Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Steam Boilers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for steam boilers
In today’s interconnected global economy, steam boilers stand as a cornerstone for numerous industrial applications, from manufacturing to energy production. Their critical role in generating steam for heating, sterilization, and power generation cannot be overstated. For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of steam boiler selection is paramount to optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring regulatory compliance.
This guide aims to equip international buyers with comprehensive insights into the steam boiler market. It covers a wide array of topics, including types of boilers, such as fire-tube and water-tube designs, and the various materials used in construction, emphasizing durability and efficiency. Additionally, the guide delves into manufacturing quality control standards, offering benchmarks for selecting reliable suppliers. Cost considerations are also examined, providing a framework for budget planning and investment justification.
Furthermore, this resource addresses market trends and dynamics, ensuring that buyers are informed about the latest innovations and competitive pricing strategies. With a dedicated FAQ section, the guide answers common queries, facilitating a deeper understanding of steam boiler procurement. By leveraging this knowledge, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that enhance productivity and drive sustainable growth in their operations.
Understanding steam boilers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fire-Tube Boiler | Hot gases pass through tubes, water surrounds them. | Food processing, textile, and chemical industries | Pros: Lower upfront cost, simple design. Cons: Limited steam pressure and capacity. |
| Water-Tube Boiler | Water circulates in tubes heated by combustion gases. | Power generation, large manufacturing plants | Pros: High efficiency, capable of high pressures. Cons: Higher initial investment and complexity. |
| Electric Boiler | Uses electricity to heat water, producing steam. | Hospitals, laboratories, and small-scale industries | Pros: Low emissions, compact size. Cons: Higher operational costs, dependent on electricity supply. |
| Biomass Boiler | Burns organic materials (wood, agricultural waste) for steam. | Renewable energy projects, eco-friendly industries | Pros: Sustainable fuel source, lower emissions. Cons: Requires fuel storage and handling. |
| Modular Steam Boiler | Compact, scalable units that can be combined for larger output. | Hotels, commercial laundry, and food service | Pros: Flexible installation, quick deployment. Cons: May have higher per-unit costs. |
Fire-Tube Boiler
Fire-tube boilers are characterized by their design, where hot gases produced from combustion pass through tubes that are surrounded by water. This type is particularly suitable for industries such as food processing and textiles, where lower steam pressures are adequate. When considering a fire-tube boiler, buyers should evaluate the balance between upfront costs and the limitations in steam capacity, making it an attractive option for smaller operations.
Water-Tube Boiler
Water-tube boilers feature a design that allows water to circulate in tubes heated by combustion gases, enabling them to produce high-pressure steam efficiently. These boilers are ideal for power generation and large manufacturing plants where high efficiency and steam capacity are crucial. However, they come with a higher initial investment and complexity, which buyers must consider in their purchasing decisions, especially in terms of operational maintenance.
Electric Boiler
Electric boilers utilize electricity to heat water, making them suitable for applications in hospitals and laboratories where low emissions are a priority. Their compact size is a significant advantage in facilities with limited space. However, the operational costs can be higher compared to traditional fuel-based boilers, and buyers need to consider the reliability of the electricity supply in their region.
Biomass Boiler
Biomass boilers use organic materials, such as wood and agricultural waste, as fuel to generate steam. This type is increasingly popular in renewable energy projects and eco-friendly industries due to its sustainable fuel source and lower emissions. Buyers should be aware of the additional requirements for fuel storage and handling, which can complicate logistics and operational efficiency.
Modular Steam Boiler
Modular steam boilers consist of smaller, scalable units that can be combined to meet larger steam demands. They are particularly well-suited for industries like hospitality and commercial laundry, where flexibility and quick deployment are essential. While they offer advantages in installation and scalability, buyers should also consider the potentially higher costs per unit, which can impact overall budget planning.
Related Video: Steam Boilers | Principle of Working | Instrumentation & Controls | Process Industry | Utilities
Key Industrial Applications of steam boilers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Steam Boilers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Cooking, pasteurization, and sterilization processes | Ensures food safety, enhances quality, and increases production efficiency | Compliance with food safety regulations, energy efficiency, and reliability of supply |
| Textile | Dyeing and finishing processes | Improves color quality, reduces cycle time, and enhances fabric durability | Temperature control, steam quality, and material compatibility |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterilization and equipment cleaning | Guarantees product safety, meets regulatory standards, and minimizes contamination risks | Compliance with GMP standards, steam purity, and equipment reliability |
| Chemical Processing | Reaction and distillation processes | Increases reaction efficiency, enhances product yield, and reduces operational costs | Compatibility with chemicals, safety features, and energy efficiency |
| Healthcare | Sterilization of surgical instruments and equipment | Protects patient safety, ensures compliance with health regulations, and improves operational efficiency | Compliance with health regulations, steam quality, and reliability of supply |
Food & Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, steam boilers are crucial for cooking, pasteurization, and sterilization processes. These boilers provide the necessary heat to eliminate pathogens, ensuring food safety and enhancing product quality. International buyers should prioritize sourcing boilers that comply with local food safety regulations and are energy-efficient. Reliability is also essential, as production downtime can significantly impact business operations.
Textile
Steam boilers play a vital role in the textile industry, particularly in dyeing and finishing processes. They provide consistent steam quality and temperature control, which are critical for achieving high-quality colors and fabric durability. Buyers in this sector need to consider the compatibility of steam systems with various textile materials and the efficiency of the boiler to minimize operational costs. International buyers should also be aware of local regulations regarding emissions and energy consumption.
Pharmaceuticals
In pharmaceuticals, steam boilers are essential for sterilization and cleaning of equipment. They help ensure that products meet stringent safety and quality standards, thereby minimizing contamination risks. Buyers must ensure that the boilers comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, focusing on steam purity and system reliability. International buyers should also consider the technical support and service availability in their region to maintain operational efficiency.
Chemical Processing
Steam boilers are used extensively in chemical processing for reactions and distillation. They enhance reaction efficiency and product yield while reducing operational costs. For international buyers, it’s crucial to source boilers that are compatible with specific chemicals being processed and equipped with necessary safety features to handle high pressures and temperatures. Energy efficiency is another key consideration, as it directly impacts production costs.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, steam boilers are vital for sterilizing surgical instruments and equipment. They ensure patient safety by eliminating harmful microorganisms and complying with health regulations. Buyers should focus on the reliability and steam quality of the boilers, as any failure can compromise patient care. Additionally, it’s important to consider the availability of maintenance services and parts, especially for international buyers in regions with limited access to technical support.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for steam boilers
When selecting materials for steam boilers, it is crucial to consider factors such as temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and overall compatibility with the intended application. Here, we analyze four common materials used in steam boiler manufacturing: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron, and Copper. Each material has unique properties and implications for performance, cost, and regulatory compliance, particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its excellent strength and high-temperature resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 450°C and can withstand high pressure, making it suitable for various steam applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its durability and relatively low cost, making it a popular choice for many industrial applications. However, it is prone to corrosion, especially in high-moisture environments, which can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with saturated steam and is often used in power generation and manufacturing processes. However, its susceptibility to corrosion necessitates regular inspections and potential protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM A106 or DIN 17175. In regions with high humidity, additional protective measures may be necessary to mitigate corrosion risks.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and can handle temperatures up to 600°C. Its alloy composition provides strength and durability, making it ideal for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust and corrosion, which reduces maintenance needs. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel, and its manufacturing process can be more complex, potentially leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suitable for applications involving corrosive media, such as in the chemical and food processing industries. Its high strength makes it ideal for high-pressure steam systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 and JIS G3459 is essential. Buyers should also consider local availability and costs, as stainless steel may be subject to tariffs in certain regions.
Cast Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent thermal conductivity and ability to withstand high temperatures, typically up to 400°C. It also has good wear resistance.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of cast iron include its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, it is brittle, which can lead to cracking under stress or impact, and it is not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is commonly used in low-pressure steam applications, such as residential heating systems. Its thermal properties make it effective for heat retention.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM A48 and DIN 1691 when sourcing cast iron components. Its brittleness may not be ideal for regions prone to seismic activity.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper is highly conductive and resistant to corrosion, with a temperature rating of up to 200°C. It is also lightweight and easy to fabricate.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its excellent thermal conductivity, which enhances energy efficiency. However, it is more expensive than other materials and may not be suitable for high-pressure steam applications.
Impact on Application: Copper is often used in smaller, low-pressure steam systems, such as those found in residential or commercial settings. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for applications involving water or steam.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B280 is necessary. Additionally, buyers should consider the volatility of copper prices in global markets, which can impact overall project costs.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for steam boilers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Power generation, manufacturing processes | Durable and cost-effective | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure steam systems in corrosive media | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Cast Iron | Low-pressure steam applications | Cost-effective and good thermal conductivity | Brittle and not suitable for high pressure | Low |
| Copper | Residential/commercial low-pressure systems | Excellent thermal conductivity | High cost and limited pressure rating | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for steam boilers
Manufacturing Processes for Steam Boilers
The manufacturing of steam boilers is a complex process that requires precision, adherence to safety standards, and quality control at every stage. Below, we break down the typical manufacturing stages and the key techniques used in producing reliable steam boilers.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Materials: The primary materials used in steam boiler construction include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steels. The selection is based on the intended application, operating pressure, and temperature.
– Cutting and Shaping: Large sheets of metal are cut into specific sizes using plasma cutting, laser cutting, or water jet cutting. This ensures that each component meets the design specifications. -
Forming
– Bending and Rolling: Metal sheets are bent into the required shapes using hydraulic presses and rollers. This process is crucial for creating the boiler shell and other curved components.
– Welding: Various welding techniques, such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), are employed to join components. The weld quality is critical for the structural integrity of the boiler. -
Assembly
– Component Integration: Once formed, components such as the boiler shell, tubes, burners, and control systems are assembled. This stage often includes the installation of insulation materials to enhance energy efficiency.
– System Testing: Initial functionality tests are conducted to ensure all components work together as intended. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: The exterior of the boiler is treated to prevent corrosion. Techniques like sandblasting and painting are commonly used.
– Final Assembly: After surface treatment, final assembly is completed, which includes attaching all necessary fittings and controls.
Key Techniques Used in Manufacturing
- Automated Welding: Enhances precision and reduces human error during the welding process.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiography are employed to inspect weld integrity without damaging the components.
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC): CNC machines are used for precise cutting and shaping of materials, ensuring high repeatability and accuracy in production.
Quality Assurance in Steam Boiler Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the steam boiler manufacturing process to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with international standards. Here are the key aspects of QA relevant to international B2B buyers:
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for the design and fabrication of pressure vessels, including steam boilers, particularly for the oil and gas industry.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements. This includes checking for certifications and conducting material tests. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Throughout the manufacturing process, various checkpoints are established to monitor critical aspects such as welding quality, dimensional accuracy, and assembly integrity. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– A comprehensive inspection is performed before shipping. This includes pressure testing, functionality testing, and visual inspections to ensure the final product meets all specifications.
Common Testing Methods
- Hydrostatic Testing: Used to test the strength and leak-tightness of the boiler under pressure.
- Performance Testing: Assesses the efficiency and operational capabilities of the boiler, often conducted under simulated operating conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring supplier quality is essential. Here are actionable steps to verify the QC processes of potential suppliers:
- Conduct Audits: Perform regular audits of the manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with quality standards and operational practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for documentation of their quality assurance processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to evaluate the quality of the boilers before shipment. This can provide an unbiased assessment of the product’s compliance with international standards.
Navigating Quality Control Nuances
International B2B buyers must be aware of regional regulations and standards that may differ from their home countries. For example:
- Documentation Requirements: Different countries may have specific requirements for documentation (e.g., certificates of compliance) that suppliers must provide.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Understanding how quality is perceived and prioritized in different regions can aid in establishing effective communication with suppliers.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for steam boilers is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality products that meet their operational needs while complying with international standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for steam boilers Sourcing
When sourcing steam boilers, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section will break down the key components of costs, the factors influencing pricing, and actionable tips for buyers to navigate the procurement process effectively.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in steam boiler pricing is the raw materials used, including steel, insulation, and refractory materials. Prices fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should stay informed about global commodity trends to anticipate changes in costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and installation. These costs can vary significantly by region, influenced by local labor laws and availability of skilled labor. Buyers should consider suppliers with efficient labor practices to mitigate expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, maintenance, and factory rent. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, making it beneficial for buyers to evaluate a supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Depending on the complexity of the boiler design, tooling costs can be significant. Customization requirements may necessitate specialized tools, impacting overall pricing. Buyers should discuss tooling costs upfront, especially for bespoke designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes incurs additional costs but is crucial for ensuring product reliability and compliance with industry standards. Buyers should inquire about the QC measures employed by suppliers and consider these in their pricing evaluations.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, can add significant expenses, particularly for international buyers. Factors like distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms will influence logistics costs. Buyers should factor in these costs when comparing supplier quotes.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and earn a profit. Margins can vary widely based on market competition, supplier reputation, and the complexity of the boiler design. Understanding market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better terms.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully and negotiate volume discounts where possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Unique specifications or customized solutions typically increase costs. Clearly defining requirements upfront can help avoid unexpected expenses later in the process.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO or ASME) can raise costs but may lead to long-term savings through improved efficiency and reliability. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of a supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their proven track record but can offer better support and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery can significantly affect pricing. Different Incoterms allocate costs and responsibilities differently, which can impact the total landed cost of the boiler.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing. Leverage quotes from multiple suppliers to foster competition, but be cautious about disclosing sensitive information.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the boiler’s lifespan. This broader view can reveal the most cost-effective options.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences and potential tariffs or import duties that may apply to international shipments. Understanding these factors can help avoid unexpected costs.
Disclaimer
Prices for steam boilers can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions and specific buyer requirements. The information provided is for indicative purposes only and should not be considered as fixed pricing. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Spotlight on Potential steam boilers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘steam boilers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for steam boilers
Key Technical Properties of Steam Boilers
When evaluating steam boilers for industrial applications, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the most critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The construction material of a steam boiler significantly affects its performance and longevity. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. Each material has specific properties that determine its suitability for different applications, including resistance to corrosion and high-temperature performance. Buyers must assess the operational environment to select a boiler that meets their durability and safety standards. -
Pressure Rating
Steam boilers are categorized by their maximum operating pressure, typically measured in pounds per square inch (psi). This rating impacts the boiler’s efficiency and the type of applications it can support. For instance, high-pressure steam is often required in power generation or chemical processing, while lower pressure may suffice for heating systems. Understanding pressure ratings helps buyers ensure compliance with industry regulations and optimize their operations. -
Efficiency Rating
Efficiency is a critical factor that indicates how well a boiler converts fuel into usable energy. It is usually expressed as a percentage; higher efficiency ratings lead to reduced fuel costs and lower emissions. Buyers should consider the efficiency rating as it directly affects operational costs and environmental impact, especially in regions with strict emissions regulations. -
Heat Transfer Surface Area
This specification refers to the total area available for heat exchange between the combustion gases and the water/steam in the boiler. A larger surface area can lead to more efficient heating and improved steam production rates. B2B buyers must evaluate the heat transfer area to ensure that the boiler can meet the steam demand of their specific application. -
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in the operation of steam boilers. Critical safety features include pressure relief valves, low-water cut-off devices, and automatic shutdown systems. These components help prevent accidents and ensure safe operation. Buyers should inquire about the safety certifications of the boiler to guarantee compliance with international safety standards.
Common Trade Terminology in the Steam Boiler Industry
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the steam boiler sector, buyers often deal directly with OEMs to ensure they receive high-quality, compatible components for their systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For steam boilers, understanding MOQ is vital as it can affect inventory costs and lead times. Buyers should negotiate these terms to align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
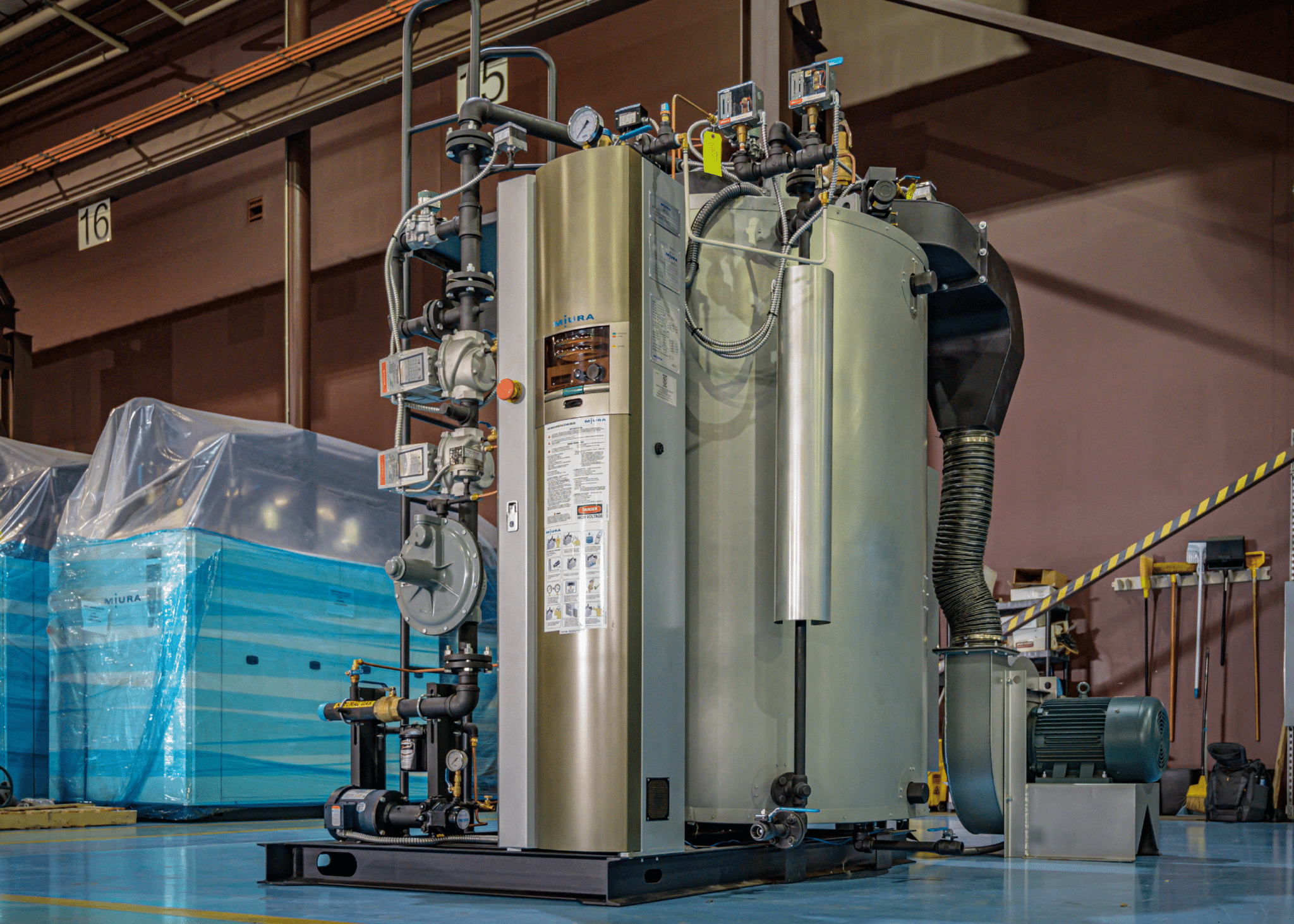
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products. In the steam boiler industry, submitting RFQs allows buyers to compare offers, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. In the steam boiler industry, lead times can vary significantly based on the complexity of the boiler and the supplier’s production schedule. Buyers should consider lead times when planning their procurement processes to avoid operational disruptions. -
Certification Standards
This refers to the various industry standards and regulations that a steam boiler must meet to ensure safety and efficiency. Common certifications include ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and CE (Conformité Européenne). Buyers should verify that the boilers they intend to purchase meet the necessary certification standards, which can impact their operations and compliance with local regulations.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can navigate the steam boiler market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the steam boilers Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global steam boiler market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising industrialization, the need for efficient energy solutions, and the shift towards sustainable practices. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, increasing demand for steam boilers across sectors like food and beverage, textiles, and pharmaceuticals is notable. As industries expand, particularly in emerging markets, the demand for reliable steam generation solutions is set to rise.
Current trends indicate a significant shift towards smart technology integration in steam boilers. This includes IoT-enabled systems that allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Furthermore, the adoption of modular boiler systems is gaining traction, enabling businesses to scale their operations flexibly based on demand. Buyers should be aware of the importance of energy efficiency ratings, as regulations tighten globally to promote sustainability.
Emerging sourcing trends focus on local procurement strategies to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains. For international buyers, establishing relationships with local manufacturers or suppliers can lead to reduced lead times and lower transportation costs. Additionally, leveraging digital platforms for sourcing can streamline the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare products and prices more efficiently.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is at the forefront of the steam boiler industry, with environmental impacts becoming a significant concern for B2B buyers. The traditional reliance on fossil fuels is giving way to more sustainable energy sources such as biomass, solar, and electric steam boilers. These alternatives not only reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also align with global efforts to combat climate change.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally crucial. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical labor practices and transparency in their supply chains. This includes obtaining certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety. Such certifications ensure that the materials used in steam boiler production meet high environmental and ethical standards.
Moreover, green certifications such as Energy Star or EcoLabel are becoming essential in the purchasing decision for steam boilers. These certifications indicate that the products have been tested for energy efficiency and environmental impact, providing buyers with confidence that they are making responsible choices.
Brief Evolution/History
The steam boiler has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 18th century, when it was primarily used for powering steam engines. As industrial processes advanced, the demand for more efficient and reliable steam generation systems grew. The introduction of fire-tube and water-tube designs revolutionized boiler technology, allowing for greater efficiency and safety.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and innovation, with manufacturers investing in research and development to create eco-friendly steam solutions. The rise of digital technologies has further transformed the sector, leading to smarter, more connected systems that enhance operational efficiencies and reduce environmental impact. Understanding this evolution helps B2B buyers appreciate the technological advancements that can benefit their operations today.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of steam boilers
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of steam boilers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, certifications, and customer reviews. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry (e.g., food processing, textiles). Ensure they comply with international standards such as ISO 9001 and have relevant certifications for quality assurance. Engage in direct communication to assess their responsiveness and willingness to provide technical support. Additionally, inquire about their after-sales service and maintenance capabilities, as ongoing support is crucial for the longevity of your steam boiler. -
Can I customize steam boilers to meet specific operational needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor steam boilers to your unique operational requirements. This can include adjustments in size, fuel type, pressure ratings, and additional features like energy-saving technologies. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and request detailed proposals that outline customization capabilities. Ensure that any modifications comply with local regulations and industry standards to avoid operational issues post-installation. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for steam boilers?
MOQs and lead times can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, MOQs for steam boilers range from one unit for small manufacturers to several units for larger suppliers. Lead times can vary from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the boiler and the supplier’s production schedule. Always confirm these details early in your discussions to align your project timelines with the supplier’s capabilities and avoid delays in your operations. -
What payment terms are common in international steam boiler transactions?
Payment terms vary by supplier and are often influenced by the buyer’s creditworthiness and relationship with the supplier. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, and net payment terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect both parties, ensuring that you have sufficient time to inspect the equipment upon arrival. Always document these terms clearly in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and compliance with certifications?
To ensure quality assurance, request copies of all relevant certifications from your supplier, including ISO standards and any specific industry certifications. You can also ask for third-party inspection reports and factory audit results. Implement a quality control process that includes pre-shipment inspections and testing of the boilers. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the regulatory standards in your country to ensure that the boilers comply with local laws and industry practices. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing steam boilers?
Logistics is crucial in the procurement of steam boilers, especially when dealing with international suppliers. Consider the shipping methods available, customs clearance processes, and any potential tariffs or duties that may apply. Work with logistics providers experienced in heavy machinery to ensure safe and timely delivery. Additionally, plan for storage and installation logistics at your facility to minimize downtime during the transition period. -
What steps should I take in case of a dispute with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first attempt to resolve the issue amicably through direct communication with the supplier. Document all correspondence and agreements related to the transaction. If informal resolution fails, refer to the contract for dispute resolution clauses, which may include mediation or arbitration processes. Consider involving a legal professional with experience in international trade to advise on your options and rights under the governing law specified in your contract. -
How do I assess the total cost of ownership for steam boilers?
Evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO) involves more than just the initial purchase price. Consider ongoing operational costs, including fuel consumption, maintenance, and potential downtime. Assess the expected lifespan of the boiler and any warranties or service agreements offered. Calculate energy efficiency ratings to estimate fuel costs over time. By considering these factors, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your long-term operational budget and sustainability goals.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for steam boilers
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of steam boilers is pivotal for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, businesses can ensure they meet their operational demands while optimizing their supply chains. Key considerations include understanding local regulations, evaluating supplier capabilities, and assessing the total cost of ownership, which encompasses installation, maintenance, and operational efficiency.
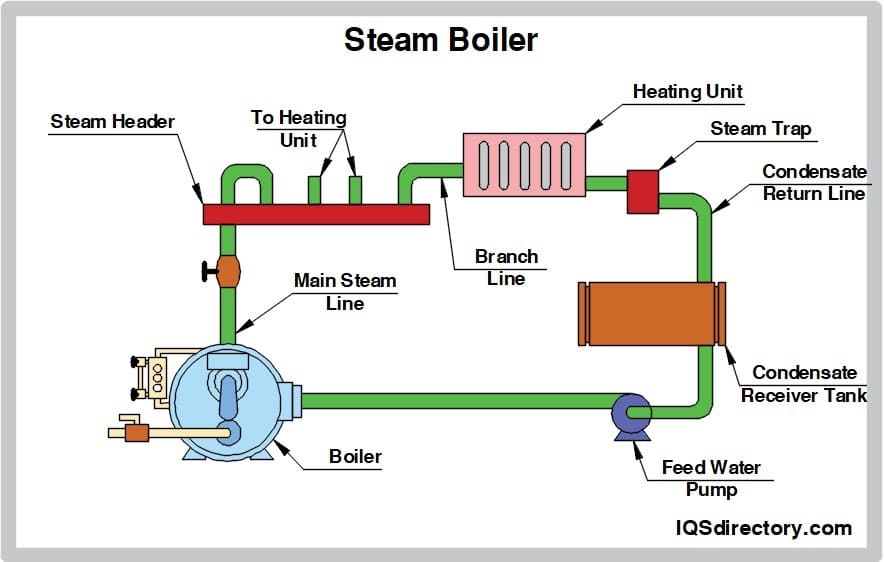
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Furthermore, leveraging advanced technologies and sustainable practices can significantly enhance boiler performance and reduce environmental impact. As industries increasingly focus on sustainability, investing in energy-efficient and eco-friendly steam solutions will not only improve productivity but also align with global sustainability goals.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers that offer customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs. By fostering collaborative relationships and staying informed on market trends, businesses can navigate challenges and seize opportunities in the evolving steam boiler market. Now is the time to act—enhance your sourcing strategy and position your organization for success in a competitive landscape.