Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Static Eliminator
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for static eliminator
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, the significance of static eliminators cannot be overstated. These devices play a crucial role in mitigating the adverse effects of static electricity, which can lead to operational disruptions such as jams, clogs, and even catastrophic incidents like fires and explosions. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of static eliminators is essential for ensuring efficient production processes and maintaining high-quality standards.
This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for sourcing static eliminators effectively. It covers a wide array of topics including the different types of static eliminators, the materials used in their construction, and best practices in manufacturing and quality control. Furthermore, it provides insights into reputable suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends, enabling buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
By navigating this guide, B2B buyers will be empowered to choose the right static elimination solutions that enhance their operational efficiency and safety. Whether you are based in the bustling industrial hubs of South Africa or Turkey, this guide equips you with the knowledge needed to tackle static-related challenges head-on, ultimately driving productivity and profitability in your operations.
Understanding static eliminator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionizing Bars | Emit ions to neutralize static charges on surfaces. | Printing, packaging, textile industries. | Pros: Effective in high-speed applications. Cons: Requires proper positioning for optimal performance. |
| Blowers | Use ionized air to eliminate static over larger areas. | Food processing, electronics assembly. | Pros: Versatile and covers wide areas. Cons: Can be noisy and require maintenance. |
| Handheld Static Eliminators | Portable devices for localized static elimination. | Electronics, laboratories, maintenance. | Pros: Easy to use and transport. Cons: Limited effectiveness in large environments. |
| Static Eliminator Mats | Grounded mats that dissipate static charges when contacted. | Electronics manufacturing, clean rooms. | Pros: Simple installation and effective in preventing static. Cons: Limited to areas where mats can be used. |
| Static Neutralizing Bars | Designed for specific applications, often with adjustable lengths. | Automated assembly lines, conveyor systems. | Pros: Customizable for various setups. Cons: Installation may require technical expertise. |
Ionizing Bars
Ionizing bars are a widely used static eliminator type that emit ions to neutralize static charges on surfaces. They are particularly effective in fast-paced environments such as printing and packaging, where static can disrupt operations. When considering ionizing bars, B2B buyers should focus on the specific positioning and installation requirements, as the effectiveness can vary significantly based on proximity to the material being treated.
Blowers
Static eliminator blowers utilize ionized air to eliminate static charges over larger areas, making them ideal for industries like food processing and electronics assembly. They offer versatility in application but may produce noise and require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Buyers should evaluate the operational environment to determine if the noise level is acceptable and whether the blowers can be easily integrated into existing workflows.
Handheld Static Eliminators
These portable devices are designed for localized static elimination, providing flexibility for use in various settings, including electronics and laboratory environments. Handheld static eliminators are easy to transport and operate, making them ideal for maintenance tasks. However, their effectiveness is limited in larger environments, so buyers should assess the scale of their needs before investing in these devices.
Static Eliminator Mats
Static eliminator mats are grounded surfaces that dissipate static charges upon contact, commonly used in electronics manufacturing and clean room environments. They are relatively simple to install and highly effective in preventing static buildup. However, their usage is limited to areas where mats can be laid down, necessitating consideration of the layout of workspaces and the potential need for multiple mats.
Static Neutralizing Bars
Static neutralizing bars are tailored for specific applications and often come with adjustable lengths to fit various setups, making them suitable for automated assembly lines and conveyor systems. They can effectively neutralize static in dynamic environments but may require technical expertise for installation. Buyers should consider the compatibility of these bars with their existing machinery and the skill level of their installation team.
Key Industrial Applications of static eliminator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Static Eliminator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Use in packaging lines to prevent static cling on films | Reduces jams and misfeeds, improving production efficiency | Ensure compatibility with different materials and line speeds |
| Textiles | Installation in textile manufacturing to eliminate static | Prevents fabric sticking and contamination, enhancing quality | Consider the operational environment and maintenance needs |
| Electronics | Application in electronics assembly to control ESD | Protects sensitive components, reducing defects and returns | Verify ESD protection ratings and installation ease |
| Food Processing | Utilization in food packaging to avoid static cling | Ensures smooth product flow, reducing waste and downtime | Look for hygiene compliance and ease of cleaning |
| Printing | Deployment in printing processes to manage paper static | Improves print quality and reduces paper jams | Assess integration with existing machinery and power supply |
Packaging Industry
In the packaging sector, static eliminators are crucial for ensuring smooth operation in packaging lines, particularly with plastic films. Static cling can lead to jams and misfeeds, significantly slowing down production. By strategically positioning static eliminators near the packaging machinery, businesses can maintain a steady flow of materials, thus enhancing overall productivity. Buyers should focus on sourcing static eliminators that are compatible with various packaging materials and can withstand the operational speeds of their specific lines.
Textiles Industry
Static electricity in textile manufacturing can cause fabrics to stick together, leading to production inefficiencies and contamination issues. The installation of static eliminators helps to neutralize the static charge, ensuring that fabrics move smoothly through processing equipment without clumping. For international buyers, it’s essential to consider the operational environment, including humidity levels, as these can affect the performance of static eliminators. Regular maintenance and accessibility for cleaning should also be factored into sourcing decisions.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics sector, static eliminators are vital for controlling electrostatic discharge (ESD) during assembly processes. ESD can damage sensitive components, resulting in costly defects and returns. By integrating static eliminators into the assembly line, companies can protect their products and maintain quality control. Buyers should ensure that the static eliminators they source have appropriate ESD protection ratings and are easy to install within existing systems, especially in diverse international markets.
Food Processing Industry
Static cling can pose significant challenges in food packaging, leading to product sticking and inefficient flow. The application of static eliminators in food processing helps maintain a smooth operation, reducing waste and minimizing downtime. For buyers in this sector, it is crucial to ensure that the static eliminators meet hygiene standards and are easy to clean, particularly in regions with strict food safety regulations. This consideration is vital to maintain compliance and protect product integrity.
Printing Industry
In the printing industry, static electricity can result in paper jams and poor print quality. Deploying static eliminators in printing processes helps manage static levels, ensuring that paper feeds smoothly and consistently. This not only improves the quality of the final product but also reduces downtime associated with equipment malfunctions. When sourcing static eliminators, buyers should evaluate how well these devices can be integrated into existing machinery and consider the power supply requirements to ensure seamless operation.
Related Video: 1250 – Powerful, marketing leading Static Eliminator for industrial applications
Strategic Material Selection Guide for static eliminator
When selecting materials for static eliminators, it is crucial to consider how different materials will affect performance, durability, and compatibility with various applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in static eliminators, offering insights tailored for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making it suitable for various industrial environments. It typically withstands temperatures up to 800°F (427°C) and has a high tensile strength.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is one of its main advantages, providing a long lifespan even in harsh conditions. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, which may impact budget constraints. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it requires specialized tools for cutting and shaping.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including chemicals and moisture, making it ideal for environments where static charge can lead to contamination or safety hazards.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for material specifications. In regions like South Africa and Turkey, it’s essential to consider local sourcing options to minimize costs and lead times.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum offers a good balance of strength and weight, with a melting point around 1,220°F (660°C). It is also resistant to corrosion, particularly when anodized.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is generally more cost-effective than stainless steel and easier to machine, which simplifies manufacturing processes. However, it may not be as durable under extreme conditions, and its lower strength compared to stainless steel can limit its applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight is a concern, such as portable static eliminators. It performs well in environments with moderate temperatures and humidity.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in South America and the Middle East should consider the availability of aluminum and its compliance with local regulations. Understanding the differences in alloy grades can also impact performance and cost.
3. Polycarbonate
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is a high-performance plastic known for its impact resistance and lightweight properties. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 270°F (132°C).
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its resistance to shattering, making it ideal for environments where safety is a concern. However, it may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals, and its long-term durability can be affected by UV exposure.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is suitable for static eliminators used in cleanroom environments or where visibility is essential. Its non-conductive nature prevents accidental shocks to operators.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with safety standards like JIS and ASTM. In Europe, understanding the REACH regulations regarding materials is crucial for compliance.
4. Conductive Rubber
Key Properties:
Conductive rubber combines the flexibility of rubber with conductive properties, allowing it to dissipate static charges effectively. It operates well within a temperature range of -40°F to 200°F (-40°C to 93°C).
Pros & Cons:
The flexibility of conductive rubber allows for easy installation and adaptability to various shapes. However, its durability may be lower than metals, and it can be more expensive than traditional rubber materials.
Impact on Application:
Conductive rubber is particularly effective in applications where flexibility is needed, such as in conveyor systems or areas with dynamic movement.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Understanding the specific conductivity requirements for different applications is essential. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should also consider local suppliers who can provide compliant products efficiently.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for static eliminator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Industrial static eliminators | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to other materials | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight static eliminators | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Lower durability under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Cleanroom applications | Impact-resistant and lightweight | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Conductive Rubber | Conveyor systems | Flexible and easy to install | Lower durability than metals | Medium |
This guide provides actionable insights for B2B buyers, ensuring they can make informed decisions based on material properties, application needs, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for static eliminator
The manufacturing process and quality assurance of static eliminators are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in various industrial applications. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can help in making informed purchasing decisions. Below is a detailed overview of the typical manufacturing stages, quality assurance protocols, and verification methods.
Manufacturing Process
Material Preparation
The initial stage involves selecting high-quality materials that exhibit excellent electrical conductivity and durability. Common materials used include:
– Conductive metals (e.g., copper, aluminum) for the ionizing elements.
– Insulating plastics (e.g., polycarbonate) for the casing to prevent electrical hazards.
– High-voltage cables with metal braiding for safety and performance.
Materials undergo rigorous testing for purity and electrical properties before being approved for use. This step ensures that the final product meets the required performance specifications.
Forming
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This includes:
– Machining: Components such as ionizing bars are precisely machined to achieve the required dimensions and tolerances.
– Molding: For plastic parts, injection molding techniques are employed to create durable and lightweight casings.
Advanced techniques such as CNC machining may be used to enhance precision, which is critical in ensuring that ionizing points are correctly positioned for maximum effectiveness.
Assembly
During assembly, components are brought together in a controlled environment to minimize contamination. This stage involves:
– Integration of ionizing elements with the power supply units.
– Wiring: High-voltage cables are securely connected to ensure that they are properly shielded and grounded.
– Testing: Initial functional tests are performed to ensure that all components work together as intended.
Proper grounding techniques are emphasized to prevent electrical shocks and to ensure operational safety.
Finishing
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the product’s durability and aesthetics. This includes:
– Coating: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear.
– Labeling: Marking products with necessary safety and operational information.
Final inspections are conducted to ensure that the product meets design specifications and is free from defects.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance for static eliminators is governed by international standards and industry-specific regulations to ensure product reliability and safety.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is essential for manufacturers looking to demonstrate consistent quality.
- CE Marking: This indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for manufacturers supplying to the oil and gas industry, ensuring that products meet specific safety and quality requirements.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous checks during the manufacturing process to detect any deviations from quality standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product to ensure it meets all specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods used in the quality assurance of static eliminators include:
– Electrical Testing: Measuring the ionization effectiveness and ensuring that electrical safety standards are met.
– Mechanical Testing: Assessing the durability of materials under stress and environmental conditions.
– Performance Testing: Evaluating the static elimination efficiency under various operational conditions.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are some effective methods:
Audits
Conducting supplier audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards. Regular audits can identify potential risks and areas for improvement.
Quality Reports
Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their quality assurance processes, including the results of testing and compliance with standards.
Third-Party Inspection
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality. This is especially beneficial for buyers unfamiliar with local manufacturing practices.
QC/Cert Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances when dealing with quality control and certifications:
– Regional Standards: Different regions may have unique standards and regulations. Familiarity with these can enhance compliance and market access.
– Cultural Considerations: Understanding local practices and expectations can facilitate smoother supplier relationships and negotiations.
– Documentation: Ensure that all necessary certifications and quality reports are properly documented and verifiable.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols of static eliminators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements. This knowledge not only helps in selecting the right products but also fosters stronger supplier partnerships, ultimately leading to improved business outcomes.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing – Lean Factory Tour – FastCap
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for static eliminator Sourcing
Cost Structure of Static Eliminators
When sourcing static eliminators, international B2B buyers must consider a comprehensive cost structure that includes several key components:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in static eliminators include conductive materials, plastics, and electronic components. The choice of materials can significantly affect both performance and price. High-quality, durable materials may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to lower long-term maintenance expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the overall pricing of static eliminators. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, manufacturers may charge more. Conversely, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs may provide opportunities for savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with production facilities, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, allowing suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific static eliminator designs can be a significant initial investment. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs, particularly for customized solutions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure that the products meet industry standards and specifications, which can add to the overall cost. However, investing in quality assurance can prevent costly failures and downtime in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the origin and destination of the products. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties should be carefully evaluated.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and generate profit. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can aid in negotiations.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of static eliminators:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs and consider purchasing larger quantities to benefit from volume discounts.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized static eliminators designed for specific applications will generally incur higher costs. Buyers must weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Higher-quality materials typically lead to better performance and longevity but come with a higher price tag.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific industry certifications may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and safety. Buyers should verify certifications relevant to their industry.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might provide competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (Incoterms) can affect the overall cost. Buyers should be aware of who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs clearance to avoid unexpected expenses.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Buyers should approach negotiations with a clear understanding of their needs and market prices. Leverage quotes from multiple suppliers to drive down costs.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. A cheaper static eliminator may lead to higher long-term costs if it requires frequent replacements or repairs.
-
Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the operational costs associated with the static eliminators. This includes energy consumption and maintenance requirements.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider currency fluctuations and potential tariffs. Understanding the local market conditions can provide additional leverage in negotiations.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: It’s essential to recognize that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, raw material costs, and geopolitical factors. Always seek updated quotes and clarify the terms before finalizing any agreements.
By understanding these components and strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints when sourcing static eliminators.
Spotlight on Potential static eliminator Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘static eliminator’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for static eliminator
Key Technical Properties of Static Eliminators
Understanding the essential technical properties of static eliminators is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when selecting equipment that minimizes static-related issues in manufacturing processes. Here are the critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The grade of materials used in static eliminators, typically high-quality plastics and metals that resist wear and corrosion.
– Importance: High-grade materials ensure durability and longevity, reducing replacement costs and downtime, which is vital for maintaining production efficiency. -
Operating Distance
– Definition: The effective range within which a static eliminator can neutralize static charges, usually specified in inches.
– Importance: Knowing the optimal operating distance (typically ½ inch to 1 ½ inches) helps in the correct installation of the device, ensuring maximum effectiveness and minimizing operational issues. -
Ionization Efficiency
– Definition: A measure of how effectively a static eliminator can neutralize static charges, often expressed as a percentage.
– Importance: Higher ionization efficiency translates to faster static neutralization, which is essential in high-speed manufacturing environments to prevent jams and mis-feeds. -
Power Supply Specifications
– Definition: Specifications related to the voltage and current requirements of the static eliminator’s power supply.
– Importance: Ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems is critical for safe operation and avoiding electrical hazards. Proper grounding of the power supply is also essential for effective performance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Mounting Options
– Definition: The available methods for securely attaching the static eliminator to machinery, which may include clamps or brackets.
– Importance: Versatile mounting options allow for easier integration into existing systems, facilitating prompt installation and adjustment as needed. -
Environmental Tolerance
– Definition: The operational limits regarding temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants.
– Importance: Understanding these limits helps in selecting static eliminators suited for specific industrial environments, ensuring reliability and consistent performance.
Common Trade Terminology in Static Eliminator Procurement
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms related to static eliminators:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces components or products that are used in another company’s end product.
– Importance: Identifying reputable OEMs ensures high-quality components, which is critical for performance and reliability in static elimination systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ helps buyers gauge purchase feasibility and manage inventory levels, particularly for large-scale operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services.
– Importance: Sending RFQs allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, leading to better purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms aids in understanding shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, which is essential for smooth international trade. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Importance: Knowing lead times helps businesses plan production schedules and manage inventory effectively, reducing the risk of operational delays. -
Warranty
– Definition: A guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the product and the terms for repair or replacement.
– Importance: A solid warranty provides assurance of quality and reliability, which is critical for minimizing future maintenance costs and operational disruptions.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and minimize risks associated with static electricity in manufacturing processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the static eliminator Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The static eliminator market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for operational efficiency across various manufacturing sectors. Industries such as packaging, textiles, and electronics are particularly affected by static-related challenges, including jams, mis-feeds, and contamination. As production processes become more automated, the demand for effective static control solutions has surged, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Current trends indicate a shift towards smart technology integration in static eliminators. Companies are increasingly adopting IoT-enabled devices that allow for real-time monitoring and remote management, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Additionally, there is a growing preference for air-assisted static eliminators, which offer greater effectiveness in neutralizing static charges across a wider range of materials. Buyers are also prioritizing customization to address specific industry needs, which is driving manufacturers to offer tailored solutions.
International B2B buyers should be aware of the regional market dynamics. For example, in Africa and South America, the focus is on cost-effective solutions, while in Europe and the Middle East, buyers are more inclined towards high-quality, advanced technology products. Understanding these dynamics can help buyers make informed sourcing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the static eliminator sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and material waste, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through eco-friendly practices and materials.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are urged to evaluate their suppliers’ sourcing practices, ensuring that they adhere to ethical labor standards and environmental regulations. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for responsible business practices.
Buyers should also consider green certifications when sourcing static eliminators. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) indicate that a manufacturer is committed to reducing its environmental footprint. Additionally, the use of recyclable materials in the production of static eliminators is becoming a key differentiator in the market, appealing to environmentally-conscious buyers.
Brief Evolution/History
The development of static eliminators has evolved significantly since their inception. Initially, these devices were rudimentary and primarily mechanical. Over the decades, technological advancements have led to the introduction of ionizing bars and high-frequency generators, which provide more efficient and effective static control solutions. The shift towards electronic and smart technologies in recent years has further transformed the industry, making static eliminators indispensable in modern manufacturing processes. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers to understand the technological advancements and their implications for operational efficiency in their respective industries.
In conclusion, as the static eliminator market continues to evolve, international B2B buyers must remain vigilant about market dynamics, prioritize sustainability, and leverage historical insights to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational and ethical standards.
Related Video: Global trade will never be the same again, says Christine Lagarde | Power & Politics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of static eliminator
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of static eliminators?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience and reputation. Check for certifications relevant to your region, such as ISO standards, which indicate quality assurance. Request references from previous clients in similar industries, and verify their track record for on-time delivery and customer service. It’s also beneficial to assess their capacity for customization, as your specific operational needs may require tailored solutions. -
Can static eliminators be customized for my specific application?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific application needs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers, including dimensions, ionization types, and power supply specifications. A reputable supplier will work with you to create a solution that effectively addresses your unique challenges, such as material types and operational environments. Ensure that any custom features are documented in your agreement. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for static eliminators?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Common MOQs range from 10 to 50 units. Lead times typically range from 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the level of customization and the supplier’s production capacity. Always confirm these details upfront to avoid delays in your operations. For larger orders, negotiate better terms, including potential discounts or improved lead times. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing static eliminators?
Payment terms can differ between suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipment. For larger orders, consider negotiating payment terms that may include a letter of credit or installment payments. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly stated in the contract to avoid misunderstandings later on. Additionally, verify if the supplier accepts various payment methods that suit your financial processes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for static eliminators?
Request documentation of quality assurance processes and certifications relevant to your industry. Look for certifications such as CE marking in Europe or UL certification in the United States. Ask suppliers about their quality control measures, including testing procedures for performance and safety. Establish clear quality expectations in your contract and consider conducting factory audits, especially if sourcing from international suppliers. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing static eliminators?
When importing static eliminators, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential duties. Choose a logistics partner familiar with your region’s import regulations to streamline the process. Ensure that your supplier provides accurate shipping documentation and product classifications to avoid customs delays. Additionally, factor in lead times for shipping, as international transport can add several weeks to your timeline. -
How should I handle disputes with a supplier regarding static eliminators?
Establish clear communication channels and escalation procedures in your contract. If a dispute arises, document all correspondence and maintain records of agreements. Attempt to resolve issues amicably through negotiation first. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as stipulated in your contract. Ensure that you understand the legal framework governing the agreement, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
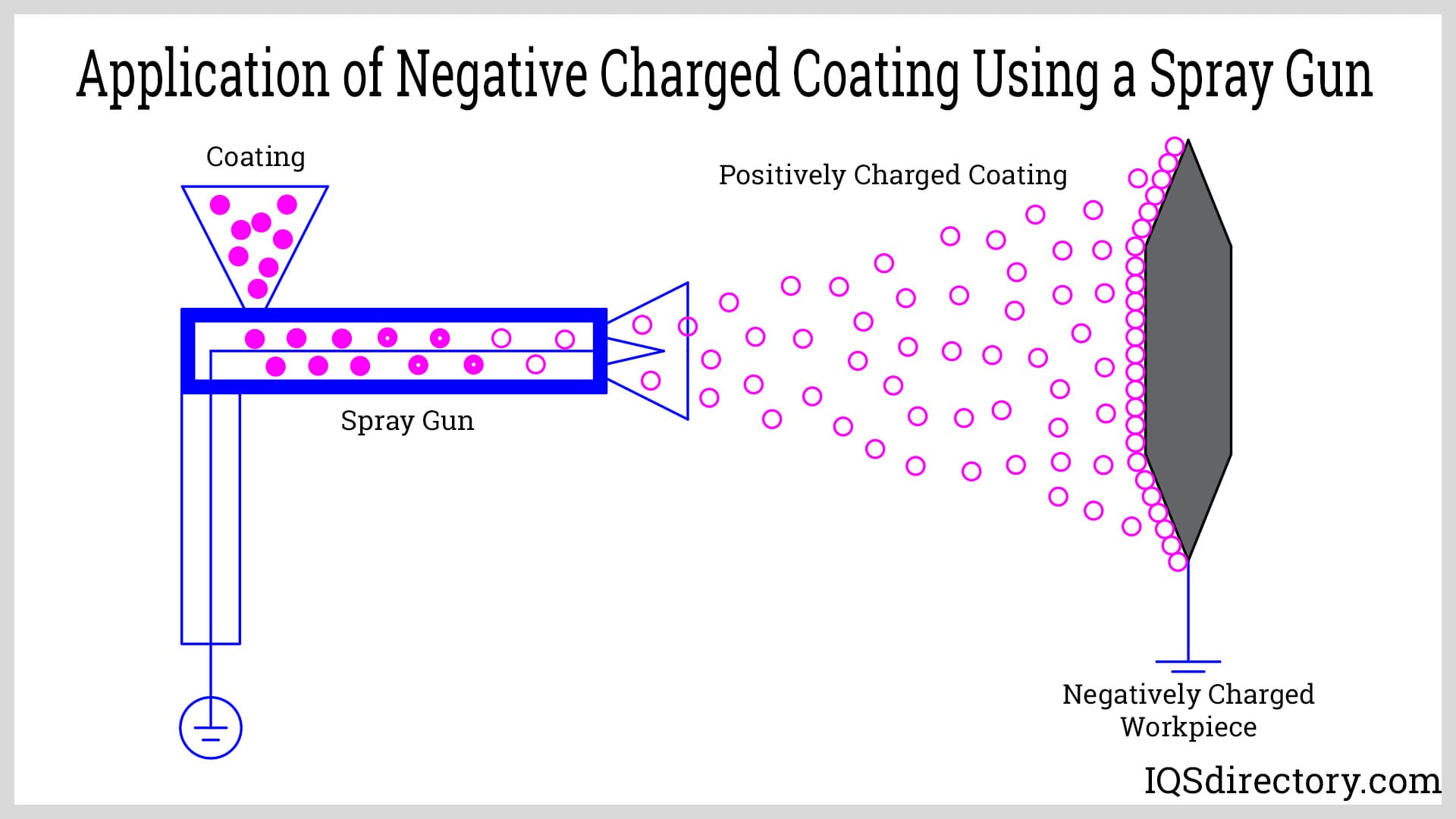
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- What is the best way to follow up on the performance of static eliminators post-purchase?
After installation, establish a routine for monitoring the performance of static eliminators. Schedule regular maintenance checks and keep a log of any issues encountered. Request feedback from operators who interact with the equipment to identify potential improvements. Additionally, maintain open lines of communication with your supplier for ongoing support and potential upgrades, ensuring that the equipment continues to meet your operational needs effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for static eliminator
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of static eliminators is essential for mitigating the operational challenges posed by static electricity in various industries. By understanding the specific needs of your manufacturing processes and selecting the right equipment, businesses can significantly reduce costly issues such as jams, mis-feeds, and even potential hazards like fires and explosions.
Key takeaways for B2B buyers include the importance of proper installation and positioning of static eliminators to maximize their effectiveness, as well as ensuring that all equipment is adequately grounded. This not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the equipment, leading to better return on investment.
As international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to seek innovative solutions, prioritizing high-quality static eliminators will be crucial in maintaining efficiency and safety in production lines.
Moving forward, it is vital to stay informed about advancements in static elimination technologies and supplier capabilities. Engage with trusted manufacturers and distributors to explore tailored solutions that meet your unique operational needs, ensuring your business remains competitive in a rapidly evolving market.