Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing The Heat Transfer Equipment
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for the heat transfer equipment company
Navigating the complexities of the global market for heat transfer equipment is essential for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their operations and improve efficiency. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, highlighting the critical role of heat transfer equipment in various industrial applications, from energy production to manufacturing processes. Understanding the types of equipment available, such as plate heat exchangers, shell and tube systems, and spiral heat exchangers, is vital for selecting the right solution tailored to specific operational needs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets such as Italy and France), will benefit from insights into materials, manufacturing standards, and quality control measures that ensure reliability and performance. This guide addresses key factors influencing procurement decisions, including cost considerations, supplier reliability, and market trends, enabling informed sourcing strategies.
Additionally, the guide includes a section dedicated to frequently asked questions, demystifying common queries related to installation, maintenance, and compliance with international standards. With a focus on actionable insights, this resource empowers B2B buyers to make strategic decisions that enhance operational efficiency and competitive advantage in their respective markets. Explore the nuances of heat transfer equipment to harness its full potential and drive sustainable growth in your operations.
Understanding the heat transfer equipment company Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers | Composed of a series of tubes; efficient for high-pressure applications. | Oil refineries, chemical processing. | Pros: High durability, effective heat transfer. Cons: Bulky, requires significant maintenance. |
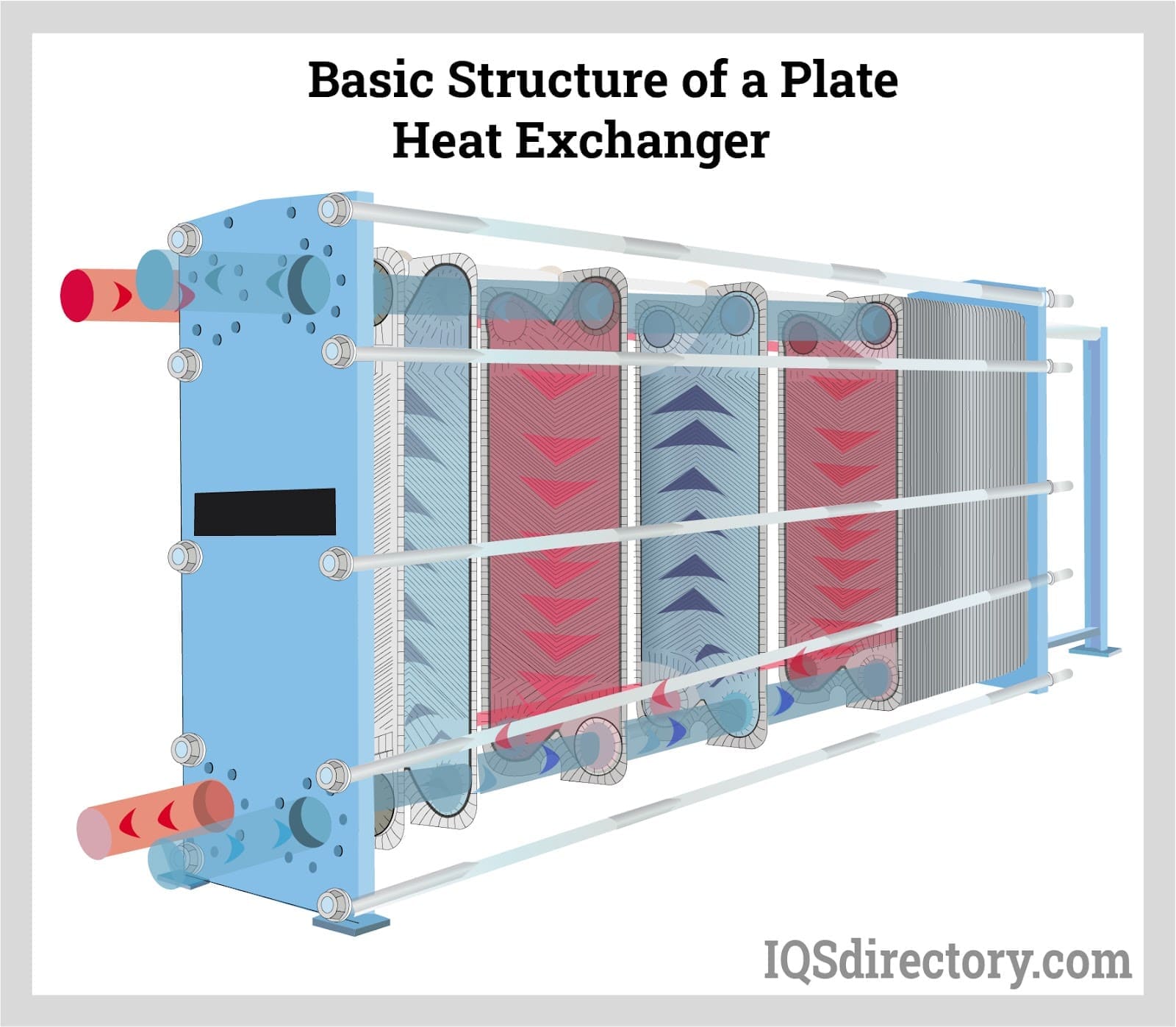
| Plate Heat Exchangers | Made up of multiple thin plates; compact and efficient. | Food processing, HVAC systems. | Pros: Space-saving, easy to clean. Cons: Limited pressure tolerance, potential for leaks. |
| Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers | Utilizes air as the cooling medium; no water required. | Power plants, petrochemical industries. | Pros: Water conservation, lower operational costs. Cons: Less effective in high humidity, larger footprint. |
| Coil Heat Exchangers | Uses coiled tubes to transfer heat; versatile in application. | Refrigeration, HVAC systems. | Pros: Flexible design, suitable for various fluids. Cons: Performance can be affected by fouling. |
| Spiral Heat Exchangers | Features a spiral design for enhanced heat transfer. | Waste heat recovery, chemical industries. | Pros: Compact, efficient for viscous fluids. Cons: Higher initial cost, complexity in cleaning. |
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers are among the most widely used types in industrial applications. They consist of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other the cold fluid, allowing for effective heat transfer between the two. These units are particularly suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, making them ideal for oil refineries and chemical processing plants. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider the maintenance requirements and available space, as these units can be bulky and require significant upkeep.
Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are designed with multiple thin plates that create a large surface area for heat exchange. Their compact design makes them ideal for applications in food processing and HVAC systems where space is limited. B2B buyers should note that while plate heat exchangers are efficient and easy to clean, they have limitations in terms of pressure tolerance and can be prone to leaks if not properly maintained. It’s crucial to assess the specific needs of the application to determine suitability.
Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Air-cooled heat exchangers use ambient air to cool fluids, making them a sustainable option as they do not require water. These systems are commonly used in power plants and petrochemical industries. Buyers should weigh the benefits of water conservation and lower operational costs against potential downsides, such as reduced efficiency in humid climates and a larger physical footprint. Understanding the environmental conditions of the installation site is essential for making an informed decision.
Coil Heat Exchangers
Coil heat exchangers consist of coiled tubes that facilitate heat transfer between fluids. Their versatility allows them to be used in various applications, including refrigeration and HVAC systems. Buyers should consider the flexibility in design and compatibility with different fluids; however, fouling can impact performance, necessitating regular cleaning. Evaluating the specific fluid characteristics and operational conditions can help in selecting the right coil heat exchanger.
Spiral Heat Exchangers
Spiral heat exchangers feature a unique spiral design that enhances heat transfer efficiency, especially for viscous fluids. They are particularly useful in waste heat recovery and chemical industries. While they offer compactness and high efficiency, buyers should consider the higher initial cost and the complexity involved in cleaning these units. Assessing the application requirements and potential return on investment is vital for B2B buyers when considering spiral heat exchangers.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of the heat transfer equipment company
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of the heat transfer equipment company | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Heat exchangers for oil cooling systems | Enhanced thermal efficiency and reduced operational costs | Material compatibility, pressure ratings, and maintenance needs |
| Food & Beverage | Plate heat exchangers for pasteurization | Improved product safety and consistency in processing | Compliance with food safety standards and cleaning requirements |
| Chemical Processing | Shell and tube heat exchangers for chemical reactions | Increased reaction efficiency and better temperature control | Customization options and resistance to corrosive substances |
| HVAC | Water to air heat exchangers for climate control systems | Energy savings and improved indoor air quality | Size, efficiency ratings, and installation compatibility |
| Renewable Energy | Heat exchangers in geothermal systems | Maximized energy extraction and sustainability | Efficiency metrics and environmental compliance |
Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas sector, heat exchangers are crucial for cooling systems that manage the temperature of oil during extraction and processing. The heat transfer equipment company provides robust solutions that enhance thermal efficiency, leading to reduced operational costs. International buyers, especially from regions with extreme temperatures, should consider material compatibility with various oil types, pressure ratings, and specific maintenance needs to ensure optimal performance.
Food & Beverage
The food and beverage industry relies heavily on heat transfer equipment, particularly plate heat exchangers, for processes like pasteurization. These systems are designed to improve product safety by efficiently transferring heat to eliminate pathogens while maintaining product quality. Buyers must ensure compliance with stringent food safety standards, as well as consider the cleaning requirements and ease of maintenance to avoid contamination and ensure operational efficiency.
Chemical Processing
In chemical processing, shell and tube heat exchangers are vital for regulating temperatures during chemical reactions. The heat transfer equipment company offers solutions that increase reaction efficiency and provide better temperature control, which is crucial for product quality. Buyers should focus on customization options that meet specific process requirements and ensure that materials can withstand corrosive substances prevalent in chemical manufacturing.
HVAC
In the HVAC industry, water to air heat exchangers play a significant role in climate control systems. These systems are designed to enhance energy savings while improving indoor air quality, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to reduce energy costs. When sourcing, buyers should consider size, efficiency ratings, and installation compatibility to ensure that the equipment integrates seamlessly into existing systems.
Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector utilizes heat exchangers in geothermal systems to maximize energy extraction from the earth. The heat transfer equipment company provides solutions that not only enhance efficiency but also support sustainability goals. Buyers should evaluate efficiency metrics and ensure compliance with environmental regulations to optimize their investments in renewable energy technologies.
Related Video: Plate Heat Exchanger Applications and working principle hvac heat transfer
Strategic Material Selection Guide for the heat transfer equipment company
When selecting materials for heat transfer equipment, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of heat transfer equipment, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C (1472°F) and can handle pressures exceeding 100 bar.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel makes it ideal for long-term applications, but it can be more expensive than other materials. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it requires specialized welding techniques. Its suitability for a wide range of fluids, including corrosive substances, is a significant advantage.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including water, oil, and chemicals, making it versatile for different industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 and EN 10088. In regions like Europe, certifications related to food safety may also be necessary.
Copper
Key Properties:
Copper has excellent thermal conductivity, making it highly effective for heat transfer applications. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and pressures around 20 bar.
Pros & Cons:
While copper’s thermal efficiency is a key advantage, it is prone to corrosion, especially in saline environments. Its cost is moderate, and the manufacturing process is relatively straightforward, though care must be taken to avoid oxidation during production.
Impact on Application:
Copper is particularly effective in applications involving water and refrigerants but may not be suitable for aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the local corrosion conditions and ensure compliance with ASTM B280 for copper tubing. In regions like South America, where humidity can be high, additional protective coatings may be necessary.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability, capable of withstanding high pressures (up to 250 bar) and temperatures (up to 400°C or 752°F). However, it has limited corrosion resistance unless treated.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of carbon steel is its low cost and availability. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion limits its application in corrosive environments, necessitating protective coatings or linings.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is suitable for applications involving non-corrosive fluids, such as water and steam, but should be avoided in chemical processing.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards like ASTM A106 and DIN 17175 is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East should be particularly aware of the environmental conditions that may affect the longevity of carbon steel.
Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and can handle extreme temperatures (up to 600°C or 1112°F) and pressures (over 50 bar). It is lightweight yet incredibly strong.
Pros & Cons:
Though titanium’s corrosion resistance is a significant advantage, its high cost and complex manufacturing processes can be limiting factors. Specialized welding techniques are often required.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is ideal for applications involving seawater and aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for marine and chemical industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM B348 and other relevant standards. In Europe, certifications for aerospace or medical applications may be necessary.
| Material | Typical Use Case for the heat transfer equipment company | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, food and beverage industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Copper | HVAC systems, refrigeration applications | Superior thermal conductivity | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Steam systems, water heating applications | Low cost and high strength | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Titanium | Marine applications, chemical processing | Exceptional corrosion resistance | High cost and complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for the heat transfer equipment company
Manufacturing Processes for Heat Transfer Equipment
The manufacturing processes for heat transfer equipment involve several key stages, each critical to producing high-quality products that meet industry standards. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This stage includes:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right materials is vital, often involving stainless steel, copper, or aluminum, depending on the application’s thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance requirements.
- Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut and shaped into specific dimensions using laser cutting or plasma cutting techniques. Precision is essential to ensure proper fitting during assembly.
2. Forming
In this phase, materials undergo various processes to achieve the desired shapes and configurations:
- Bending and Forming: Techniques such as roll bending and press forming are used to create complex geometries needed for heat exchangers.
- Welding: Advanced welding methods, including TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas), are employed to join components. The quality of welds is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity and leak-proof nature of the equipment.
3. Assembly
Once individual components are formed, the assembly process begins:
- Component Assembly: This involves the integration of various parts, such as tubes, plates, and headers. Automated assembly lines enhance efficiency and accuracy.
- Sealing: Proper sealing techniques, including the use of gaskets or o-rings, are critical to prevent leaks, which can compromise performance.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage prepares the equipment for shipment and installation:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like polishing or coating (e.g., powder coating) enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
- Final Inspection: A thorough inspection ensures all parts meet specified dimensions and quality standards before leaving the facility.
Quality Assurance in Heat Transfer Equipment Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA processes and certifications can significantly impact their purchasing decisions.
International Standards and Certifications
Manufacturers of heat transfer equipment typically adhere to several international standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines a quality management system (QMS) that ensures consistent quality in products and services. It emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: For companies exporting to Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides guidelines for the oil and gas industry, ensuring that heat exchangers are suitable for high-pressure applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications. This step helps prevent defects in the final product.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor processes and identify any deviations from standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, they undergo final testing and inspection to verify performance and compliance with specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods play a crucial role in validating the quality and performance of heat transfer equipment:
- Hydrostatic Testing: This test checks for leaks by pressurizing the unit with water. It’s commonly used for heat exchangers to ensure they can withstand operational pressures.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiographic testing evaluate the integrity of welds and materials without damaging the product.
- Performance Testing: Equipment is tested under operational conditions to ensure it meets thermal performance specifications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some actionable strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help ensure adherence to quality standards. Buyers should consider scheduling both announced and unannounced audits to gain a full understanding of the supplier’s practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation that details their quality control processes, test results, and certifications. This transparency fosters trust and reliability.
- Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control systems and product compliance.
Navigating Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, B2B buyers must be aware of potential quality control nuances:
- Cultural Differences: Attitudes toward quality and compliance can vary significantly across regions. Buyers should consider local practices and expectations, especially when sourcing from Africa, South America, or the Middle East.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding manufacturing and safety standards. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations to avoid legal complications.
- Language Barriers: Communication is vital in ensuring quality assurance. Buyers should work with suppliers who can provide documentation and support in their preferred language to avoid misunderstandings.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place at heat transfer equipment companies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish strong partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for the heat transfer equipment company Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of heat transfer equipment is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis focuses on the components that contribute to overall costs, the influencers of pricing, and strategic tips for buyers to optimize their procurement processes.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost of heat transfer equipment. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and specialized alloys. Prices fluctuate based on global supply and demand, with stainless steel often being the most cost-effective choice due to its durability and corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the manufacturer’s location. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Western Europe, overall pricing may be elevated. Conversely, manufacturers in regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing but might face challenges regarding quality and compliance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can lower overhead costs, which can be passed on to buyers in the form of competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized equipment can significantly add to upfront costs. Buyers should consider the long-term implications of tooling investments, especially if they require customized heat transfer solutions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that products meet industry standards and certifications, such as TEMA and ASME. While higher QC costs might raise the initial price, they can reduce long-term operational risks and maintenance expenses.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are a critical component, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) play a significant role in logistics costs, which can affect the total cost of ownership.
-
Margin: Manufacturer margins vary based on competition, market demand, and the perceived value of the product. Understanding the typical margin in the industry can help buyers identify reasonable pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often secure better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and explore bulk purchasing options.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized equipment tailored to specific applications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should balance their need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Equipment manufactured from high-quality materials that meet stringent certifications tends to be more expensive. However, investing in quality can lead to lower maintenance and operational costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and customer service can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may charge a premium, but they often provide better after-sales support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect overall costs and risk allocation between buyers and sellers.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations by understanding the cost structure. Highlighting your commitment to volume purchases can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime when evaluating equipment.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of regional pricing differences. Buyers from Africa or South America may encounter additional tariffs or import duties that can affect the final cost.
-
Comparative Quotes: Always obtain multiple quotes from various suppliers. This not only provides a benchmark for pricing but also highlights differences in service levels and product offerings.
Disclaimer
Prices and costs mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, specific buyer requirements, and supplier negotiations. Always conduct thorough research and engage with suppliers to obtain the most accurate and current pricing information.
Spotlight on Potential the heat transfer equipment company Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘the heat transfer equipment company’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for the heat transfer equipment company
Key Technical Properties for Heat Transfer Equipment
Understanding the essential technical properties of heat transfer equipment is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact performance, reliability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in heat exchangers, such as stainless steel, copper, or titanium, determines the equipment’s durability and resistance to corrosion. High-grade materials are essential for applications involving aggressive fluids or extreme temperatures. For buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs. -
Thermal Conductivity
This property measures a material’s ability to conduct heat. Higher thermal conductivity materials enhance heat transfer efficiency, which can lead to energy savings. B2B buyers should prioritize equipment with optimal thermal conductivity to maximize system performance and reduce operational expenses. -
Pressure Rating
The maximum pressure the equipment can withstand is critical, especially in high-pressure applications. Pressure ratings ensure safety and prevent failures. Buyers must match the pressure rating of the heat transfer equipment with the operational conditions of their processes to avoid catastrophic failures and costly downtimes. -
Flow Capacity
This specification refers to the volume of fluid that can pass through the heat exchanger within a given time frame. Adequate flow capacity is essential for maintaining system efficiency and achieving desired thermal performance. Buyers should assess their process requirements to select equipment that meets or exceeds the necessary flow rates. -
Tolerance
Tolerance levels define the permissible limits of variation in dimensions during manufacturing. High tolerance levels are vital for ensuring proper fit and functionality in complex systems. Buyers should seek equipment that adheres to industry standards to ensure compatibility with existing systems and reduce installation issues.
Common Trade Terminology in Heat Transfer Equipment
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the heat transfer equipment market. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the heat transfer industry, working with OEMs can assure buyers of receiving high-quality, reliable components that meet specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to avoid overcommitting to large orders and managing inventory effectively, especially for smaller businesses. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to invite them to bid on a specific product or service. It is crucial for buyers to provide detailed specifications in their RFQs to receive accurate quotes, ensuring they can compare prices and terms effectively.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized standard trade terms used in sales contracts to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, which can significantly impact total costs. -
Lead Time
This term indicates the time from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times is essential for buyers to manage project timelines and ensure that heat transfer equipment is available when needed, preventing delays in production. -
Certification Standards
These are industry-specific standards that equipment must meet to ensure safety and reliability, such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) or TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association). Buyers should verify that equipment complies with relevant certification standards to mitigate risks associated with safety and performance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right heat transfer equipment for their specific needs while fostering effective communication with suppliers.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the the heat transfer equipment company Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global heat transfer equipment market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing energy efficiency demands and the expansion of industries such as HVAC, petrochemical, and food processing. Key trends influencing this market include the integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled systems that allow for real-time monitoring and optimization of heat transfer processes. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the rising demand for customized solutions tailored to specific operational needs, leading to a growing emphasis on collaboration with manufacturers that can provide bespoke engineering services.
Additionally, sustainability initiatives are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing carbon footprints and enhancing energy efficiency in their products. The market is also seeing a shift towards modular and compact designs, which not only improve space utilization but also streamline installation and maintenance processes. As regulations surrounding emissions and energy consumption tighten, sourcing equipment that meets or exceeds these standards will be crucial for compliance and operational efficiency.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the heat transfer equipment sector, with growing awareness of the environmental impacts associated with traditional manufacturing processes. B2B buyers are urged to consider suppliers who actively implement eco-friendly practices, such as utilizing recyclable materials and employing energy-efficient manufacturing techniques. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chain transparency is crucial. Buyers should seek out manufacturers who prioritize fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Engaging with suppliers who demonstrate a robust commitment to social responsibility can not only enhance brand reputation but also foster long-term partnerships that align with global sustainability goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The heat transfer equipment industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by traditional designs, the sector has seen a shift towards advanced technologies that enhance performance and efficiency. The introduction of digital solutions, including predictive maintenance tools and automated systems, has revolutionized operational capabilities. Today, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on innovation, collaborating with research institutions and leveraging advanced materials to meet the diverse needs of international B2B buyers. This evolution is indicative of a broader trend towards smart manufacturing and sustainability, setting the stage for future advancements in heat transfer technology.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of the heat transfer equipment company
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of heat transfer equipment?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, certifications, and customer reviews. Look for companies that adhere to international standards such as ASME, API, and TEMA. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and after-sales support. Additionally, request references from other clients in your region to assess their reliability and service quality. This thorough vetting ensures you partner with a supplier that can meet your specific technical and logistical requirements. -
Can heat transfer equipment be customized to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many heat transfer equipment manufacturers offer customization options. Discuss your specific requirements, such as size, material, and thermal performance with potential suppliers. Custom solutions can be tailored to unique applications across various industries, ensuring optimal efficiency. Make sure to communicate your needs clearly and verify that the supplier has experience in producing custom solutions for similar applications. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for heat transfer equipment?
MOQs and lead times vary by supplier and the complexity of the equipment. Generally, MOQs can range from a single unit for custom designs to several units for standard models. Lead times can be anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the manufacturing process and whether the equipment requires customization. It’s essential to discuss these details upfront to align your procurement timeline with your project needs. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by heat transfer equipment suppliers?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers. Common options include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established clients. It is advisable to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring security for both parties. Always clarify the payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, credit card) and ensure they are compliant with international trade regulations. -
How can I ensure the quality of heat transfer equipment before making a purchase?
To ensure quality, request documentation of certifications and quality assurance processes from the supplier. Many manufacturers follow stringent QA protocols and can provide test reports for their equipment. If possible, arrange for a factory visit or request samples for testing. Additionally, consider third-party inspections to verify compliance with international standards before shipment. -
What certifications should I look for when sourcing heat transfer equipment?
Look for suppliers with recognized certifications such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers), TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association), and API (American Petroleum Institute). These certifications indicate adherence to industry standards for safety and performance. Inquire if the equipment meets local regulations in your region, as compliance can impact the installation and operation of the equipment. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing heat transfer equipment?
Logistics for importing heat transfer equipment involve several factors, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Understand the total landed cost, which includes shipping, duties, and taxes. Collaborate with suppliers to ensure they provide all necessary shipping documentation. It’s also advisable to work with a logistics partner experienced in international trade to navigate potential challenges smoothly. -
How can I resolve disputes with suppliers if issues arise?
To effectively resolve disputes, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements and correspondences. Before entering a contract, include clauses for dispute resolution, such as mediation or arbitration, to ensure a structured approach. If issues arise, engage the supplier in discussions to identify solutions amicably. If necessary, refer to third-party mediation services to facilitate a resolution, ensuring that all parties adhere to agreed terms.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for the heat transfer equipment company
In the dynamic landscape of heat transfer equipment, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial element for international buyers seeking to optimize performance while managing costs. By leveraging diverse suppliers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, companies can access cutting-edge technologies and innovative solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Key takeaways for B2B buyers include:
- Evaluate Supplier Credentials: Focus on manufacturers with strong quality certifications (e.g., ASME, TEMA) to ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Consider Future Needs: Anticipate potential growth or changes in operational requirements when selecting heat transfer solutions, as adaptability is vital for long-term success.
- Engage in Collaborative Partnerships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to enhanced service, innovation, and better pricing structures.
As we look ahead, the heat transfer equipment market is poised for growth driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for energy efficiency. International buyers are encouraged to actively explore partnerships with reputable manufacturers to secure their supply chains and gain a competitive edge. Invest in strategic sourcing today to unlock the full potential of your operations and drive sustainable growth in the future.