Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Speed Reducers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for speed reducers
In today’s dynamic industrial landscape, speed reducers play a pivotal role in optimizing machinery performance across a multitude of sectors. These mechanical devices not only reduce the rotational speed of motors but also enhance torque, facilitating precise control over heavy loads. As global demand for efficiency and reliability in operations escalates, understanding the intricacies of speed reducers becomes crucial for international B2B buyers.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of speed reducers—such as worm, planetary, helical, and bevel—while also examining the materials and manufacturing processes involved. Buyers will gain insights into quality control standards that ensure product reliability, alongside a curated list of reputable suppliers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Additionally, we provide a thorough analysis of market trends and pricing structures, equipping buyers with the knowledge to make informed sourcing decisions. Common FAQs address key considerations in selecting the right speed reducer for specific applications, ensuring that buyers can navigate the complexities of this critical component with confidence.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By leveraging the insights in this guide, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and foster long-term partnerships with suppliers, ultimately driving success in a competitive global market.
Understanding speed reducers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Worm Gear Reducer | High torque output, right-angle design, smooth operation | Conveyors, material handling, lifting equipment | Pros: Quiet operation, compact size. Cons: Lower efficiency, higher friction losses. |
| Planetary Gear Reducer | Compact design, multiple gears, high torque-to-size ratio | Robotics, automotive, heavy machinery | Pros: High efficiency, excellent load distribution. Cons: Complex design may increase cost. |
| Helical Gear Reducer | Angled teeth for gradual meshing, quieter operation | Compressors, industrial mixers | Pros: Smooth operation, good for high-speed applications. Cons: More expensive than spur gears. |
| Bevel Gear Reducer | Changes direction of force, suitable for right-angle setups | Agricultural machinery, heavy-duty applications | Pros: Versatile direction changes, robust design. Cons: Can be bulky, requiring more space. |
| Spur Gear Reducer | Simple design, straight teeth, cost-effective | General machinery, automotive applications | Pros: Easy to manufacture, reliable for low speeds. Cons: Noisy operation, less efficient at high speeds. |
Worm Gear Reducer
Worm gear reducers are characterized by their unique design that includes a worm (screw) and a worm wheel, enabling high torque output and smooth operation. They are particularly suitable for applications requiring significant speed reduction and high torque, such as conveyors and lifting equipment. When considering a worm gear reducer, B2B buyers should evaluate the balance between the required torque and the efficiency of the system, as these reducers tend to have higher friction losses, which can impact overall performance.
Planetary Gear Reducer
Planetary gear reducers feature a compact design with multiple gears rotating around a central sun gear. This configuration allows for a high torque-to-size ratio, making them ideal for applications in robotics and heavy machinery. Buyers should focus on the efficiency and load distribution capabilities of planetary gear reducers, as they can handle significant loads while maintaining precision. However, their complexity may result in higher costs, which should be justified by the performance requirements of the application.
Helical Gear Reducer
Helical gear reducers utilize angled teeth that mesh gradually, providing a quieter and smoother operation compared to other gear types. They are well-suited for high-speed applications such as compressors and industrial mixers. B2B buyers should consider the operational environment and the need for noise reduction when selecting helical gear reducers, as their design can be more expensive but offers enhanced performance and durability.
Bevel Gear Reducer
Bevel gear reducers are designed to change the direction of force, making them useful for right-angle applications in agricultural machinery and heavy-duty equipment. Their robust design allows them to handle heavy loads effectively. Buyers should assess the space constraints and the specific application needs, as bevel gear reducers can be bulkier than other types. While they offer versatility, their size may require careful planning in system design.
Spur Gear Reducer
Spur gear reducers are known for their straightforward design and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for general machinery and automotive applications. They operate using straight teeth and are reliable for low-speed applications. However, buyers should be aware that spur gear reducers can be noisier and less efficient at high speeds. Evaluating the trade-offs between cost and performance is essential when considering spur gear reducers for specific applications.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of speed reducers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of speed reducers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Enhanced control of material flow, reducing downtime and waste. | Consider durability, torque requirements, and compatibility with existing machinery. |
| Agriculture | Agricultural Equipment (e.g., tractors, harvesters) | Improved efficiency in power transmission for heavy-load operations. | Assess torque needs, environmental resilience, and maintenance support. |
| Mining | Crushing and Grinding Machines | Increased operational efficiency and reduced energy consumption. | Look for robust designs, high torque ratings, and reliability under heavy loads. |
| Robotics | Robotic Arms and Automated Systems | Precision control for accurate movements and task execution. | Evaluate size constraints, weight, and responsiveness of the reducer. |
| Material Handling | Forklifts and Lifting Equipment | Enhanced lifting capacity and operational safety. | Focus on safety certifications, load capacity, and maintenance requirements. |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, speed reducers are integral to conveyor systems, where they control the speed of material transport. This ensures a consistent flow of materials, minimizing delays and operational downtime. Buyers should prioritize durability and torque specifications to match the demands of their specific applications. Furthermore, compatibility with existing machinery is crucial to avoid costly retrofitting.
Agriculture
In agricultural applications, speed reducers are commonly used in tractors and harvesters to optimize power transmission. They allow for efficient operation under heavy loads, which is vital for tasks like plowing and harvesting. B2B buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should consider the torque requirements based on the type of crop and terrain. Additionally, sourcing reducers that can withstand harsh environmental conditions can significantly enhance equipment longevity.
Mining
In the mining industry, speed reducers are essential for powering crushing and grinding machines. These devices help increase operational efficiency while reducing energy consumption, which is critical in a sector where costs can spiral quickly. Buyers should focus on robust designs capable of handling high torque and the harsh conditions prevalent in mining operations. Reliability is key to minimizing maintenance costs and downtime.
Robotics
Speed reducers play a crucial role in robotics, particularly in robotic arms and automated systems where precision is paramount. They facilitate accurate movements and enable robots to perform complex tasks with high reliability. Buyers in this sector, especially from Europe and the Middle East, must evaluate the size constraints and weight of reducers to ensure they fit within their robotic designs. Responsiveness and control precision are also critical factors to consider.
Material Handling
In material handling applications, speed reducers are used in forklifts and lifting equipment to enhance lifting capacity and operational safety. They help manage heavy loads efficiently, ensuring that equipment can operate safely and effectively. When sourcing reducers for this application, it is essential to focus on safety certifications and load capacity to meet regulatory standards. Maintenance requirements should also be assessed to ensure longevity and reliability in operations.
Related Video: Proper Industrial Gearbox, Gearmotor & Speed Reducer Lubrication | WCHYWT #1
Strategic Material Selection Guide for speed reducers
When selecting materials for speed reducers, it is crucial to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of commonly used materials. The choice of material directly impacts the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the speed reducer in various applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of speed reducers.
1. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for high-load applications. It typically has a temperature rating up to 300°C and excellent wear resistance, which is critical in high-friction environments.
Pros & Cons:
Steel’s primary advantage is its robustness and ability to withstand heavy loads. However, it can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which may lead to premature failure in humid or corrosive environments. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, with processes such as forging and machining being common.
Impact on Application:
Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, making it versatile for various industrial applications. However, in environments with high moisture or chemical exposure, additional protective coatings may be necessary.
Considerations for Buyers:
International buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100. In regions like Africa and South America, where corrosion may be prevalent, selecting corrosion-resistant grades or coatings is advisable.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, with good corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 150°C and is less dense than steel, making it easier to handle and install.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which reduces overall equipment weight, enhancing energy efficiency. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-load applications. Manufacturing processes can be more complex due to the need for precision machining.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is ideal for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace or automotive industries. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for environments with exposure to moisture.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM B221. In Europe, aluminum alloys are often specified according to EN 573. Understanding local preferences for aluminum grades can also aid in selection.
3. Cast Iron
Key Properties:
Cast iron has excellent wear resistance and good vibration-damping properties. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 400°C) and provides a high level of rigidity.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of cast iron is its durability and ability to absorb vibrations, making it suitable for heavy machinery. However, it is brittle and can fracture under high impact loads. The manufacturing process is relatively straightforward, but the weight can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a concern.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is often used in heavy-duty applications such as mining and construction equipment. Its ability to withstand high pressures makes it suitable for hydraulic applications.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A48. In regions like the Middle East, where heavy machinery is prevalent, cast iron’s properties align well with local industry needs.
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite materials, often a combination of plastics and fibers, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They can operate effectively at moderate temperatures (up to 120°C) and are non-magnetic.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of composites is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for a variety of environments. However, they can be more expensive than metals and may not withstand high loads as effectively as steel or cast iron.
Impact on Application:
Composites are ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. They are also suitable for environments where chemical resistance is crucial.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with relevant standards, such as ASTM D638 for plastics. In regions like Europe, understanding the specific requirements for composite materials can enhance product selection.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for speed reducers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy machinery, automotive | High tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Mining, construction equipment | Excellent durability | Brittle under high impact loads | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace, automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost, lower load capacity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for speed reducers, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance requirements, environmental conditions, and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for speed reducers
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for speed reducers are critical considerations for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these elements not only ensures that buyers select reliable products but also helps them navigate the complexities of global supply chains. This section outlines the typical manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and relevant standards that international buyers should consider.
Manufacturing Processes for Speed Reducers
The production of speed reducers involves several key stages, each integral to the final product’s performance and reliability.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing speed reducers is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include:
- Metals: Steel, aluminum, and cast iron are prevalent due to their strength and durability.
- Lubricants: Essential for ensuring smooth operation and minimizing wear during the reducer’s lifecycle.
Materials undergo rigorous inspections to confirm they meet specific mechanical properties and standards before being processed.
2. Forming
The forming stage involves several techniques to create the various components of the speed reducer:
- Machining: This is the primary method for shaping parts like gears and housings. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is often employed for its precision.
- Forging: Used for producing strong components, particularly those subject to high stress.
- Casting: Employed for parts with complex geometries, casting allows for the economical production of bulk components.
Each technique has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the design requirements, volume of production, and cost considerations.
3. Assembly
Once components are formed, they are assembled into complete speed reducers. This stage includes:
- Gear Assembly: Gears are carefully meshed to ensure optimal performance and minimal backlash.
- Shaft Installation: Input and output shafts are aligned and secured.
- Housing Assembly: The outer casing is assembled to protect the internal components.
Precision during assembly is crucial; misalignment can lead to increased wear and reduced efficiency.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the product’s durability and performance through various processes:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like hardening, coating, or anodizing can improve wear resistance and reduce friction.
- Balancing: Rotating components are balanced to minimize vibrations during operation.
- Inspection: Visual and dimensional inspections are conducted to ensure all components meet specifications.
Quality Assurance for Speed Reducers
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of speed reducers, as it directly impacts performance and reliability. A robust QA process includes adherence to international standards and specific industry requirements.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management system standard that ensures consistent quality in manufacturing processes. Suppliers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for products used in the oil and gas industry, including specific types of gear reducers.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet required specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks during production help identify and rectify issues early, ensuring components are manufactured within tolerance levels.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes thorough testing, including dimensional checks, load testing, and performance evaluations.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability and efficiency of speed reducers:
- Performance Testing: Evaluates the reducer’s ability to handle specified loads and speeds.
- Vibration Analysis: Monitors for excessive vibrations that could indicate misalignment or imbalance.
- Thermal Imaging: Identifies hot spots that may indicate lubrication issues or excessive wear.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct audits to assess the supplier’s manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party audits.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for their quality control documentation, including inspection reports and test results. This transparency can help gauge their commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection services to verify product quality before shipment. This can reduce risks associated with receiving non-compliant or defective products.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must navigate various challenges when dealing with suppliers from different regions:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality can influence supplier selection. For example, some regions may prioritize cost over quality.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with local regulations that may affect product specifications or quality standards.
- Communication Barriers: Ensure clear communication regarding quality expectations and standards to avoid misunderstandings.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with speed reducers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they procure reliable and high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for speed reducers Sourcing
The cost structure and pricing of speed reducers are influenced by various components and factors that international B2B buyers must understand to make informed purchasing decisions. This analysis will cover the primary cost components, key price influencers, and practical tips for effective sourcing, particularly for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in speed reducer manufacturing include metals such as steel, aluminum, and iron. The quality and type of materials directly impact the durability and performance of the reducers, which can affect pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on geographical location and labor market conditions. Skilled labor is essential for the precision manufacturing of speed reducers, and regions with higher labor costs may see an increase in overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, allowing suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers may encounter higher prices if specific tooling is required for unique specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Stringent quality control measures are necessary to ensure reliability and compliance with industry standards. The costs associated with QC processes can be reflected in the final product price.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling are crucial components of the total cost, particularly for international buyers. Logistics costs can vary based on distance, shipping method, and import duties, which need to be factored into the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. This margin can fluctuate based on market conditions and competition.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly influence pricing. Higher order volumes often lead to discounted rates, making bulk purchases more economical.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized materials or tooling. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts both performance and cost. Premium materials may enhance durability but come at a higher price.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet specific quality standards or certifications often command higher prices. Buyers should assess the importance of these certifications based on their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge more due to their reliability and quality assurance. New or lesser-known suppliers might offer lower prices but could carry higher risks.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is critical for international buyers. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer, influencing the total landed cost.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations to secure better pricing. Understanding the cost structure can provide leverage during discussions with suppliers.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and longevity of the product.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing strategies compared to those in Africa or South America due to local economic conditions and market demands.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service terms. Loyalty can often yield discounts or favorable conditions in future transactions.
Disclaimer
Prices can fluctuate based on market dynamics, supplier changes, and regional economic conditions. Therefore, it is advisable for buyers to conduct their own market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are getting a fair deal.
Spotlight on Potential speed reducers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘speed reducers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for speed reducers
Key Technical Properties of Speed Reducers
When selecting speed reducers for industrial applications, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
- Material Grade
The material from which the speed reducer is made significantly affects its durability and performance. Common materials include high-strength steel, aluminum, and plastic composites. High-grade steel is preferred for heavy-duty applications due to its strength and resistance to wear, while aluminum may be chosen for lightweight, low-torque applications. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material can lead to reduced maintenance costs and improved operational efficiency.
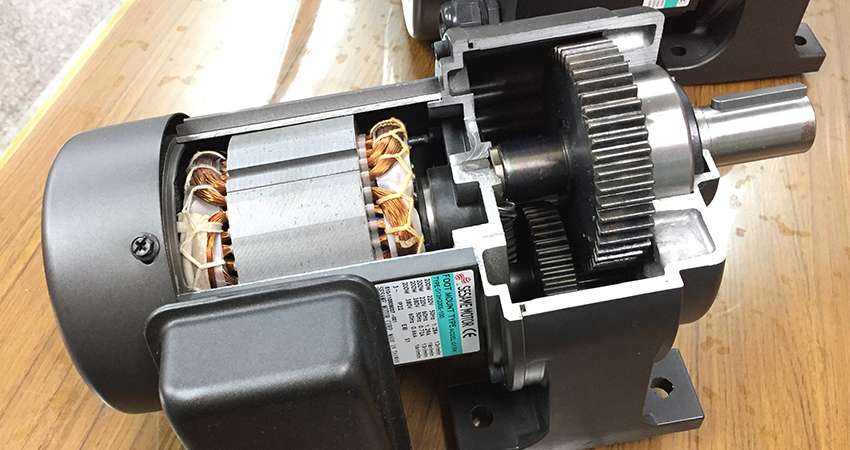
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Gear Ratio
The gear ratio determines how much the speed is reduced and how much torque is increased. It is calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the driven gear by the number of teeth on the driving gear. A higher gear ratio means lower output speed and higher torque, which is essential for applications requiring significant force. Understanding gear ratios helps buyers match speed reducers to specific operational needs, ensuring machinery functions effectively. -
Load Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum load that the speed reducer can handle without failure. It is essential to choose a reducer with a load capacity that exceeds the operational demands of the application. Insufficient load capacity can lead to premature wear or failure, resulting in costly downtime. Buyers should evaluate load requirements carefully to select a suitable product that aligns with their operational needs. -
Efficiency
Efficiency measures how much input energy is converted into useful output work. In speed reducers, efficiency is often expressed as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating lower energy losses. Efficient reducers can lead to significant energy savings, making them more cost-effective in the long run. B2B buyers should prioritize high-efficiency models to enhance overall energy consumption and operational costs. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In speed reducers, tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring smooth operation and reducing wear. Components with precise tolerances minimize backlash and improve performance. Buyers should assess the tolerances specified by manufacturers to ensure compatibility with their equipment and applications.
Common Trade Terminology
Understanding industry jargon is vital for effective communication in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to speed reducers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEMs are companies that produce components that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of speed reducers, OEMs design and manufacture the reducers used in original machinery. Buyers often prefer OEM parts for their compatibility and reliability, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. It is essential for buyers to be aware of MOQ requirements, as they can impact inventory management and cash flow. Understanding MOQ helps buyers negotiate better terms and plan their purchases effectively, especially for large-scale projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. In the context of speed reducers, an RFQ enables buyers to compare offers from different manufacturers and negotiate favorable terms. Properly crafted RFQs can streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where international trade practices may vary. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the speed reducer industry, lead times can vary significantly based on supplier capabilities and production schedules. Understanding lead times is critical for buyers to manage project timelines and ensure that machinery is operational when needed.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing speed reducers, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the speed reducers Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global speed reducers market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating an increase from USD 10,527.9 million in 2023 to USD 17,588.4 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.93%. This growth is driven by rising industrial automation, the need for energy-efficient solutions, and advancements in manufacturing technology. Key sectors such as automotive, material handling, and robotics are increasingly adopting speed reducers for their ability to enhance efficiency and control in machinery operations.
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing a shift towards sourcing suppliers that offer customized solutions. Emerging technologies like IoT and AI are reshaping the landscape, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of speed reducers. Buyers are also looking for suppliers that provide comprehensive support, including installation and after-sales service, which enhances the operational reliability of equipment.
Regional dynamics play a significant role in sourcing trends. For instance, the Middle East is focusing on energy-efficient technologies in line with sustainability initiatives, while African markets are increasingly prioritizing local suppliers to reduce lead times and costs. Buyers from Europe and South America are gravitating towards suppliers that can offer competitive pricing without compromising quality, often leveraging e-commerce platforms for streamlined procurement processes.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As global awareness of environmental issues rises, sustainability has become a critical factor for B2B buyers in the speed reducers sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that implement sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing emissions during production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with companies expected to maintain transparency in their supply chains. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and have certifications that demonstrate their commitment to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or LEED for sustainable manufacturing practices.
Incorporating green certifications and materials into the supply chain not only enhances brand reputation but also appeals to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers. Moreover, companies that adopt sustainable practices often experience long-term cost savings, as energy-efficient products can reduce operational costs and improve overall productivity.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of speed reducers dates back to the early industrial revolution when simple mechanical devices were used to reduce speed and increase torque for machinery. Over time, technological advancements led to the development of more complex gear systems, including worm gears and planetary reducers, which provided greater efficiency and versatility in various applications.
In recent decades, the integration of electronics and automation has transformed speed reducers into sophisticated components essential for modern machinery. Today, they are not just passive devices; they are integral to systems that require precision control and efficiency. This evolution reflects broader trends in industrial automation, where speed reducers are crucial for optimizing performance across diverse sectors, from manufacturing to renewable energy.
Understanding this historical context can help B2B buyers appreciate the advancements in technology and the importance of selecting the right speed reducers to meet their operational needs.
Related Video: India-US Trade Deal: Trump Wants To Open Up India With Trade Deal | WION
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of speed reducers
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for speed reducers?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, years of experience, and customer reviews. Verify their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate quality management practices. Request references from other international buyers, particularly those in your region, to gauge reliability. Additionally, assess their production capabilities and whether they can meet your specific requirements, including customization options and technical support. -
Can I customize speed reducers to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for speed reducers. This may include adjustments in gear ratios, size, and material specifications to suit particular applications. When seeking customization, provide detailed specifications and discuss your requirements with the supplier’s engineering team. It’s crucial to ensure that they have the capability to deliver tailored solutions without compromising quality or lead times. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for speed reducers?
MOQs vary significantly among suppliers based on factors such as manufacturing processes and demand for specific models. For custom orders, MOQs may be higher due to the added complexity. Lead times can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the customization level and the supplier’s production schedule. It’s advisable to clarify these details during the initial discussions to align expectations with your project timelines. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation proving that the speed reducers meet international standards such as ISO 9001 or specific industry certifications relevant to your sector. Conducting an audit of the supplier’s manufacturing processes can also be beneficial. Additionally, consider requesting sample units for testing prior to placing large orders, which can help confirm the quality and performance of the products. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing speed reducers?
Logistics can be complex when importing speed reducers. Key considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties applicable in your country. Work closely with your supplier to understand the shipping terms (Incoterms) and ensure that they handle necessary paperwork for customs clearance. It’s also wise to engage a reliable freight forwarder familiar with handling industrial equipment to avoid delays. -
How can disputes be resolved if issues arise with my order?
Dispute resolution can often be addressed through clear contractual terms established before the transaction. Ensure that your contract includes provisions for handling disputes, such as mediation or arbitration processes. Maintain open communication with your supplier to resolve issues amicably. If necessary, involve a third-party mediator to facilitate discussions. Document all communications and agreements to support your position during disputes. -
What payment methods are commonly accepted for international orders of speed reducers?
Common payment methods for international orders include wire transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal. Wire transfers are widely accepted but ensure that you are using secure banking channels. Letters of credit provide a level of security for both parties, as they guarantee payment upon meeting specified conditions. Discuss payment terms with your supplier early in negotiations to establish trust and prevent misunderstandings. -
How do I evaluate the long-term reliability of speed reducers?
To evaluate long-term reliability, consider the manufacturer’s track record and warranty offerings. Reliable suppliers typically provide extensive warranties that cover defects and performance issues. Additionally, look for products that have undergone rigorous testing and have certifications indicating durability. Engaging in post-purchase support, including maintenance services and availability of spare parts, can also enhance the reliability of your speed reducer over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for speed reducers
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of speed reducers is essential for international B2B buyers to enhance operational efficiency and ensure competitive advantage. As the speed reducers market is projected to grow significantly, understanding the industrial chain—from raw material sourcing to final distribution—empowers buyers to make informed decisions.
Key takeaways for buyers include the importance of evaluating suppliers based on their technological capabilities, product reliability, and support services. Emphasizing the right specifications such as torque requirements and gear ratios tailored to specific applications will facilitate the selection of the most appropriate speed reducer. Additionally, fostering relationships with reputable manufacturers and distributors can lead to more favorable terms and enhanced product performance.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage this growth by proactively sourcing quality speed reducers. This strategic approach will not only optimize machinery performance but also drive long-term business success. Take action today: assess your current suppliers, explore new partnerships, and invest in high-quality speed reducers that meet your operational needs.