in hazardous environments | Consider coils with corrosion resistance and explosion-proof ratings. |
Manufacturing: Pneumatic Actuation Systems
In manufacturing, solenoid coils are integral to pneumatic actuation systems, controlling the movement of cylinders and valves. This application allows for rapid and precise control of machinery, which significantly enhances automation efficiency and reduces operational downtime. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable and high-response solenoid coils is crucial. Factors such as voltage compatibility, environmental conditions, and maintenance support should be thoroughly evaluated to ensure optimal performance.
Food & Beverage: Automated Dosing Systems
Automated dosing systems in the food and beverage industry utilize solenoid coils for precise ingredient mixing. This application is vital for maintaining quality and consistency in production processes. Buyers must ensure that the coils meet stringent food safety regulations, including material certifications like FDA compliance. Additionally, sourcing should focus on coils that can withstand frequent cleaning cycles and high hygiene standards, especially in regions with varying regulatory frameworks.
HVAC: Temperature Control Valves
In HVAC systems, solenoid coils are employed to regulate the flow of refrigerants and air, significantly improving energy efficiency and maintaining desired temperature levels. This application is essential for commercial and residential buildings, particularly in regions with extreme climates. Buyers should consider the environmental adaptability of coils, ensuring they can operate in high humidity or temperature variations. Selecting coils with low power consumption can also provide long-term cost savings.
Medical Equipment: Fluid Control in Devices like Dialysis Machines
Solenoid coils play a critical role in medical devices, particularly in fluid control for dialysis machines. They ensure reliable switching of fluids, which is vital for patient safety. Buyers in the medical sector must prioritize sourcing coils with stringent quality control measures and relevant certifications, such as ISO and CE marks. Additionally, understanding the specific electrical and thermal performance requirements is essential for compliance and operational efficiency.
Petrochemical: Valve Control in Chemical Processing
In the petrochemical industry, solenoid coils are used for valve control in various chemical processing applications. This is crucial for enhancing safety and efficiency in environments that handle hazardous materials. When sourcing for this application, buyers should look for coils made from corrosion-resistant materials and those with explosion-proof ratings. Understanding regional regulations and compliance standards is also critical, especially in areas like the Middle East, where safety regulations are stringent.
Related Video: Solenoid Basics Explained – Working Principle
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solenoid coil
When selecting materials for solenoid coils, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific applications. The following analysis covers four common materials used in solenoid coils: copper, iron, plastic, and varnish. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly influence the performance of solenoid coils in various industrial applications.
Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, with high thermal conductivity and low electrical resistance. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 200°C and can withstand moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons:
Copper coils are known for their durability and efficiency. They provide excellent performance in terms of electromagnetic properties, leading to reliable and fast actuation. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials, and its susceptibility to corrosion can be a concern in certain environments.
Impact on Application:
Copper is compatible with various media, including air and non-corrosive liquids. Its high conductivity makes it ideal for applications requiring rapid response times, such as in automation systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire. In regions like Africa and South America, where copper prices can fluctuate, understanding local market conditions is crucial for cost management.
Iron
Key Properties:
Iron is commonly used for the core of solenoid coils, providing a strong magnetic field. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 300°C) and is often treated for corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
Iron cores improve the efficiency of solenoid coils by enhancing magnetic performance. However, they can be heavy and may require additional protective coatings to prevent rust, increasing manufacturing complexity and cost.
Impact on Application:
Iron is suitable for applications involving moderate to high pressure and is often used in industrial automation and HVAC systems. Its magnetic properties make it ideal for solenoid valves that control fluid flow.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as DIN 17200 for iron materials. In the Middle East, where high humidity can lead to corrosion, selecting treated iron can enhance product longevity.
Plastic
Key Properties:
Plastics, particularly thermoplastics like PA66, offer good electrical insulation and can operate at temperatures up to 120°C. They are lightweight and resistant to many chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
Plastic solenoid coils are cost-effective and provide excellent insulation, reducing the risk of electrical faults. However, their mechanical strength is lower than metals, which can limit their use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Plastics are suitable for applications involving non-corrosive fluids and gases. They are often used in consumer products and light industrial applications where weight and cost are critical factors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should be aware of material certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. In Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is essential for plastics used in solenoid coils.
Varnish
Key Properties:
Varnish is used for insulation and protection of solenoid coils, typically made from epoxy or polyurethane. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 180°C) and provides excellent moisture resistance.
Pros & Cons:
Varnish enhances the durability and reliability of solenoid coils by preventing short circuits and corrosion. However, the application process can increase manufacturing time and costs.
Impact on Application:
Varnished coils are ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as automotive and industrial machinery, where exposure to moisture and contaminants is common.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that varnish used meets relevant safety and performance standards, such as UL 1446 for electrical insulation systems. In regions with extreme weather, selecting high-quality varnish can be critical for product reliability.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for solenoid coil | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Automation systems, HVAC | Excellent conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Iron | Industrial automation, HVAC | Strong magnetic performance | Heavy, requires protective coatings | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer products, light industrial | Cost-effective, lightweight | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Varnish | Automotive, industrial machinery | Moisture resistance | Increases manufacturing time | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in solenoid coils, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solenoid coil
The manufacturing process of solenoid coils is intricate and requires precision at every stage to ensure high performance and reliability. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes and the associated quality assurance standards is crucial for making informed procurement decisions.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. High-quality copper wire is essential for conductivity, and its price can significantly impact the overall cost. Iron core materials, such as silicon steel, are selected based on the required electromagnetic performance. Insulation materials, including varnish and insulating tape, are also prepared to ensure the coils can withstand operational stresses.
2. Forming
The forming stage includes the winding of copper wire around the iron core. This process can be automated or manual:
– Automated Winding: Using CNC machines enhances consistency and efficiency, allowing for higher production volumes at lower costs per unit. This method is ideal for standardized coils.
– Manual Winding: Suitable for custom orders or small batches, although it tends to be labor-intensive and more expensive. It allows for flexibility in design but can introduce variability in quality.
3. Assembly
Once the coils are formed, they are assembled into their final configuration. This includes attaching terminals and ensuring that all components fit together correctly. Quality control measures are critical at this stage to prevent defects that could lead to coil failure in operation.
4. Finishing
The finishing process involves applying protective coatings, such as varnish or epoxy, to enhance insulation and environmental resistance. This stage may also include curing processes that increase the durability of the coils. Proper finishing is vital for ensuring the coils can operate effectively in various conditions, including high temperatures or humidity.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a fundamental aspect of solenoid coil manufacturing. Adhering to international standards helps ensure that products meet customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality. Manufacturers should be certified to this standard to demonstrate their commitment to quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with safety and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For coils used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute standards is essential.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control is typically segmented into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify issues early, reducing waste and rework.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product ensures it meets all specifications before shipping.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of various testing methods used to verify the performance and reliability of solenoid coils:
– Electrical Testing: Measures resistance, inductance, and insulation resistance to ensure the coil operates within specified parameters.
– Thermal Testing: Assesses performance under different temperature conditions to simulate operational environments.
– Mechanical Testing: Evaluates the structural integrity of the coil under stress to ensure durability.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international buyers, especially those from diverse regions, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital. Here are actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting onsite audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Ensure they adhere to relevant international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask for detailed quality assurance reports, including test results and compliance certifications. These documents should outline the testing methods used and the results obtained.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. This is particularly useful in regions where local regulations may vary.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
Navigating quality assurance and certification can be complex, especially for international buyers. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations.
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with local certification requirements and ensure that your suppliers can meet these standards. For instance, products sold in the EU require CE marking, while those in the Middle East may need to comply with local Gulf standards.
-
Communication with Suppliers: Establish clear communication with suppliers regarding their quality control processes and certifications. This can help mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and ensure that products meet your expectations.
-
Consideration of Trade Policies: Be aware of trade policies and tariffs that may affect the cost and availability of materials and components. This awareness can help in negotiating better terms and ensuring a stable supply chain.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for solenoid coils is essential for international B2B buyers. By prioritizing suppliers that adhere to rigorous quality standards and employing effective verification methods, buyers can significantly reduce risks and ensure reliable performance in their applications.
Related Video: How to make a solenoid valve coil
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solenoid coil Sourcing
The cost structure of solenoid coils involves multiple components that contribute to the final pricing. Understanding these components can help international B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials include copper wire, iron cores, and insulation materials. Copper prices fluctuate based on global demand, impacting costs directly. Iron core materials, such as silicon steel or ferrite, also vary in price according to their magnetic properties and manufacturing processes. High-quality insulation increases durability but raises costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region and can impact the overall cost structure. Automated manufacturing processes reduce labor intensity but involve higher initial investments. In contrast, manual production methods may lead to increased labor costs, especially in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production methods can mitigate overhead costs, making it essential to consider the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tooling is necessary for producing custom or high-spec coils. Tooling costs can be amortized over larger production runs, thus reducing the per-unit cost for bulk orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability but can increase costs. Certifications and compliance with international standards add further expenses, particularly for industries with strict regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, the chosen Incoterms, and the mode of transportation. Buyers should factor in both shipping costs and potential tariffs when calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the level of service provided. High-quality suppliers may command higher prices, justified by better reliability and customer support.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements typically increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications increase costs but can enhance reliability and performance. Buyers should weigh these factors against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capabilities, and geographic location can all influence pricing. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. Different terms can significantly affect the total landed cost of products.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Be prepared to leverage volume commitments to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance costs, and potential downtime. Opt for suppliers who can demonstrate lower TCO through superior product quality and support.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local economic conditions that can affect pricing. Establishing a clear understanding of these factors can aid in budgeting and financial planning.
Disclaimer
Prices for solenoid coils can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential solenoid coil Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘solenoid coil’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solenoid coil
In the procurement of solenoid coils, understanding essential technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section outlines the key specifications and terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with to enhance their sourcing strategies.
Critical Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality and type of materials used in the coil, primarily copper for the winding and various metals for the core.
– Importance: Higher-grade materials, such as oxygen-free copper, offer superior conductivity and longevity. Selecting the right material grade can significantly impact the performance and reliability of the solenoid coil in demanding applications. -
Winding Configuration
– Definition: The arrangement of wire turns in the coil, which can be either single-layer or multi-layer.
– Importance: The configuration affects the coil’s inductance and resistance. A well-designed winding configuration can optimize the coil’s electromagnetic efficiency and reduce energy loss, which is vital for cost-effective operations. -
Electrical Specifications
– Definition: Parameters such as voltage rating, resistance, inductance, and power consumption.
– Importance: These specifications determine how the solenoid coil will perform under different operational conditions. Understanding these metrics helps buyers ensure compatibility with their existing systems and prevents costly malfunctions. -
Temperature Rating
– Definition: The maximum operating temperature of the solenoid coil, often specified in degrees Celsius.
– Importance: Coils operating beyond their temperature rating can fail prematurely. Selecting coils with appropriate temperature ratings is essential for applications in high-heat environments, ensuring longevity and reliability.
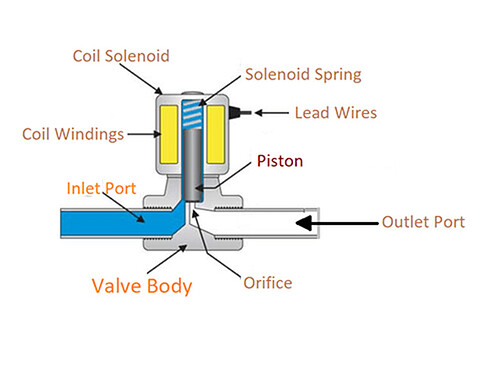
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: The allowable variation in the coil’s dimensions and electrical properties.
– Importance: Tight tolerances are critical in precision applications where performance is paramount. Understanding tolerance levels can help buyers avoid issues related to fit and function in their systems. -
Coil Resistance
– Definition: The resistance of the coil, measured in ohms, which affects how much current flows through it.
– Importance: Low resistance is preferred for efficient operation, as it reduces heat generation and energy loss. Buyers should assess the coil resistance to ensure it meets the demands of their application.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can indicate the quality and reliability of the solenoid coils, as OEMs often adhere to stringent manufacturing standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their purchasing needs without incurring excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products.
– Relevance: RFQs are vital for comparing prices and terms from different suppliers, enabling buyers to secure the best deals based on their specifications and quantities. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ensuring smooth logistics and compliance in international sourcing. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods.
– Relevance: Knowing lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should account for lead times to avoid disruptions in their operations. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Compliance with industry-specific standards, such as ISO or UL certifications.
– Relevance: Certifications ensure that solenoid coils meet safety, reliability, and performance criteria. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide certified products to mitigate risks and ensure quality.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terminology, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and enhance the performance of their systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the solenoid coil Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The solenoid coil market is experiencing transformative growth driven by automation across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and HVAC systems. Global demand for efficient fluid control systems is pushing innovation, with solenoid coils being central to this evolution. Key trends influencing the market include the integration of smart technologies, where solenoid coils are increasingly embedded in IoT-enabled devices, allowing for real-time monitoring and control. This is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in Africa and South America, where industrial automation is rapidly advancing.
Additionally, the rise of sustainability consciousness among consumers and businesses is reshaping sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials. The demand for customized solutions is also on the rise, with businesses needing coils tailored to specific operational requirements, reflecting a shift from one-size-fits-all products to specialized offerings. Furthermore, regional market dynamics play a crucial role; for instance, European buyers often face stricter regulatory standards compared to their counterparts in Africa and the Middle East, which can influence sourcing strategies.
International B2B buyers must remain vigilant to fluctuating raw material prices, particularly copper and iron, which directly impact production costs. The ongoing geopolitical issues and trade policies can also affect supply chains, making it essential for buyers to establish robust relationships with multiple suppliers to mitigate risks and ensure a steady supply of high-quality solenoid coils.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the solenoid coil sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes—ranging from raw material extraction to production waste—has prompted companies to adopt green practices. This includes sourcing materials from suppliers that employ sustainable mining practices for metals like copper and iron, reducing carbon footprints, and minimizing waste in production.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly prioritized, with buyers favoring manufacturers who adhere to environmental regulations and social responsibility standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, the use of recyclable materials and eco-friendly insulation options in solenoid coils is gaining traction, appealing to buyers focused on reducing their environmental impact.
B2B buyers should also consider suppliers that offer transparency in their sourcing practices, ensuring that materials are not only sustainable but ethically obtained. This focus on ethical sourcing not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for responsible manufacturing practices, ultimately influencing purchasing decisions in the global market.
Brief Evolution/History
The solenoid coil has its roots in the 19th century, emerging from advancements in electromagnetism. Initially used in simple telegraph systems, the solenoid coil evolved through the industrial revolution, finding applications in various automated systems. As industries transitioned towards more complex machinery, solenoid coils became integral components in fluid control systems, enhancing operational efficiency.
Today, solenoid coils are ubiquitous across multiple sectors, including automotive, healthcare, and industrial automation. The evolution continues as modern technology integrates solenoid coils into smart systems, paving the way for innovations in automation and control. This historical context highlights the importance of understanding the advancements in solenoid technology, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on past developments and future potential.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solenoid coil
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of solenoid coils?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, technical expertise, and manufacturing capabilities. Check for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Review their product range to ensure they offer the specific solenoid coils you need, including customization options. Assess their financial stability through credit checks or references from other clients. Finally, consider their responsiveness and communication skills, as these are crucial for effective collaboration and problem resolution. -
Can I customize solenoid coils to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for solenoid coils. You can specify parameters such as coil dimensions, wire gauge, voltage ratings, and insulation materials. Discuss your specific application needs with potential suppliers to ensure they can accommodate your requirements. Keep in mind that customization may affect lead times and costs, so clarify these aspects upfront to avoid surprises later in the procurement process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for solenoid coils?
Minimum order quantities for solenoid coils can vary significantly based on the supplier and the level of customization required. Standard products might have lower MOQs, while customized coils may require larger quantities. Lead times can also vary; typically, expect anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of your order and the supplier’s production schedule. Always confirm these details during the initial discussions to align your procurement timeline with your project needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing solenoid coils internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common practices include partial upfront payments (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. For first-time transactions, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always clarify payment terms in your contract, including currency, payment method, and any penalties for late payments. This clarity helps prevent disputes and ensures a smoother transaction process.
-
What quality assurance measures should I look for in solenoid coil suppliers?
Seek suppliers that implement rigorous quality assurance processes, including in-process inspections and final testing of solenoid coils. Ask about their testing standards, such as electrical resistance and thermal performance evaluations. Certifications like CE, UL, or RoHS can indicate compliance with international safety and environmental standards. Request samples for evaluation before placing larger orders, allowing you to assess the product quality directly and reduce the risk of defects in your supply chain. -
How can I ensure proper logistics and shipping for my solenoid coil orders?
To ensure smooth logistics, clarify shipping terms with your supplier, including Incoterms (like FOB or CIF), which define responsibilities for shipping costs and risks. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling international shipments to navigate customs and documentation. Additionally, confirm the packaging methods to ensure the coils are protected during transit. Tracking shipments is essential for timely delivery, so request tracking information to monitor your order’s progress. -
What should I do if there are disputes with the supplier regarding quality or delivery?
In the event of a dispute, first, communicate directly with your supplier to address the issue. Document all correspondence and maintain a clear record of contracts, specifications, and agreements. If the matter cannot be resolved through direct negotiation, refer to any dispute resolution clauses outlined in your contract, which may include mediation or arbitration. Engaging a legal expert with international trade experience can also provide guidance on the best course of action to protect your interests. -
What certifications should I look for in solenoid coils when sourcing internationally?
Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international quality and safety standards. Common certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management, UL certification for electrical safety, and CE marking for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Additionally, industry-specific certifications may be relevant, such as ATEX for hazardous environments or FDA compliance for food-grade applications. These certifications not only ensure product reliability but also facilitate smoother customs clearance in international trade.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solenoid coil
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of solenoid coils is paramount for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Understanding the critical factors that influence pricing—such as raw material costs, manufacturing processes, and performance specifications—enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific needs.
Investing time in evaluating suppliers based on their product quality, certifications, and after-sales service can yield significant long-term benefits. Additionally, considering the regional market dynamics in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is essential, as they can directly impact availability and pricing.
As the industry moves towards greater automation and efficiency, sourcing high-quality solenoid coils will be a key driver of innovation and productivity. International buyers are encouraged to leverage these insights to build robust supplier relationships and foster sustainable practices. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your procurement strategies and ensure your operations are equipped with reliable solenoid coils for future growth and success.