Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Vacuum Forming Services
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vacuum forming services
In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, vacuum forming services have emerged as an essential technique for producing high-quality, cost-effective components across diverse industries. This process, characterized by its ability to create intricate shapes from thermoplastic sheets, is particularly valuable for B2B buyers seeking rapid prototyping, efficient production runs, and innovative design capabilities. As companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive to maintain competitive advantages, understanding the nuances of vacuum forming becomes imperative for informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of the vacuum forming landscape, covering various types of vacuum forming processes and their optimal applications. Buyers will gain insights into material selection, ensuring that the chosen plastics meet performance and compliance requirements. Additionally, the guide delves into manufacturing and quality control best practices that mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
A thorough examination of supplier evaluation frameworks and regional market dynamics further empowers decision-makers to identify reliable partners, while a detailed cost breakdown allows for clearer budgeting and financial planning. To address common concerns, the guide also includes FAQs that clarify logistics, contracts, and industry standards.
By leveraging the insights provided, international B2B buyers—whether from Nairobi to Rome—can confidently navigate the complexities of the vacuum forming market, optimize their procurement strategies, and drive innovation within their organizations.
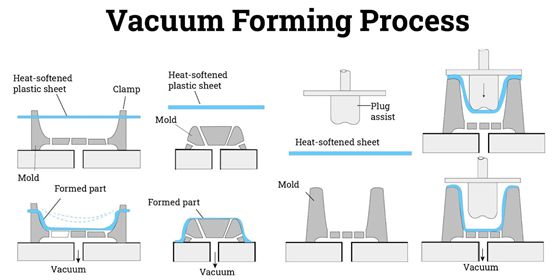
Understanding vacuum forming services Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Vacuum Forming | Utilizes a single mold to shape heated plastic sheets | Packaging, display cases, automotive parts | Cost-effective for low to medium volumes; limited design complexity. |
| Twin Sheet Vacuum Forming | Involves two sheets forming a hollow part through simultaneous forming | Medical devices, containers, automotive components | Stronger parts with internal structures; higher tooling costs. |
| Heavy Gauge Vacuum Forming | Uses thicker plastic sheets for larger parts | Industrial applications, large containers | Suitable for high-strength applications; longer cooling times. |
| Vacuum Thermoforming | Combines heating and vacuum for precision shaping | Consumer products, appliances, custom parts | High detail and finish; may require higher initial investment. |
| Clear Vacuum Forming | Employs clear materials for transparency | Lenses, displays, protective covers | Ideal for aesthetic applications; may involve more complex quality control. |
Standard Vacuum Forming
Standard vacuum forming is a widely adopted technique that utilizes a single mold to shape heated plastic sheets. This method is particularly effective for producing packaging, display cases, and automotive parts. B2B buyers appreciate its cost-effectiveness for low to medium volume runs; however, it has limitations in terms of design complexity and precision. When sourcing this service, buyers should consider the material options available and how they align with their product specifications.
Twin Sheet Vacuum Forming
Twin sheet vacuum forming is an advanced variation that involves two heated plastic sheets being formed simultaneously to create hollow parts. This method is particularly beneficial for applications in the medical and automotive industries, where strength and internal structures are crucial. While it offers enhanced durability and design flexibility, the tooling costs are generally higher. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between the initial investment and the long-term benefits of producing stronger components.
Heavy Gauge Vacuum Forming
Heavy gauge vacuum forming employs thicker plastic sheets, making it suitable for producing larger parts, such as industrial applications and large containers. This technique provides the necessary strength and durability for demanding environments. However, the cooling times are longer, which can affect production speed. B2B buyers should assess their production timelines and volume needs against the benefits of using thicker materials.
Vacuum Thermoforming
Vacuum thermoforming is a refined approach that combines heating and vacuum techniques to achieve high precision in shaping plastic materials. This method is ideal for consumer products, appliances, and custom parts that require a high level of detail and finish. While it can deliver superior quality, the initial investment may be higher due to the necessary technology and equipment. Buyers should weigh the quality benefits against their budget constraints.
Clear Vacuum Forming
Clear vacuum forming focuses on using transparent materials to create visually appealing products such as lenses, displays, and protective covers. This technique is essential for applications where aesthetics and visibility are paramount. Although it may require more complex quality control processes to ensure clarity and surface finish, the final product can significantly enhance the customer experience. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with expertise in clear materials to ensure high-quality outcomes.
Related Video: Vacuum Forming Machine V-series vacuum forming ABS plastic 3 mm
Key Industrial Applications of vacuum forming services
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Vacuum Forming Services | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of interior trim and dashboards | Lightweight, durable components that enhance aesthetics and functionality | Material selection for heat resistance and durability; compliance with safety standards |
| Medical | Creation of sterile packaging and equipment trays | Ensures safety and compliance with regulatory standards; protects sensitive medical devices | Material biocompatibility; precise dimensional accuracy; ability to meet sterilization requirements |
| Consumer Goods | Packaging for electronics and household items | Cost-effective, attractive packaging that protects products during transit | Customization options; sustainability of materials; design flexibility |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of interior panels and enclosures | High-strength, lightweight components that contribute to overall aircraft efficiency | Strict adherence to aerospace standards; rigorous quality assurance processes |
| Retail Display | Production of custom displays and signage | Eye-catching, tailored solutions that enhance customer engagement and brand visibility | Design capabilities; material options for durability and aesthetics; rapid prototyping availability |
Automotive Applications
Vacuum forming services are extensively used in the automotive industry to create components such as dashboards, door panels, and interior trim. This process allows manufacturers to produce large, lightweight parts that are both durable and aesthetically pleasing. For B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing partners must ensure that materials used can withstand high temperatures and meet safety standards. The ability to customize designs for specific vehicle models adds significant value, making it essential for buyers to work closely with suppliers to meet these requirements.
Medical Applications
In the medical sector, vacuum forming is critical for producing sterile packaging and equipment trays. This process allows for the creation of biocompatible parts that meet stringent regulatory standards, ensuring the safety of sensitive medical devices. B2B buyers from the Middle East and Europe must prioritize sourcing materials that are not only compliant with health regulations but also capable of maintaining the integrity of sterile environments. Additionally, precision in dimensions is crucial to ensure that medical devices fit securely within their packaging, which requires reliable quality assurance practices from suppliers.
Consumer Goods Applications
Vacuum forming is widely utilized for packaging in the consumer goods sector, particularly for electronics and household items. This method allows for the production of cost-effective, visually appealing packaging that protects products during transit. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, it is vital to consider customization options to reflect brand identity and consumer preferences. Sustainability is also a growing concern, so sourcing partners should offer eco-friendly material choices to align with market trends and consumer expectations.
Aerospace Applications
The aerospace industry leverages vacuum forming to manufacture interior panels and enclosures that are both lightweight and strong. These components are essential for enhancing aircraft efficiency and performance. B2B buyers must be aware of the strict standards governing aerospace materials and the necessity for rigorous quality assurance processes. Suppliers should demonstrate their capability to meet these standards and provide detailed documentation to ensure compliance, particularly for buyers from regions with stringent regulatory environments.
Retail Display Applications
In retail, vacuum forming services are employed to create custom displays and signage that attract customers and enhance brand visibility. This application allows businesses to present their products in a visually appealing manner while also being cost-effective. Buyers should focus on sourcing partners that offer robust design capabilities and a variety of material options to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal. The ability to rapidly prototype and produce small to medium runs can also help businesses stay agile in a competitive retail landscape.
Related Video: What is Vacuum Forming?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vacuum forming services
When selecting materials for vacuum forming services, B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence product performance, manufacturing complexity, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in vacuum forming, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Key Properties:
ABS is known for its excellent impact resistance and toughness, with a temperature rating of approximately 80°C (176°F). It offers good chemical resistance, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of ABS makes it ideal for products that require resilience, such as automotive components and consumer goods. However, it can be more expensive than other thermoplastics, and its processing can be complex due to its tendency to warp if not heated evenly.
Impact on Application:
ABS is compatible with a range of media, including oils and mild acids, making it suitable for automotive and household applications. However, it is not recommended for prolonged exposure to strong solvents.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that ABS products comply with local regulations, such as ASTM standards in the U.S. or EN standards in Europe. Understanding the sourcing capabilities in regions like Africa and South America, where ABS availability may vary, is crucial.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified)
Key Properties:
PETG is characterized by its excellent clarity and toughness, with a temperature resistance of up to 70°C (158°F). It has good chemical resistance and is less prone to stress cracking than other materials.
Pros & Cons:
The clarity of PETG makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring transparency, such as packaging and display cases. However, it can be more expensive than standard plastics and may require specific processing conditions to avoid deformation.
Impact on Application:
PETG is suitable for applications in the medical and food packaging industries due to its biocompatibility and recyclability. Its resistance to UV light also makes it ideal for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions with strict environmental regulations, like Europe, should consider PETG’s recyclability and compliance with sustainability initiatives. Knowledge of local suppliers who can provide high-quality PETG is essential.
Polycarbonate
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is renowned for its high impact resistance and heat tolerance, with a temperature rating of up to 120°C (248°F). It is also flame-retardant and offers good dimensional stability.
Pros & Cons:
The exceptional durability of polycarbonate makes it suitable for demanding applications, such as safety equipment and automotive parts. However, it is relatively expensive and can be more challenging to process compared to other thermoplastics.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate’s resistance to high temperatures and impact makes it ideal for applications requiring safety and reliability, such as protective covers and lenses. Its compatibility with various chemicals also enhances its usability across industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that polycarbonate products meet relevant safety standards, such as those set by ASTM or ISO. Understanding the local manufacturing capabilities in regions like the Middle East can help in sourcing reliable polycarbonate products.
Polystyrene
Key Properties:
Polystyrene is lightweight and has a temperature resistance of around 70°C (158°F). It is easy to mold and has good clarity, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
The low cost and ease of processing make polystyrene a popular choice for packaging and disposable products. However, it has lower impact resistance compared to other materials and is susceptible to environmental stress cracking.
Impact on Application:
Polystyrene is commonly used in packaging and consumer goods, where cost-effectiveness is critical. However, its limited durability makes it unsuitable for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the environmental regulations regarding polystyrene, especially in regions like Europe, where single-use plastics are under scrutiny. Ensuring compliance with local standards is vital for successful procurement.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for vacuum forming services | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Automotive parts, consumer goods | Excellent impact resistance | Higher cost, complex processing | Medium |
| PETG | Medical packaging, display cases | High clarity and recyclability | More expensive, specific processing | High |
| Polycarbonate | Safety equipment, protective covers | High durability and heat resistance | Expensive, challenging to process | High |
| Polystyrene | Packaging, disposable products | Low cost and easy to mold | Low impact resistance, environmental concerns | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights to make informed decisions when sourcing vacuum forming services, ensuring compatibility with their specific application needs and regional regulations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vacuum forming services
The manufacturing process for vacuum forming services involves several critical stages, each contributing to the efficiency and quality of the final product. For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these stages and the associated quality assurance measures is vital for ensuring optimal sourcing decisions.
Manufacturing Process
1. Material Preparation
The first step in vacuum forming is selecting the appropriate plastic material, which directly impacts the performance and durability of the final product. Common materials include:
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Known for its impact resistance and ease of fabrication.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG): Offers excellent clarity and is suitable for applications requiring transparency.
- Polycarbonate: Provides high impact resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for demanding applications.
- Polystyrene: A cost-effective option for less demanding applications.
Once the material is selected, it is cut into sheets of the required dimensions. The sheets must be uniform in thickness to ensure consistent heating and forming.
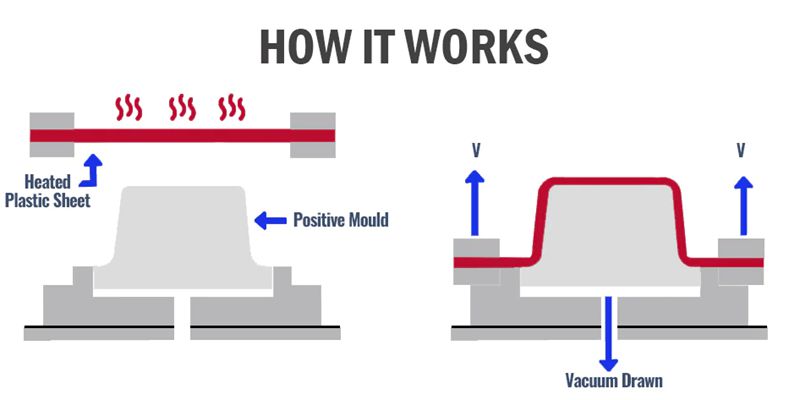
2. Heating
Heating is a crucial stage where the plastic sheets are clamped and placed in an oven until they reach a pliable state. Precise temperature control is essential to avoid overheating, which can lead to material degradation, or underheating, which can result in poor forming. The optimal temperature varies depending on the material but typically falls between 160°C to 220°C.
3. Forming
After heating, the pliable plastic sheet is transferred to the forming station. Here, it is draped over a mold, and a vacuum is applied. The vacuum removes air between the mold and the sheet, pulling the material tightly against the mold to achieve the desired shape.
Key techniques in this stage include:
- Single-stage forming: The sheet is formed in one step, suitable for simpler designs.
- Multi-stage forming: This involves multiple heating and forming cycles for more complex shapes, allowing for enhanced detail and precision.
4. Cooling
Once formed, the plastic part needs to cool to retain its shape. This can be accelerated using fans or water sprays. Effective cooling is critical to prevent warping and ensure the dimensional accuracy of the final product.
5. Assembly and Finishing
After cooling, the formed parts are removed from the mold and trimmed to eliminate excess material. Additional finishing processes may include drilling, painting, or adding hardware, depending on the product specifications. Quality checks at this stage ensure that parts meet the required standards before shipping.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) in vacuum forming is essential to guarantee that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards and the associated quality checkpoints can significantly impact sourcing decisions.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Buyers should look for suppliers that are ISO 9001 certified, as it indicates a commitment to quality.
- CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards to be marketed. A CE mark on vacuum-formed products demonstrates compliance with EU directives.
- API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas industry, API standards ensure that products meet specific safety and performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control in vacuum forming typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they are used in production. Ensuring materials meet specifications is critical for the overall quality of the formed parts.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, operators monitor various parameters such as temperature, vacuum levels, and material thickness. Regular checks at this stage help identify potential issues before they affect the final product.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the parts are finished, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to ensure they meet all specifications and standards. This may involve visual inspections, dimensional checks, and functional testing.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of several common testing methods used in the quality assurance of vacuum-formed products:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, consistency in color, and overall appearance.
- Dimensional Measurement: Using calipers and gauges to ensure parts meet specified dimensions.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring the product performs as intended, especially for components used in critical applications like medical devices or automotive parts.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are several strategies to ensure supplier reliability:
-
Conducting Audits: Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and quality management systems. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party audit services.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide quality control reports that detail their processes, testing results, and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These services can conduct independent quality checks before shipment, helping to mitigate risks associated with sourcing from unfamiliar suppliers.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers must also consider regional nuances in quality control. For example, suppliers in Africa may face different regulatory environments compared to those in Europe or the Middle East. Understanding these differences and the associated risks is vital for international sourcing strategies.
Buyers should also be aware of cultural and communication barriers that may affect quality assurance processes. Building strong relationships with suppliers and establishing clear expectations can help ensure that quality standards are consistently met across different regions.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating across diverse regions, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for vacuum forming services is essential. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, and robust quality control frameworks, buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies and ensure high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vacuum forming services Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of vacuum forming services is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those in emerging markets like Africa and South America, as well as established markets in Europe and the Middle East. Below, we break down the essential cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable buyer tips to optimize sourcing strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of plastic materials significantly affects costs. Common materials such as ABS, PETG, and polycarbonate vary in price based on properties like strength and clarity. Sustainable options, like biodegradable plastics, may also come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate depending on the region. For example, manufacturing labor in Africa may be more cost-effective than in Europe, but this can also impact the skill level and efficiency of production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. In regions with higher operational costs, such as Western Europe, overhead may constitute a larger portion of the total cost.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are significant in vacuum forming, particularly for custom molds. Initial investment in high-quality tooling can be substantial, but it is amortized over the production run, making it essential to consider projected volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through stringent QC processes adds to overall costs. Buyers should evaluate suppliers’ QC certifications and practices, as this can impact both costs and product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary widely based on distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. For international buyers, understanding these costs is vital for accurate total landed costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can differ based on competition and market positioning. Negotiating favorable terms can help buyers secure better pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing structures often benefit bulk orders. Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can lead to economies of scale, reducing the unit price significantly.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom parts will generally incur higher costs due to the additional time and materials required for unique designs. Clear communication of specifications can help avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: Prices can fluctuate based on material availability and market demand. Buyers should keep abreast of market trends to anticipate changes in pricing.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products meeting higher industry standards often come at a premium. Certifications such as ISO can reassure buyers of quality but may also increase costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more but offer better assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers to determine who bears the costs and risks during transportation. This can significantly impact total costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume purchases or long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Building strong relationships with suppliers can also facilitate more favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential rework costs. This holistic view aids in making informed sourcing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of local market conditions and currency fluctuations that may affect pricing. For example, buyers in Africa may face different logistical challenges compared to those in Europe.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Assess suppliers based on quality, delivery times, and flexibility in meeting custom requests. A thorough vetting process can prevent costly errors and delays.
Disclaimer
Prices and costs mentioned are indicative and can vary significantly based on specific project requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough due diligence and request detailed quotes tailored to their needs.
Spotlight on Potential vacuum forming services Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘vacuum forming services’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vacuum forming services
Key Technical Properties for Vacuum Forming Services
When sourcing vacuum forming services, understanding the technical specifications of the materials and processes involved is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of plastic used in the vacuum forming process, such as ABS, PETG, or polycarbonate. Each material has unique properties, such as impact resistance, heat tolerance, and clarity. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring that the final product meets the intended performance requirements and regulatory standards, especially in industries like automotive and medical.
2. Thickness Tolerance
Thickness tolerance indicates the acceptable variation in the thickness of the formed plastic sheet. It is crucial for ensuring consistent part quality and performance. In vacuum forming, standard tolerances typically range from ±0.5 mm to ±1 mm, depending on the material. Understanding these tolerances helps buyers maintain quality control and minimize rework costs, especially in applications where dimensional accuracy is critical.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture and appearance of the formed part. Options can range from matte to glossy finishes, which affect aesthetic appeal and functionality (e.g., glare reduction). For B2B buyers, specifying the desired surface finish is important to align with branding, product usability, and market expectations, particularly in consumer goods and electronics.
4. Cycle Time
Cycle time refers to the total time taken to complete one production cycle, including heating, forming, cooling, and trimming. Understanding cycle times helps B2B buyers evaluate production efficiency and lead times, which are crucial for meeting tight market deadlines. Faster cycle times can significantly enhance a company’s responsiveness to market changes.
5. Dimensional Accuracy
Dimensional accuracy is the degree to which the produced part conforms to the specified dimensions. This property is essential for applications requiring high precision, such as medical devices or intricate components. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s capabilities to ensure that the parts produced will meet their specific requirements and tolerances.
Common Trade Terminology in Vacuum Forming Services
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can streamline communication with suppliers and enhance negotiation outcomes. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable partners for sourcing components that integrate seamlessly into their products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is critical for buyers to manage inventory effectively and avoid excess stock or insufficient supply, particularly when dealing with new product launches.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific quantity of products or services. For B2B buyers, crafting a detailed RFQ can lead to better pricing and service terms, ensuring that all specifications and requirements are clearly communicated.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to minimize risks and costs associated with international logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the finished product. Awareness of lead times helps buyers plan their production schedules and inventory management, ultimately ensuring that they can meet customer demands without delays.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and foster stronger partnerships with vacuum forming service providers.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vacuum forming services Sector
Global manufacturers are increasingly recognizing the versatility of vacuum forming services as a solution for producing high-quality parts across various industries. The demand for custom, lightweight, and durable components is being driven by several factors, including the rise of sustainable practices, technological advancements, and the need for rapid prototyping. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are navigating a landscape that is shaped by these trends.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Market Overview & Key Trends
The vacuum forming market is experiencing significant growth, primarily fueled by the automotive, medical, and consumer goods sectors. Technological advancements such as automation and IoT are enhancing production efficiency and precision, allowing manufacturers to optimize their processes. Emerging materials like biodegradable plastics and advanced polymers are broadening the scope of applications, making vacuum forming a viable option for companies aiming to meet environmental standards.
In Africa, manufacturers are leveraging local resources and establishing agile production networks, while South America is seeing a rise in innovative startups focusing on flexible manufacturing. The Middle East is positioning itself as a hub for high-tech manufacturing, driving demand for precision components. Meanwhile, Europe’s established industries are increasingly adopting vacuum forming for its cost-effectiveness and ability to produce complex geometries.
International buyers should prioritize supplier evaluation based on technological capabilities, production capacity, and compliance with international standards. Understanding regional market dynamics is essential for securing competitive pricing and ensuring product quality. Keeping abreast of these trends will empower buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their strategic goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical component of procurement strategies in the vacuum forming sector. The environmental impact of plastic production and disposal is prompting companies to seek ethical sourcing practices. Buyers should look for suppliers committed to reducing their carbon footprint through energy-efficient manufacturing processes and waste reduction initiatives.
The use of green certifications and sustainable materials is increasingly important. Materials such as recycled PETG and biodegradable plastics are gaining traction, enabling businesses to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Furthermore, suppliers that adhere to ethical labor practices and transparent supply chains are becoming more attractive to buyers, particularly in regions where corporate responsibility is prioritized.
Incorporating sustainability into the sourcing strategy not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. B2B buyers should engage with suppliers to understand their sustainability initiatives and ensure that their procurement practices contribute to a circular economy.
Brief Evolution/History
The vacuum forming process has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially used for simple packaging solutions, advancements in material science and technology have expanded its applications to complex components in various industries. The introduction of automation and digital monitoring systems has transformed vacuum forming into a high-efficiency manufacturing method, enabling rapid prototyping and production of intricate designs.
As sustainability became a global priority, the industry has adapted by incorporating eco-friendly materials and practices, ensuring that vacuum forming remains relevant in today’s manufacturing landscape. International B2B buyers can benefit from this evolution by leveraging advanced vacuum forming solutions to meet their production needs while adhering to sustainability goals.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vacuum forming services
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers for vacuum forming services?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience and expertise in vacuum forming. Request case studies or samples of previous work to assess quality. Verify certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and other relevant industry standards. Evaluate their production capacity and technology to ensure they can meet your specific needs. Finally, check client testimonials and references to gauge reliability and customer service. -
Can I customize my vacuum-formed products, and what are the limitations?
Yes, customization is a significant advantage of vacuum forming. You can tailor designs, dimensions, colors, and materials to suit your requirements. However, keep in mind that complex geometries may increase production costs and lead times. Discuss your design with the supplier early to understand any limitations related to mold capabilities or material selection, ensuring that your vision aligns with technical feasibility. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for vacuum forming services?
MOQs for vacuum forming can vary widely based on the supplier and specific project requirements. Generally, you might expect MOQs ranging from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times typically range from 2 to 6 weeks, depending on factors such as mold preparation, material availability, and production schedules. It’s advisable to communicate your volume needs and timelines during initial discussions to ensure alignment with the supplier’s capabilities.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How do payment terms and conditions typically work in international vacuum forming contracts?
Payment terms can differ among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon completion or before shipment. Consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow, such as net 30 or net 60 days. Always ensure that payment methods are secure, and be aware of any foreign exchange risks when dealing with international suppliers. Clear communication on payment terms should be established in the contract. -
What quality assurance processes should I expect from a vacuum forming supplier?
A reputable vacuum forming supplier should implement a robust quality assurance (QA) process. This includes material inspections, in-process checks, and final product evaluations against agreed specifications. Ask about their QA certifications and whether they utilize standardized testing methods. Additionally, inquire if they can provide documentation or certificates of compliance for materials used, particularly for industries with strict regulatory standards, such as medical or automotive. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping when sourcing vacuum-formed products internationally?
Effective logistics management is crucial for international sourcing. Confirm whether the supplier offers shipping options, including freight forwarders or direct shipping. Understand the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) that will govern the transaction, as they dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Consider working with a logistics partner who specializes in international trade to help navigate complexities such as tariffs and import regulations. -
What steps should I take if there is a dispute with a vacuum forming supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first, attempt to resolve the issue amicably through direct communication with the supplier. Document all correspondences and agreements for reference. If resolution fails, refer to the contract for dispute resolution clauses, which may include mediation or arbitration. Engaging a legal advisor familiar with international trade laws can provide guidance on your rights and obligations. Maintaining a professional relationship is essential, even in challenging situations. -
What certifications or standards should vacuum forming suppliers have to ensure product safety and compliance?
Depending on your industry, suppliers should hold relevant certifications that demonstrate adherence to safety and quality standards. For example, ISO 9001 indicates a commitment to quality management, while FDA approval is crucial for medical applications. Additionally, check for compliance with environmental standards such as RoHS or REACH if applicable. Request documentation to confirm these certifications, which can mitigate risks associated with product safety and regulatory compliance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vacuum forming services
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of vacuum forming services offers international B2B buyers a pathway to enhance product quality while optimizing costs. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of selecting the right suppliers who can demonstrate advanced capabilities in material selection, process innovation, and sustainable practices. By leveraging technological advancements and understanding regional market dynamics, companies can effectively navigate the complexities of the vacuum forming landscape.
Value Proposition: The ability to produce high-quality, customized parts quickly and efficiently makes vacuum forming an indispensable asset across industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods. Establishing partnerships with reliable suppliers will not only mitigate risks but also foster innovation and agility in product development.
As global markets continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace a proactive approach in sourcing vacuum forming services. Take action today: Evaluate your current suppliers, explore new partnerships, and invest in technologies that enhance your manufacturing capabilities. By doing so, you position your business for success in an increasingly competitive landscape.