Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Thermal Technology
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thermal technology
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, thermal technology stands at the forefront of innovation and efficiency across various industries. From energy production to manufacturing processes, the ability to manage heat effectively is critical for optimizing performance and sustainability. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of thermal technology is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of thermal technology, encompassing a wide range of topics. You will explore the different types of thermal solutions, including heating, cooling, and insulation technologies. We delve into the materials that drive these innovations, ensuring you can assess the best fit for your specific needs. The guide also covers manufacturing and quality control standards, providing insights into supplier capabilities and product reliability.
Furthermore, we analyze market trends and pricing structures, equipping you with the knowledge to negotiate better deals and establish fruitful partnerships. To facilitate your decision-making process, we include a frequently asked questions (FAQs) section, addressing common concerns and clarifying complex concepts.
By empowering you with actionable insights and a thorough understanding of thermal technology, this guide serves as a vital resource for navigating the global market and enhancing your procurement strategies. Embrace the potential of thermal technology to drive your business forward in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Understanding thermal technology Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convection Heating | Utilizes air movement to transfer heat. | HVAC systems, industrial heating | Pros: Energy-efficient; Cons: Slower heating times. |
| Radiant Heating | Transfers heat directly through infrared radiation. | Floor heating, greenhouses | Pros: Quick heat response; Cons: Higher installation costs. |
| Induction Heating | Uses electromagnetic fields to heat conductive materials. | Manufacturing, food processing | Pros: High efficiency; Cons: Limited to specific materials. |
| Heat Pump Technology | Moves heat from one location to another using refrigerants. | Residential and commercial heating/cooling | Pros: Versatile; Cons: Performance decreases in extreme temperatures. |
| Thermal Storage Systems | Stores excess thermal energy for later use. | Renewable energy integration, district heating | Pros: Reduces peak demand; Cons: Space-intensive. |
Convection Heating
Convection heating systems operate by circulating warm air throughout a space. This technology is widely used in HVAC systems and industrial heating applications. When considering convection heating for a B2B purchase, buyers should evaluate energy efficiency ratings and the system’s ability to maintain consistent temperatures. While convection heating is generally energy-efficient, it can take longer to heat spaces compared to other methods, making it less suitable for urgent heating needs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Radiant Heating
Radiant heating systems distribute heat through infrared radiation, warming objects and surfaces directly rather than relying on air movement. This type of heating is particularly effective in applications such as floor heating and greenhouses, where uniform temperature control is crucial. B2B buyers must consider installation costs and the potential for higher energy bills in some cases. However, the quick response time and comfort level provided by radiant heating can justify the initial investment.
Induction Heating
Induction heating employs electromagnetic fields to heat conductive materials, making it an efficient choice for manufacturing and food processing industries. This technology offers rapid heating and precise temperature control, which can enhance productivity and product quality. Buyers should evaluate the types of materials that can be heated and the overall system efficiency. While induction heating is highly efficient, it may not be suitable for all applications due to its material limitations.
Heat Pump Technology
Heat pumps transfer heat using refrigerants, providing both heating and cooling capabilities. This technology is versatile and can be used in residential and commercial applications. When considering heat pumps, B2B buyers should assess the system’s efficiency ratings and the specific climate conditions of their region, as performance can diminish in extreme temperatures. The initial investment may be higher, but the long-term energy savings can be significant.
Thermal Storage Systems
Thermal storage systems are designed to store excess thermal energy for later use, making them ideal for integrating renewable energy sources and managing district heating needs. B2B buyers should consider the space requirements and the technology’s compatibility with existing systems. While thermal storage can reduce peak demand and enhance energy efficiency, it requires a larger footprint and careful planning for optimal performance.
Key Industrial Applications of thermal technology
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Thermal Technology | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Heat Treatment of Metals | Enhances material properties, increasing durability | Look for suppliers with ISO certifications and local support. |
| Food Processing | Pasteurization and Sterilization | Extends shelf life and ensures food safety | Ensure compliance with local health regulations and certifications. |
| Energy Production | Thermal Energy Storage Systems | Optimizes energy use and reduces operational costs | Evaluate technology compatibility with existing systems. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Controlled Heating for Drug Formulation | Improves product efficacy and consistency | Assess supplier’s experience with regulatory compliance. |
| Textiles | Dyeing and Finishing Processes | Enhances colorfastness and reduces water usage | Consider suppliers that offer sustainable and eco-friendly solutions. |
Manufacturing: Heat Treatment of Metals
Thermal technology plays a crucial role in the heat treatment of metals, a process that alters the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material. This application improves strength, toughness, and wear resistance, making it essential for industries like automotive and aerospace. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and South Africa, sourcing heat treatment services requires attention to local standards, certifications, and the supplier’s technological capabilities to ensure quality and compliance with industry norms.
Food Processing: Pasteurization and Sterilization
In the food processing sector, thermal technology is employed for pasteurization and sterilization, which are vital for ensuring food safety and extending shelf life. This application eliminates harmful microorganisms while preserving the nutritional value of food products. Buyers in Africa and South America should prioritize suppliers that adhere to international food safety standards and can demonstrate compliance with local regulations. This ensures that the thermal technology employed will meet health and safety requirements, safeguarding public health.
Energy Production: Thermal Energy Storage Systems
Thermal energy storage systems utilize thermal technology to store excess thermal energy for later use, which is increasingly important in renewable energy applications. This technology allows businesses to optimize energy consumption, reduce costs, and enhance grid stability. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it is crucial to assess the compatibility of these systems with existing energy infrastructures and to evaluate suppliers based on their innovation and reliability in energy solutions.
Pharmaceuticals: Controlled Heating for Drug Formulation
In the pharmaceutical industry, controlled heating is essential for drug formulation processes, ensuring that active ingredients are processed at precise temperatures to maintain efficacy and consistency. This application is critical for meeting stringent regulatory requirements. International B2B buyers from regions like Europe must choose suppliers with proven expertise in pharmaceutical thermal technologies and a strong understanding of compliance with local and international regulations to ensure product safety and effectiveness.
Textiles: Dyeing and Finishing Processes
Thermal technology is extensively used in the dyeing and finishing processes of textiles, enhancing colorfastness and reducing water consumption. This application not only improves product quality but also aligns with sustainability goals. Buyers from Africa and South America should seek suppliers that offer eco-friendly thermal solutions, as there is a growing demand for sustainable practices in the textile industry. Ensuring that suppliers can provide innovative solutions that meet environmental standards will be key to maintaining a competitive edge.
Related Video: Vacuum/Thermal Forming Explained
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thermal technology
When selecting materials for thermal technology applications, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that can significantly impact product performance and suitability. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in thermal technology, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and durability. It can withstand temperatures of up to 1,600°F (870°C) and pressures exceeding 30,000 psi, making it suitable for demanding thermal applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust and corrosion, which reduces maintenance costs over time. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing can be complex, requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for industries such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A312 for pipes and ASTM A240 for sheets. In regions like South Africa and Spain, local certifications may also be required, impacting sourcing decisions.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, with a melting point around 1,220°F (660°C). It is also resistant to corrosion due to a natural oxide layer that forms on its surface.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce shipping costs and ease installation. However, it has a lower temperature tolerance compared to stainless steel and may not perform well under high-pressure conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in heat exchangers and thermal management systems. Its compatibility with non-corrosive media makes it suitable for applications in HVAC and automotive sectors.
Considerations for Buyers: International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for extruded shapes and ANSI H35.2 for aluminum alloys. In Europe, the EN 573 standard may also apply, which can influence material selection.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper boasts exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity, with a melting point of approximately 1,984°F (1,085°C). It is also resistant to corrosion in many environments, particularly when alloyed.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its superior heat transfer capabilities, making it ideal for thermal applications. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be susceptible to corrosion in certain conditions, particularly in marine environments.
Impact on Application: Copper is widely used in heat exchangers, refrigeration systems, and electrical applications due to its excellent thermal properties.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B280 for copper tubes and ASTM B75 for copper and copper alloys. In regions like the Middle East, local regulations regarding copper usage in construction may also affect procurement.
Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composite materials, often made of a combination of polymers and fibers, can withstand a wide range of temperatures and pressures depending on their formulation. They are lightweight and can be engineered for specific thermal properties.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of composites is their versatility and ability to be tailored for specific applications. However, they can be more costly to manufacture and may have limitations in terms of long-term durability compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in aerospace and automotive applications where weight reduction is critical, and thermal performance is required.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards such as ASTM D3039 for tensile properties and ASTM E1952 for thermal properties. In Europe, adherence to EN 13126 for performance requirements may also be necessary.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for thermal technology | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Oil & gas pipelines, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | HVAC systems, automotive applications | Lightweight, good thermal conductivity | Lower temperature tolerance | Medium |
| Copper | Heat exchangers, refrigeration systems | Superior heat transfer capabilities | Higher cost, corrosion susceptibility | High |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Versatile, tailored properties | Higher manufacturing costs | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for thermal technology applications, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thermal technology
Manufacturing thermal technology products involves a series of well-defined processes that ensure efficiency, performance, and reliability. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below is an overview of the typical manufacturing stages, key techniques, and quality assurance measures that you should consider when sourcing thermal technology products.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The initial stage of manufacturing involves selecting and preparing the right materials. Common materials used in thermal technology include metals (like aluminum and copper), ceramics, and advanced composites.
- Material Selection: It is vital to choose materials that possess high thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock. For instance, copper is often preferred for heat exchangers due to its excellent thermal properties.
- Pre-treatment Processes: This includes cleaning, cutting, and shaping raw materials to meet specifications. Techniques such as laser cutting or water jet cutting are commonly employed for precision.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes to shape them into the desired components.
- Techniques: Common forming techniques include extrusion, stamping, and casting. For example, extrusion is frequently used for creating tubes or profiles that require uniform thermal properties.
- Molding: In cases where ceramic materials are used, injection molding may be employed to achieve complex shapes while maintaining thermal efficiency.
3. Assembly
After individual components are formed, they are assembled into final products.
- Welding and Joining: Techniques such as TIG welding or brazing are essential for joining metal components, ensuring structural integrity while minimizing thermal resistance.
- Modular Assembly: In complex thermal systems, modular assembly techniques are adopted to facilitate easier maintenance and upgrades.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves refining the product to enhance performance and appearance.
- Surface Treatments: Processes such as anodizing or powder coating are utilized to improve corrosion resistance and thermal performance.
- Quality Checks: This stage often incorporates initial quality checks to ensure that products meet the desired specifications before final testing.
Quality Assurance
To maintain high standards in thermal technology manufacturing, quality assurance is critical. B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international and industry-specific standards.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This is the most recognized quality management standard worldwide, ensuring that organizations meet customer and regulatory requirements. Suppliers should provide evidence of ISO 9001 certification.
- CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards to bear the CE mark, indicating compliance with EU legislation.
Industry-Specific Standards
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for products used in the oil and gas industry, which can be crucial for thermal technology applications in these sectors.
- ASTM Standards: The American Society for Testing and Materials provides specifications for materials and products, ensuring they meet certain performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints established to ensure product integrity.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during production help identify defects early, reducing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection stage assesses the finished product against specifications, ensuring it is ready for shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing is essential to confirm that thermal technology products meet performance and safety standards. Common methods include:
- Thermal Conductivity Tests: These tests measure the material’s ability to conduct heat, crucial for assessing performance.
- Pressure Testing: Often used in heat exchangers and boilers to ensure they can withstand operational pressures without failure.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection are employed to detect internal flaws without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for risk management.
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and test results can help in assessing the reliability of the products offered.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing process can provide an unbiased view of quality compliance.
Regional Considerations
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should also consider regional nuances in quality control and manufacturing standards.
- Local Regulations: Understanding local regulations regarding product safety and environmental impact is crucial, as they can vary significantly between regions.
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of cultural differences that may influence communication and business practices with suppliers. This understanding can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships.
Conclusion
Navigating the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols in thermal technology requires careful consideration and due diligence. By familiarizing yourself with these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers capable of delivering high-quality thermal technology solutions that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thermal technology Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Thermal Technology
When sourcing thermal technology, B2B buyers must navigate a multifaceted cost structure that includes various components. A detailed understanding of these elements is crucial for effective budgeting and strategic procurement.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. High-performance materials, such as specialized alloys or advanced composites, often come with premium pricing. Buyers should assess the trade-off between material costs and performance benefits.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. In regions like Africa and South America, labor may be less expensive, but the skill level and availability can impact quality. Assessing local labor markets and supplier capabilities is essential.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturers will have lower overhead, which can translate into better pricing for buyers. Understanding a supplier’s production capacity and efficiency can provide insight into their pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for custom or specialized thermal technology products. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs upfront and consider how these costs affect the overall pricing, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes can add to the cost but is vital for ensuring product reliability. Suppliers with certifications such as ISO 9001 may charge higher prices, but this often guarantees a higher level of quality assurance.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary significantly based on the origin and destination. Incoterms play a crucial role in defining who bears these costs, which can affect total pricing. Buyers should consider the logistics network of suppliers to minimize these costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margin is influenced by market competition and demand. Understanding market trends can help buyers negotiate better pricing. It’s essential to consider both competitive pricing and the value offered.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of thermal technology:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders typically yield better pricing, so buyers should evaluate their purchasing strategy accordingly.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom solutions can drive up costs due to increased design and manufacturing complexity. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against standard options.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can increase initial costs but may lead to long-term savings through improved performance and reduced failure rates.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and financial stability can influence pricing. A well-established supplier may offer more consistent quality but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is critical for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall costs.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in open negotiations. Understanding the cost structure can provide leverage when discussing pricing. Be prepared to discuss volume commitments to achieve better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond initial pricing. Consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs associated with thermal technology. A higher upfront cost might be justified by lower TCO.
-
Pricing Nuances: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing differences. Currency fluctuations, local tariffs, and regional economic conditions can all impact pricing.
-
Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on suppliers. Request quotes from multiple vendors and assess their proposals based on the complete cost structure rather than just price.
Disclaimer
This analysis provides indicative pricing insights based on current market trends. Actual costs may vary based on specific project requirements, supplier negotiations, and changing market conditions. Always conduct a thorough review and obtain detailed quotes tailored to your unique needs.
Spotlight on Potential thermal technology Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘thermal technology’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thermal technology
Key Technical Properties in Thermal Technology
Understanding the technical properties of thermal technology is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially when sourcing equipment and materials across diverse markets. Below are several critical specifications that buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade: This refers to the classification of materials based on their properties, such as thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and strength. For instance, high-grade stainless steel is often preferred in thermal applications due to its durability and resistance to oxidation. Buyers should assess material grades to ensure that the products meet their operational requirements and comply with industry standards.
-
Thermal Conductivity: This property measures a material’s ability to conduct heat. It is typically expressed in watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K). For thermal insulation applications, a lower thermal conductivity is desirable, while materials used in heat exchangers may require higher values. Buyers should evaluate thermal conductivity to determine efficiency and performance in their specific applications.
-
Tolerance: Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or property of a product. In thermal technology, precise tolerances are essential for components that must fit together accurately, such as in heat exchangers or thermal coupling systems. Buyers should specify tolerances to ensure compatibility and performance in their installations.
-
Operating Temperature Range: This specification defines the temperatures within which a material or device can function safely and effectively. It is critical for ensuring that thermal equipment performs reliably under the expected environmental conditions. Buyers should verify that the operating temperature range aligns with their application requirements to prevent equipment failure.
-
Efficiency Rating: Efficiency ratings assess how well a thermal system converts energy into usable heat. This metric is particularly important for HVAC systems and industrial heaters, where energy consumption can significantly impact operational costs. Buyers should prioritize products with high efficiency ratings to optimize performance and reduce energy expenditures.
Common Trade Terminology in Thermal Technology
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and negotiations in the thermal technology market. Here are several essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the thermal technology sector, buyers often engage with OEMs to source specific components or systems tailored to their requirements. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers navigate sourcing and ensure quality.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This term refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and can impact purchasing decisions. Buyers should assess MOQs to align with their demand forecasts and inventory management strategies.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document issued by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This process is crucial for comparing costs and terms. Buyers should provide detailed specifications in their RFQs to receive accurate and competitive quotes.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Key Incoterms relevant to thermal technology include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify shipping responsibilities and costs.
-
Lead Time: This term indicates the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the products are delivered. In thermal technology, lead times can affect project timelines and operational readiness. Buyers should inquire about lead times to plan their supply chains effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing thermal technology solutions, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the thermal technology Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The thermal technology sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by various global factors. The increasing demand for energy efficiency and the urgency to mitigate climate change are key drivers shaping the market. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly prioritizing advanced thermal solutions that not only enhance operational efficiency but also align with sustainability goals.
Emerging trends include the adoption of smart thermal systems that leverage IoT and AI technologies to optimize energy consumption and monitor system performance in real-time. This digital transformation is crucial for businesses looking to reduce costs and improve service delivery. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards modular thermal systems, which offer flexibility and scalability, enabling companies to adapt to changing demands without significant capital investment.
Another noteworthy trend is the rise of partnerships and collaborations between technology providers and end-users. This approach facilitates the co-development of tailored solutions that meet specific industry needs, allowing buyers to tap into innovative technologies while ensuring a more integrated supply chain. For instance, buyers from Spain and South Africa are increasingly collaborating with local manufacturers to develop region-specific thermal solutions that address local climate challenges and energy policies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
In the thermal technology sector, sustainability is not just a trend; it is becoming a fundamental requirement. The environmental impact of thermal technologies, particularly in energy consumption and emissions, has prompted B2B buyers to seek solutions that minimize their ecological footprint. This shift is reflected in the increasing preference for products that are designed with energy efficiency in mind and that utilize sustainable materials.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are now scrutinizing their supply chains to ensure compliance with environmental and social governance (ESG) standards. Implementing ethical sourcing practices can enhance a company’s reputation and build trust with stakeholders. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design).
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials and technologies is gaining traction. Thermal technology solutions that incorporate recyclable materials or are produced through sustainable processes not only reduce environmental impact but can also offer cost savings over the long term. For instance, opting for thermal insulation made from recycled materials can significantly lower energy costs while enhancing thermal performance.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of thermal technology can be traced back to the early industrial revolution when steam engines and boilers became integral to manufacturing processes. Over the decades, advancements in materials and engineering led to more efficient thermal systems, paving the way for modern applications in various industries, including manufacturing, HVAC, and energy generation.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards integrating digital technologies with thermal systems, driven by the need for greater efficiency and sustainability. This transition has not only transformed how thermal solutions are designed and implemented but has also opened new avenues for international collaboration and innovation. Today, B2B buyers are at the forefront of this evolution, seeking cutting-edge solutions that align with their operational and sustainability objectives.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thermal technology
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of thermal technology?
To ensure you choose a reliable supplier, start by researching their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials. Engage in direct communication to assess their responsiveness and expertise. Request references from past clients, particularly those in your region, to gauge their experience. Additionally, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Consider visiting their facilities or participating in virtual audits to observe their operations firsthand. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing thermal technology?
Customization can significantly enhance the efficiency and performance of thermal technology in your specific application. Discuss your unique requirements with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process. Inquire about their ability to tailor products according to your specifications, including size, materials, and features. Always request samples or prototypes to evaluate the customization quality before placing a larger order. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for thermal technology products?
MOQs can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the product. It’s crucial to clarify these details upfront, as they can impact your purchasing decisions and inventory management. Lead times may also differ based on the customization required and the supplier’s production capacity. Establish a clear timeline for delivery and ensure that the supplier can meet your project deadlines to avoid disruptions. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in thermal technology suppliers?
Quality assurance is vital to ensure that the thermal technology you source meets both performance and safety standards. Ask suppliers about their quality control processes, including testing procedures and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE). Request documentation that outlines their QA protocols and any test results for the specific products you’re interested in. Regular audits and third-party inspections can also provide additional assurance of product quality.
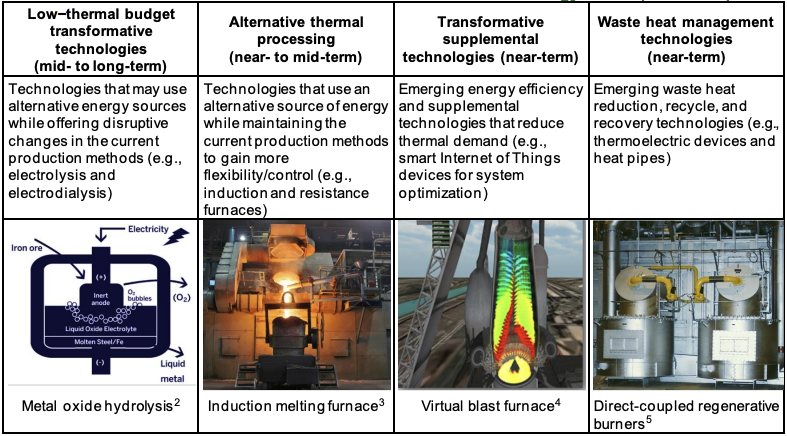
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How do I handle payment terms and conditions when sourcing internationally?
When dealing with international suppliers, it’s essential to agree on clear payment terms to mitigate financial risks. Discuss payment methods (e.g., letters of credit, bank transfers) and consider using escrow services for larger transactions. Understand the currency exchange implications and any additional fees involved. Always ensure that payment milestones are tied to specific deliverables to protect your investment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing thermal technology?
Effective logistics planning is critical when importing thermal technology. Assess the supplier’s ability to handle shipping, including packaging standards that protect products during transit. Investigate the import regulations in your country, as well as duties and tariffs that may apply. Establish a reliable logistics partner to ensure timely delivery and consider incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to clarify responsibilities between you and the supplier. -
How can I resolve disputes with thermal technology suppliers?
Dispute resolution can be challenging in international transactions. To minimize conflicts, ensure that all agreements are documented clearly, including terms of delivery, payment, and quality expectations. If disputes arise, start with direct communication to seek a resolution. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods. Always include a clause in your contracts that outlines the process for dispute resolution to avoid lengthy legal battles. -
What certifications should thermal technology products have for compliance?
Certifications are critical indicators of quality and compliance with industry standards. Depending on your market, look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management, CE marking for European markets, and UL certification for safety standards. Verify that the products you are sourcing meet local regulatory requirements, as non-compliance can lead to costly delays and fines. Request detailed documentation of certifications from your suppliers to ensure transparency and trust.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thermal technology
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of thermal technology presents a vital opportunity for international B2B buyers to enhance operational efficiency and competitiveness. By leveraging advanced thermal solutions, companies can optimize energy consumption, reduce costs, and improve sustainability practices.
Key Takeaways:
– Value Proposition: Investing in thermal technology can significantly lower operational costs while meeting increasing regulatory demands for environmental responsibility.
– Supplier Relationships: Establishing strong partnerships with innovative suppliers is crucial. This not only ensures access to cutting-edge technologies but also fosters collaboration for customized solutions tailored to specific market needs.
– Market Trends: Stay informed on emerging trends such as IoT integration and renewable energy applications within thermal technology. These innovations are shaping the future landscape and can provide a competitive edge.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize strategic sourcing initiatives that align with their long-term goals. Engaging in thorough market research and establishing a robust supplier network will position companies to navigate the evolving thermal technology landscape effectively. Take action today to harness the potential of thermal solutions and drive your business forward.