Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Spin Forming
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for spin forming
In an era where precision and efficiency are paramount, spin forming has emerged as a transformative manufacturing technique, particularly in the production of complex, high-quality components. This innovative process enables manufacturers to create intricate shapes from metal sheets, offering unparalleled advantages in terms of material utilization and structural integrity. For international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding spin forming is essential for sourcing competitive, high-performance products.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of spin forming, covering critical aspects such as types of spin forming processes, suitable materials, and essential manufacturing and quality control practices. We will also explore a curated list of reputable suppliers, offering insights into cost structures and market dynamics. By addressing frequently asked questions, this resource aims to demystify the spin forming landscape, equipping buyers with the knowledge they need to make informed sourcing decisions.
As the global market continues to evolve, understanding the nuances of spin forming is not just beneficial—it’s crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Whether you’re a buyer in the bustling markets of South America or navigating the established industries of Europe, this guide will empower you to leverage spin forming effectively, ensuring your projects are not only successful but also economically viable.
Understanding spin forming Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Spin | Utilizes a rotating workpiece and a stationary tool. | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Pros: Cost-effective, suitable for large parts. Cons: Limited to simpler geometries. |
| Differential Spin | Employs a variable speed for different zones of the workpiece. | High-performance aerospace, medical devices | Pros: Enhanced control, complex shapes possible. Cons: Higher setup complexity and cost. |
| Hydroforming Spin | Combines spin forming with hydraulic pressure. | Custom automotive parts, artistic metalworks | Pros: Excellent surface finish, intricate designs. Cons: Equipment cost and maintenance can be high. |
| Magnetic Spin | Uses magnetic forces to shape the workpiece. | Precision engineering, electronic housings | Pros: Non-contact method, ideal for delicate materials. Cons: Limited to specific materials and sizes. |
| Thermal Spin | Incorporates heat to facilitate forming. | Aerospace, energy sectors | Pros: Allows for complex shapes and materials. Cons: Energy-intensive and requires specialized equipment. |
Conventional Spin
Conventional spin forming is characterized by a rotating workpiece that is shaped by a stationary tool. This method is widely used in the production of large, symmetrical parts such as aerospace components and automotive parts. B2B buyers should consider this technique for its cost-effectiveness, especially for bulk production. However, it is essential to note that the geometry it can achieve is relatively simple, making it less suitable for intricate designs.
Differential Spin
Differential spin forming utilizes variable speeds across different zones of the workpiece, allowing for greater control and the ability to create complex shapes. This method is particularly beneficial for high-performance applications, such as in the aerospace and medical device industries. Buyers should weigh the advantages of enhanced control and design flexibility against the higher costs and complexity associated with setup and operation.
Hydroforming Spin
Hydroforming spin combines traditional spin forming with hydraulic pressure, enabling the creation of parts with excellent surface finishes and intricate designs. This method is ideal for custom automotive parts and artistic metalworks. B2B buyers should consider hydroforming for projects that require high precision and aesthetic quality. However, the initial investment in equipment can be significant, and ongoing maintenance costs should also be factored in.
Magnetic Spin
Magnetic spin forming employs magnetic forces to shape the workpiece without direct contact. This technique is particularly suited for precision engineering applications, such as electronic housings. The non-contact nature of this method allows for the manipulation of delicate materials, which is a significant advantage for buyers. However, it is important to note that the method is limited to specific materials and geometries, which may restrict its applicability for some projects.
Thermal Spin
Thermal spin forming integrates heat into the process to facilitate the shaping of materials, making it suitable for industries like aerospace and energy. This method enables the creation of complex shapes and can accommodate a variety of materials. B2B buyers should consider thermal spin for its versatility and ability to produce high-quality components. However, it is energy-intensive and requires specialized equipment, which can lead to higher operational costs.
Related Video: 10 Mental Models Explained
Key Industrial Applications of spin forming
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of spin forming | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of complex aerospace components | High strength-to-weight ratio, reduced material waste | Certification compliance, precision tolerances, and lead times |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of vehicle parts | Cost-effective production of lightweight components | Material selection, tooling costs, and scalability |
| Energy | Creation of turbine casings | Enhanced durability and performance in harsh environments | Supplier reliability, material certifications, and delivery times |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of custom prosthetics | Tailored solutions for patient-specific needs | Regulatory compliance, biocompatibility of materials, and customization capabilities |
| Consumer Electronics | Enclosures for electronic devices | Aesthetic appeal and protection for sensitive components | Design flexibility, surface finish requirements, and integration with other manufacturing processes |
Aerospace Applications
In the aerospace industry, spin forming is crucial for producing complex components such as fuselage sections and engine casings. This method allows manufacturers to create parts with a high strength-to-weight ratio, which is essential for fuel efficiency and performance. B2B buyers in this sector must ensure that suppliers meet stringent certification requirements and possess the capability to deliver parts that adhere to precise tolerances. Additionally, lead times can significantly impact production schedules, making reliable sourcing essential.
Automotive Applications
Spin forming is widely utilized in the automotive sector for the manufacture of lightweight vehicle parts, such as wheel rims and structural components. This method offers a cost-effective solution for producing high-quality parts while minimizing material waste. Buyers in this industry should focus on sourcing suppliers that can provide appropriate material selections, understand tooling costs, and demonstrate scalability for mass production. The ability to adapt designs quickly can also be a competitive advantage.
Energy Applications
In the energy sector, spin forming is employed to create turbine casings and components that must withstand extreme conditions. The durability and performance of these parts are critical for efficiency and safety in power generation. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with a proven track record of reliability, as well as those who can provide materials that meet necessary certifications. Delivery times are also a crucial factor, as delays can impact project timelines.
Medical Device Applications
The medical device industry benefits from spin forming through the fabrication of custom prosthetics and surgical instruments. This application allows for tailored solutions that meet specific patient needs, enhancing both functionality and comfort. Buyers must consider regulatory compliance, particularly regarding biocompatibility of materials used in medical applications. Additionally, the ability to customize designs and produce small batches efficiently is vital for meeting diverse patient requirements.
Consumer Electronics Applications
In the consumer electronics sector, spin forming is used to create enclosures for devices, providing both aesthetic appeal and protection for sensitive components. This application enables manufacturers to achieve intricate designs while maintaining structural integrity. B2B buyers should look for suppliers that offer design flexibility, high-quality surface finishes, and the ability to integrate spin forming with other manufacturing processes. Ensuring compatibility with existing production lines can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
Related Video: Forming Sheet Metal & Metal Forming Tools – Uses Explained By Gene Winfield at SEMA
Strategic Material Selection Guide for spin forming
When selecting materials for spin forming, it’s essential to consider various factors that impact the final product’s performance, durability, and cost. Below is an analysis of several common materials used in spin forming, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum Alloys
Key Properties:
Aluminum alloys are lightweight yet strong, with excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity. They typically have a temperature rating up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressure.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is favored for its low density, making it ideal for applications where weight is a concern. However, its cost can be higher than other metals, and it may not perform as well under extreme conditions. Manufacturing complexity can vary based on the alloy used, with some requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum’s compatibility with various media, including water and mild chemicals, makes it suitable for automotive and aerospace components. However, it may not be the best choice for highly corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider compliance with local standards like ASTM and EN. Additionally, sourcing aluminum from regions with sustainable practices can enhance corporate responsibility.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C). It is also non-reactive, making it suitable for food and medical applications.
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel is highly durable and versatile, it is generally more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to work with due to its toughness. The manufacturing process may require advanced tooling and techniques.
Impact on Application:
Its resistance to corrosion and extreme temperatures makes stainless steel ideal for applications in the chemical and food industries. However, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where lightweight materials are preferred.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards such as ISO and ASTM is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific grades of stainless steel in their region, as this can affect lead times and costs.
Copper Alloys
Key Properties:
Copper alloys exhibit excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, along with good corrosion resistance. They can handle temperatures up to 300°C and are often used in applications requiring thermal management.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of copper alloys is their conductivity, making them ideal for electrical components. However, they tend to be more expensive than aluminum and can be less durable in mechanical applications.
Impact on Application:
Copper’s compatibility with various fluids and gases makes it suitable for heat exchangers and electrical connectors. However, it may not be suitable for environments with harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for copper alloys across regions. In Europe, for example, compliance with EN standards is critical, while in South America and Africa, local regulations may differ.
Titanium Alloys
Key Properties:
Titanium alloys are renowned for their high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 600°C. They are particularly useful in aerospace and biomedical applications.
Pros & Cons:
The major advantage of titanium is its durability and performance in extreme environments. However, it is one of the most expensive materials, and the manufacturing process is complex, often requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Titanium’s biocompatibility makes it suitable for medical implants, while its strength is beneficial in aerospace applications. However, its cost can be prohibitive for some projects.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should ensure compliance with stringent aerospace and medical standards, such as ASTM F136 for medical applications. Understanding the supply chain for titanium in their region can also help mitigate costs.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for spin forming | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Higher cost than other metals | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical and food processing | High strength and corrosion resistance | More expensive and complex to work with | High |
| Copper Alloys | Electrical connectors and heat exchangers | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost and less durable | High |
| Titanium Alloys | Aerospace and biomedical applications | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | Very high cost and complex manufacturing | High |
By understanding the properties and implications of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for spin forming
Overview of Spin Forming Manufacturing Processes
Spin forming is a specialized metal forming technique that allows for the creation of complex shapes with high precision, often used for producing components in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. Understanding the manufacturing process and quality assurance practices is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as they navigate supplier selection and product quality.
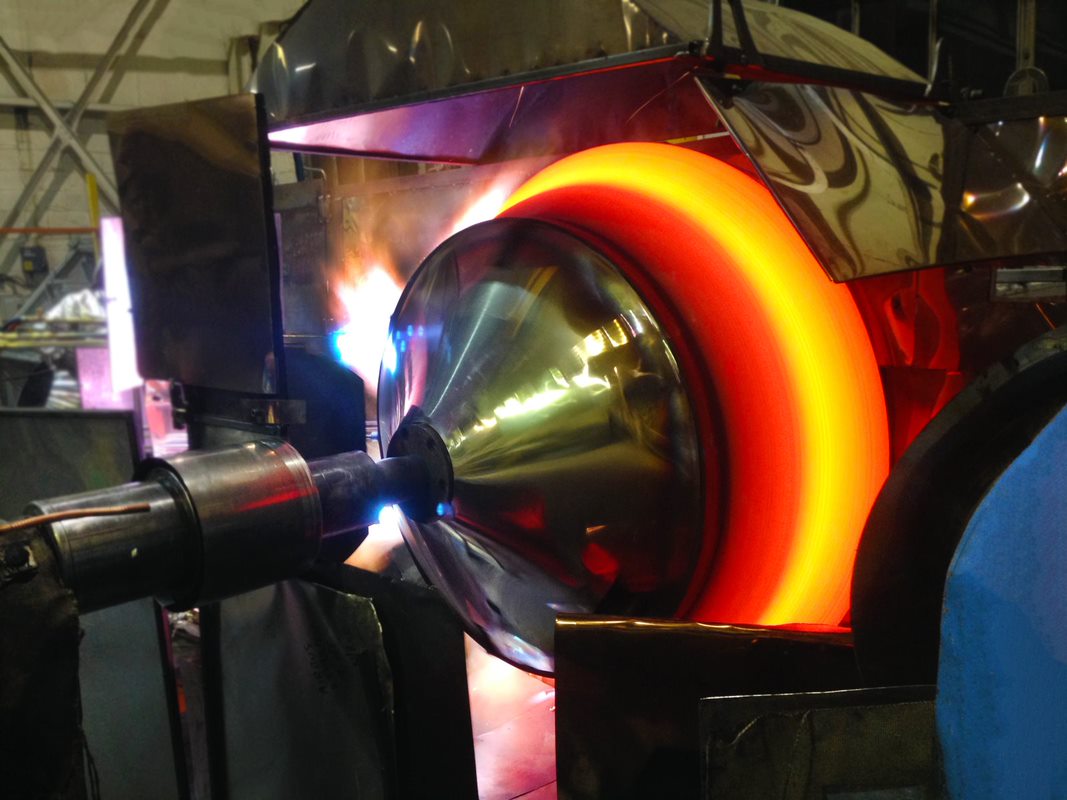
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Stages of the Manufacturing Process
-
Material Preparation
– The first stage involves selecting the appropriate material, typically metals such as aluminum, copper, or stainless steel, based on the desired properties of the final product.
– Materials are then cut to size, often in sheet or disc form, and any necessary surface treatments (like cleaning or coating) are applied to ensure optimal adhesion and formability during the spin forming process. -
Forming
– Spinning Process: The material is mounted on a lathe and rotated at high speeds. A forming tool applies pressure to the material, shaping it against a mandrel or die.
– Techniques: Common techniques include:- Conical Spinning: For creating conical shapes.
- Radial Spinning: For cylindrical shapes where material is pushed radially outward.
- Axial Spinning: For generating more complex profiles.
- The forming stage requires careful control of speed, pressure, and tool geometry to achieve the desired thickness and shape.
-
Assembly
– After forming, components may need to be assembled with other parts, which could involve welding, riveting, or fastening.
– This stage must be conducted with precision to ensure the integrity and performance of the final product. -
Finishing
– The final stage involves surface finishing processes like polishing, anodizing, or coating to enhance aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance.
– Quality of finish is critical, especially for industries requiring high standards, such as aerospace.
Quality Assurance in Spin Forming
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in spin forming to ensure that products meet international standards and customer specifications. The following sections outline relevant standards, checkpoints, testing methods, and strategies for B2B buyers to verify supplier compliance.
International Standards and Certifications
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for manufacturers to demonstrate their commitment to quality assurance. Suppliers certified under ISO 9001 have established processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For buyers in the oil and gas sector, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards provide guidelines specific to products used in these industries.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival. This includes verifying material specifications and checking for defects.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to monitor parameters such as thickness, shape, and dimensions. This step helps catch issues early, reducing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are finished, a comprehensive inspection is performed. This includes functional testing, dimensional checks, and surface quality assessments.
Common Testing Methods
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools like calipers and gauges to ensure products meet precise specifications.
- Material Testing: Techniques such as tensile testing and hardness testing are employed to verify the mechanical properties of the materials used.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal defects without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to robust quality control measures. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities can provide insight into their quality management practices. Look for documentation of processes and adherence to international standards.
-
Request Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports and compliance certificates. These documents are crucial for validating their quality claims.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly valuable when sourcing from regions where buyers may have less familiarity with local practices.
-
Understand QC/CERT Nuances: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality certifications. For instance, while CE marking is mandatory in Europe, buyers in Africa or South America might prioritize different certifications based on local regulations. Familiarizing yourself with these nuances can enhance supplier negotiations and product quality assurance.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in spin forming play a critical role in ensuring that international B2B buyers receive high-quality products. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. This due diligence is essential for maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring compliance with industry standards across different markets.
Related Video: Business English Vocabulary : VV 47 – Manufacturing & Production Process (1) | English Vocabulary
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for spin forming Sourcing
Understanding Cost Components in Spin Forming
When sourcing spin forming services, it’s essential to grasp the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of raw materials directly affect costs. Common materials used in spin forming include aluminum, steel, and titanium. Prices can vary significantly based on market demand and availability, which is crucial for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where material sourcing may involve additional logistics.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for precision in spin forming operations. Labor costs can fluctuate depending on the supplier’s location. For instance, labor rates in Eastern Europe may be lower than in Western Europe, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and other indirect costs associated with production. Efficient operations can minimize overhead, but buyers should inquire about how these costs are factored into pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, especially for unique designs. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has existing tooling or if new tools need to be created, as this can drastically influence initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability but can increase manufacturing costs. Buyers should assess the supplier’s QC measures and certifications, as these can affect pricing and product quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on distance and the chosen Incoterms. Understanding these logistics costs is vital for international buyers to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their costs. This margin can vary widely, influenced by the supplier’s market positioning and competition.
Price Influencers in Spin Forming
Several factors can influence the pricing of spin forming services:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) significantly impacts pricing. Larger volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs to negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized parts require more complex processes, which can increase costs. Buyers should be clear about their specifications to avoid miscommunication and unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: The quality of materials used and any relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100) can affect pricing. Suppliers with higher certification standards may charge more but offer better quality assurance.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a proven track record may command higher prices due to their reliability and quality. It’s essential to balance supplier reputation with cost.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can help buyers calculate total costs accurately.
Tips for B2B Buyers
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing volume and long-term potential to negotiate better pricing. Establishing a relationship with the supplier can also lead to favorable terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes all costs associated with purchasing, including maintenance and logistics. This holistic view can lead to better decision-making.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: For buyers from diverse regions, it’s crucial to be aware of local market conditions and currency fluctuations that may impact costs. Engage with local experts or consultants to navigate these complexities.
-
Evaluate Supplier Capabilities: Before finalizing a supplier, assess their production capabilities and quality assurance processes. This evaluation can mitigate risks associated with quality and delivery timelines.
-
Monitor Market Trends: Stay informed about material price trends and global supply chain issues, as these can significantly impact costs. Being proactive can help in making timely decisions.
Disclaimer
The pricing insights provided are indicative and can vary based on multiple factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential spin forming Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘spin forming’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for spin forming
Critical Technical Properties of Spin Forming
When considering spin forming for your manufacturing needs, understanding key technical properties is crucial. Here are some essential specifications that influence the quality and performance of spun parts:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific type of metal or alloy used in the spin forming process. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. The choice of material affects the part’s strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. B2B buyers should select a material grade that aligns with the operational environment and functional requirements of the final product. -
Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is a critical dimension that impacts both the strength and weight of the spun part. Variations in wall thickness can lead to inconsistencies in performance and durability. B2B buyers must ensure that the specified wall thickness meets the design requirements while considering the balance between material usage and cost efficiency.
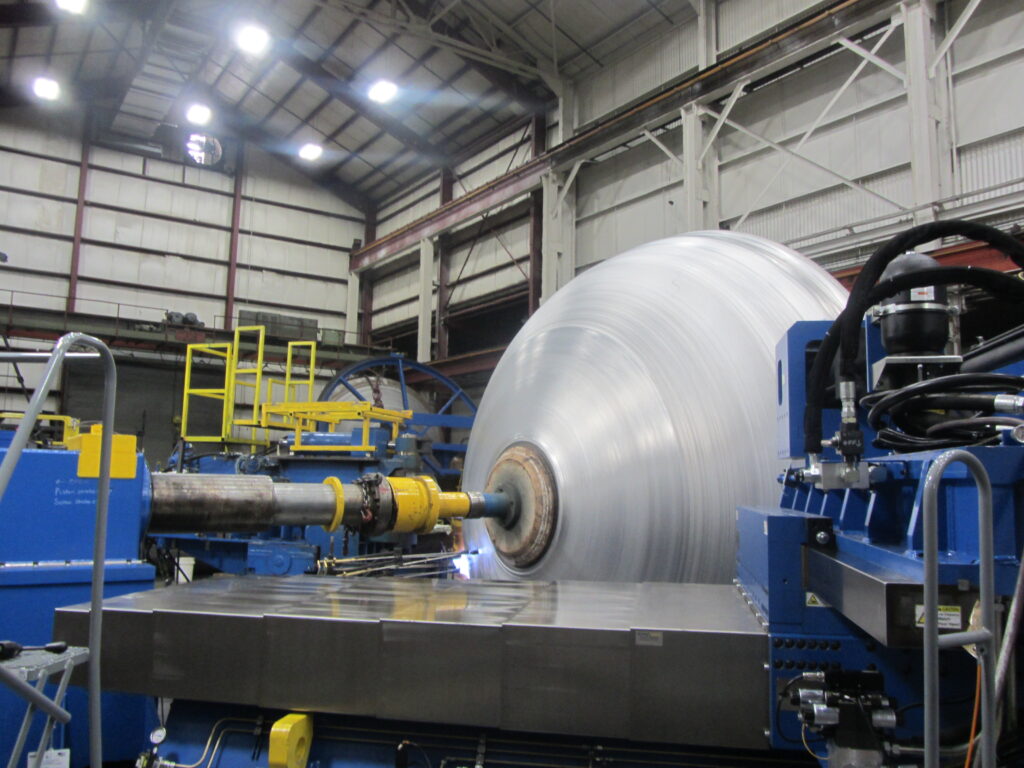

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the acceptable limits of variation in the dimensions of a part. In spin forming, maintaining tight tolerances is essential for ensuring that components fit together properly in assembly. Poor tolerance can lead to increased production costs and rework. Buyers should discuss tolerance requirements with suppliers to ensure they can meet the necessary specifications. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and quality of the part’s surface after forming. A smooth surface finish is often required for aesthetic purposes or to enhance corrosion resistance. Understanding surface finish requirements is vital for B2B buyers, as it can influence both manufacturing costs and the final product’s performance. -
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes can be applied to spun parts to enhance their mechanical properties, such as strength and ductility. Understanding the need for heat treatment can help buyers select the right supplier capable of providing parts that meet specific performance criteria, particularly in demanding applications. -
Forming Radius
The forming radius is the curvature of the part’s edges and is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. A well-defined forming radius can prevent stress concentrations and improve the part’s overall durability. Buyers should ensure that their design specifications include the desired forming radius to avoid complications during production.
Common Trade Terms in Spin Forming
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication with suppliers and understanding contracts. Here are several key terms relevant to spin forming:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that are used in another company’s end product. For buyers, partnering with an OEM can ensure high-quality components that meet specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for B2B buyers to manage inventory costs and production schedules effectively. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their project needs and budget. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, preparing a clear RFQ can lead to better pricing and faster response times, ultimately aiding in project planning and cost management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to manage risks and costs associated with international shipping and logistics. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead time is crucial for project planning, as it affects inventory levels and production schedules. Buyers should communicate their timelines clearly to suppliers to ensure timely deliveries. -
Quality Assurance (QA)
QA refers to the systematic process of ensuring that products meet specified standards before they reach the market. For B2B buyers, understanding QA processes is important to ensure that the parts received meet their quality expectations and regulatory requirements.
By grasping these essential properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing spin-formed products, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the spin forming Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The spin forming sector is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and an increasing demand for lightweight, durable materials across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and energy. In particular, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are capitalizing on these trends to optimize their supply chains and enhance product offerings. Key drivers include the rising demand for customized and complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to achieve efficiently.
Emerging technologies such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC) and automation are revolutionizing the spin forming process, enabling higher precision and reduced lead times. B2B buyers should pay attention to suppliers who leverage these technologies, as they not only enhance product quality but also improve cost efficiency. The integration of Industry 4.0 principles, including IoT and data analytics, is becoming more prevalent, allowing companies to streamline operations and better forecast market needs.
Moreover, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions have prompted buyers to diversify their supplier bases. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in regions such as Europe, where sourcing from nearby countries can mitigate risks associated with longer supply chains. Buyers should consider establishing relationships with local suppliers to enhance agility and responsiveness to market changes.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has emerged as a pivotal concern in the spin forming sector, driven by increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a focus on sustainable practices. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who adopt eco-friendly technologies and practices, such as energy-efficient machinery and waste minimization strategies.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical, as it fosters trust and long-term partnerships. Buyers should seek suppliers who maintain transparency in their supply chains and adhere to fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials in spin forming—such as recycled metals and biodegradable composites—can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of products. Buyers should engage with suppliers who are committed to sustainable material sourcing, as this not only meets regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
Brief Evolution/History
The origins of spin forming can be traced back to ancient metalworking techniques, where artisans shaped metal by spinning it on a lathe. Over the decades, this method evolved significantly with the advent of modern technology, transforming into a highly specialized manufacturing process. By the mid-20th century, spin forming gained traction in industrial applications, particularly in the aerospace and automotive sectors, due to its ability to produce lightweight components with high strength-to-weight ratios.
Today, the spin forming industry continues to innovate, integrating advanced manufacturing technologies and sustainable practices. This evolution not only enhances production capabilities but also aligns with the growing demands of international B2B buyers for quality, efficiency, and sustainability. Understanding this historical context allows buyers to appreciate the potential of spin forming as a competitive advantage in their respective markets.
Related Video: Global trade will never be the same again, says Christine Lagarde | Power & Politics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of spin forming
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for spin forming?
When vetting suppliers for spin forming, prioritize their industry experience, technological capabilities, and production capacity. Review their portfolio to assess the range and complexity of projects they’ve handled. Additionally, check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request references from previous clients to gauge reliability and customer service. Lastly, consider their location and logistics efficiency to ensure timely delivery, especially if sourcing from international markets. -
Can I customize spin-formed products to meet my specific requirements?
Yes, customization is a significant advantage of spin forming. Most suppliers offer tailored solutions, allowing adjustments in dimensions, materials, and finishes to meet your specific application needs. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and any relevant drawings. Be sure to clarify the implications of customization on lead times and costs, as highly specialized products may require additional resources or longer production schedules. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for spin forming?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for spin forming can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the project. Generally, MOQs can range from a few pieces for simple products to several hundred for more intricate designs. Lead times also differ based on the order size and customization level, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s essential to discuss these factors upfront to align expectations with your project timeline and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing spin-formed products?
Payment terms for spin forming can differ among suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits (20-50%) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established clients, especially in Europe. Always clarify the payment structure during negotiations and consider using secure payment methods to mitigate risk. Understanding the currency used in transactions is also crucial, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance in spin forming?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes, including inspection methods and testing protocols. Certifications such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific standards (e.g., AS9100 for aerospace) can indicate a commitment to quality. Consider conducting a factory audit or requesting samples for evaluation before placing a large order. Establishing clear quality expectations in your purchase agreement can also help mitigate risks. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing spin-formed products?
When importing spin-formed products, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and incoterms that define responsibilities and liabilities. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger volumes. Ensure the supplier provides proper documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and packing lists. Familiarize yourself with local import regulations in your country to avoid unexpected delays or costs. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers in international transactions?
To effectively handle disputes, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in writing, including specifications and delivery timelines. If issues arise, attempt to resolve them amicably through direct negotiation. If necessary, refer to the dispute resolution clauses in your contract, which may include mediation or arbitration. Familiarize yourself with international trade laws that may apply, as they can influence your options for resolution. -
What are the best practices for establishing long-term relationships with spin forming suppliers?
Building long-term relationships with spin forming suppliers involves regular communication and feedback. Schedule periodic reviews to discuss performance, quality, and any evolving needs. Demonstrating commitment through repeat business can also foster trust and preferential treatment in negotiations. Participate in joint development projects or collaborative initiatives, as these can enhance mutual understanding and innovation, ultimately benefiting both parties in the partnership.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for spin forming
As the global demand for precision-engineered components continues to rise, the strategic sourcing of spin forming presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers. By leveraging the advantages of spin forming—such as cost-effectiveness, material efficiency, and design flexibility—companies can significantly enhance their competitive edge.
Key Takeaways for Buyers:
– Supplier Diversification: Engaging with suppliers from diverse regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and foster innovation through varied expertise.
– Quality Assurance: Prioritizing suppliers who adhere to international quality standards is essential. This not only ensures product reliability but also builds long-term partnerships based on trust and performance.
– Sustainability Focus: As environmental concerns grow, sourcing from manufacturers who utilize sustainable practices in their spin forming processes can enhance brand reputation and align with global sustainability goals.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for B2B buyers to stay informed about advancements in spin forming technologies and market trends. By actively participating in industry dialogues and exploring new partnerships, buyers can position themselves to capitalize on future opportunities in this evolving landscape. Engage with suppliers today to unlock the full potential of spin forming for your business.