Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Which Best Describes The
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for which best describes the function of a centrifuge
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, understanding the function of a centrifuge is paramount for B2B buyers across diverse industries. Centrifuges play a critical role in the separation and purification of materials, enabling companies to enhance product quality, streamline processes, and reduce operational costs. This guide delves into the various types of centrifuges, each designed to meet specific separation needs, from microcentrifuges used in laboratories to large-scale industrial models essential for manufacturing.
Our comprehensive exploration covers essential aspects such as materials used in centrifuge construction, manufacturing and quality control processes, and insights into reliable suppliers. We also address cost considerations and market trends that influence purchasing decisions. By providing answers to frequently asked questions, this guide equips international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—regions with burgeoning industrial sectors—with the knowledge needed to make informed sourcing decisions.
Whether you are a procurement specialist in a pharmaceutical company or a quality control manager in a food processing plant, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of centrifuge selection. By understanding the critical functions and applications of centrifuges, you can optimize your operations, ensure compliance with industry standards, and ultimately achieve a competitive edge in your market.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding which best describes the function of a centrifuge Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micro Centrifuge | Compact design, low capacity (up to 2.0 ml), high RPM | Molecular biology, small-scale research | Pros: Space-efficient, ideal for small samples. Cons: Limited capacity and functionality. |
| Refrigerated Centrifuge | Temperature control (-20 to -40°C), high centrifugal force | Biological sample analysis, clinical labs | Pros: Preserves sample integrity. Cons: Higher initial cost and maintenance. |
| Ultracentrifuge | Extremely high speeds (up to 75000 RPM), specialized for macromolecule separation | Biochemistry, pharmaceuticals, advanced research | Pros: High precision separation. Cons: Complex operation and high cost. |
| Continuous Flow Centrifuge | Processes large volumes continuously, reduced manual handling | Wastewater treatment, food processing | Pros: Time-efficient, high throughput. Cons: Bulkier design may require more space. |
| Vacuum Centrifuge | Evaporates solvents under reduced pressure | Chemical analysis, sample concentration | Pros: Effective solvent removal. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
Micro Centrifuge
Micro centrifuges are designed for small volume samples, typically up to 2.0 ml, making them ideal for laboratories engaged in molecular biology and genetic research. Their compact size allows for easy integration into limited laboratory spaces. When considering a micro centrifuge, buyers should evaluate the speed range, which can reach up to 13,300 RPM, as well as the specific applications required, such as nucleic acid pelleting or protein purification. While they are space-efficient, their limited capacity may not suffice for larger sample volumes.
Refrigerated Centrifuge
Refrigerated centrifuges are equipped with temperature control mechanisms to maintain consistent temperatures between -20 to -40°C during operation. This feature is crucial for preserving the integrity of biological samples, such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. Buyers in clinical and research labs should prioritize these centrifuges for applications where sample degradation could compromise results. While they provide excellent sample preservation, the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs can be higher than standard centrifuges.
Ultracentrifuge
Ultracentrifuges operate at extremely high speeds, often exceeding 75,000 RPM, making them essential for separating macromolecules and subcellular particles. They are widely used in biochemistry and pharmaceutical applications, where precision in separating proteins and nucleic acids is critical. Buyers should consider the type of ultracentrifuge—preparative or analytical—as each serves distinct functions. Although they offer unparalleled separation capabilities, their complexity and cost can be significant barriers for smaller organizations.
Continuous Flow Centrifuge
Continuous flow centrifuges are designed to process large volumes of samples without the need for frequent loading and unloading. This feature makes them highly efficient for applications in wastewater treatment and food processing, where time and throughput are critical. B2B buyers should assess the capacity and operational requirements, as these centrifuges tend to be larger and may require more floor space. While they excel in efficiency, their size may be a drawback for smaller facilities.
Vacuum Centrifuge
Vacuum centrifuges, also known as concentrators, are utilized to evaporate solvents from samples by reducing the pressure within the chamber. This technology is particularly valuable in chemical analysis and sample concentration processes. Buyers should consider the specific applications for which they need a vacuum centrifuge, as its utility is limited to scenarios involving solvent evaporation. While they are effective in their niche, the need for specialized applications may restrict their broader use in various laboratories.
Related Video: Centrifuge Introduction
Key Industrial Applications of which best describes the function of a centrifuge
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of which best describes the function of a centrifuge | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Separation of blood components for plasma or serum collection | Enhances efficiency in drug formulation and diagnostics | Quality standards, regulatory compliance, and service support |
| Food and Beverage | Clarification of juices and oils to remove solids and impurities | Improves product quality and shelf life | Material compatibility, energy efficiency, and ease of cleaning |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Separation of chemical mixtures for purification and recovery of solvents | Increases yield and reduces waste in chemical processes | Customization options, durability, and maintenance requirements |
| Wastewater Treatment | Sludge dewatering to reduce volume and improve handling | Lowers disposal costs and enhances environmental compliance | Capacity specifications, energy consumption, and operational reliability |
| Biotechnology | Cell harvesting post-culture to extract valuable products | Maximizes yield of bioproducts and optimizes resource utilization | Scalability, integration with existing processes, and support services |
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical sector, centrifuges are crucial for the separation of blood components, specifically for plasma or serum collection. This process is vital for diagnostic testing and drug formulation. By efficiently separating these components, pharmaceutical companies can enhance their product quality while minimizing contamination risks. International buyers should prioritize equipment that meets stringent quality standards and regulatory compliance, particularly in regions with strict health regulations.
Food and Beverage Industry
Centrifuges are widely employed in the clarification of juices and oils, effectively removing solids and impurities. This application not only improves the clarity and taste of the product but also extends its shelf life. For buyers in the food and beverage sector, it is essential to consider material compatibility and energy efficiency when sourcing centrifuges to ensure compliance with food safety standards and to reduce operational costs.
Chemical Manufacturing
In the chemical manufacturing sector, centrifuges facilitate the separation of chemical mixtures, enabling the purification and recovery of solvents. This application is critical for increasing yield and minimizing waste in various chemical processes. Buyers should focus on customization options that align with their specific production needs, as well as the durability of the centrifuge to withstand harsh operational environments.
Wastewater Treatment
Centrifuges play a significant role in sludge dewatering within wastewater treatment facilities. This process reduces the volume of waste, making it easier and more cost-effective to handle and dispose of. For international buyers, understanding capacity specifications and energy consumption is vital, as these factors directly impact operational efficiency and environmental compliance.
Biotechnology
In biotechnology, centrifuges are essential for cell harvesting after culture processes, allowing for the extraction of valuable products like proteins and enzymes. This application maximizes yield and optimizes resource utilization, which is critical for the commercial viability of bioproducts. Buyers should consider the scalability of the centrifuge and its ability to integrate with existing processes to ensure seamless operations and support services.
Related Video: centrifugation | Principle | Applications | centrifuge equipment |Unit-4| pharmaceutical engineering
Strategic Material Selection Guide for which best describes the function of a centrifuge
When selecting materials for centrifuges, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in centrifuge construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°C and can handle pressures exceeding 2000 psi, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can withstand repeated use without degrading. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which can impact budget considerations. Manufacturing complexities can arise due to the need for specialized tooling and processes.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive chemicals and biological samples, making it versatile for laboratory and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Europe, certifications for food-grade stainless steel may be necessary, while buyers in Africa and South America should verify local regulations regarding material safety.
Polypropylene
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a lightweight, cost-effective thermoplastic that offers good chemical resistance and can operate at temperatures up to 100°C. It is not suitable for high-pressure applications but is often used for low-speed centrifuges.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polypropylene is its low cost and ease of manufacturing, which can lead to reduced overall equipment costs. However, it lacks the strength and temperature resistance of metals, limiting its use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is ideal for separating biological samples and low-density materials, making it popular in clinical laboratories.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with relevant standards such as JIS and ISO. In regions like the Middle East, where temperatures can be extreme, it’s crucial to ensure that polypropylene components are suitable for the intended operating conditions.
Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in aggressive environments. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and is often used in high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons:
While titanium offers superior durability and performance, it is significantly more expensive than stainless steel and polypropylene. The manufacturing process is also more complex, which can lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is particularly beneficial for applications involving aggressive solvents and high-temperature processes, making it suitable for advanced industrial centrifuges.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers must ensure that titanium components meet specific industry standards, especially in Europe where aerospace and medical applications demand stringent compliance.
Glass
Key Properties:
Glass is chemically inert and can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically up to 300°C. It is transparent, allowing for visual inspection during processes.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of glass is its chemical resistance and inertness, making it suitable for sensitive applications. However, it is fragile and can break easily, which poses safety risks and can lead to increased costs due to breakage.
Impact on Application:
Glass centrifuge tubes are often used in laboratories for sample separation, especially when contamination is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the fragility of glass components and ensure that they comply with safety standards relevant to their region. In Africa and South America, considerations for transport and handling are crucial.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for which best describes the function of a centrifuge | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High-performance industrial centrifuges | Excellent durability and strength | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Polypropylene | Clinical laboratory applications | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited temperature and pressure tolerance | Low |
| Titanium | Advanced industrial applications involving aggressive solvents | Superior corrosion resistance | Very high cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Glass | Laboratory sample separation | Chemically inert and transparent | Fragility and safety risks | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for centrifuges, highlighting the critical factors that international B2B buyers should consider to ensure optimal performance and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for which best describes the function of a centrifuge
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for centrifuges are critical components that international B2B buyers must understand to ensure they source reliable, high-performance equipment. This section delves into the typical manufacturing stages, key techniques, quality control measures, and international standards that govern centrifuge production.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of centrifuges typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage requires precision and adherence to industry standards to ensure the final product meets the necessary performance and safety specifications.
Material Preparation
-
Selection of Materials: The choice of materials is crucial, especially for components that will experience high stress or corrosive environments. Stainless steel, aluminum, and specialized polymers are common due to their strength, durability, and resistance to chemical damage.
-
Material Testing: Before use, materials undergo rigorous testing for properties such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue limits. This ensures that only materials that meet the required specifications are used in production.
Forming
-
Machining: Parts are machined using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology to achieve precise dimensions. This includes the rotor, which must be balanced to avoid vibrations during operation.
-
Fabrication Techniques: Techniques such as forging, casting, and welding may be employed depending on the component’s requirements. For instance, rotors may be forged for added strength, while casings may be welded for integrity.
Assembly
-
Component Assembly: The assembly process involves fitting together various components, including the rotor, drive system, and control panel. Each assembly is performed under strict supervision to ensure alignment and functionality.
-
Integration of Systems: Modern centrifuges often integrate advanced control systems for monitoring speed, temperature, and other parameters. This integration requires specialized knowledge in electronics and software engineering.
Finishing
-
Surface Treatment: To enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, components often undergo surface treatments such as anodizing or electroplating.
-
Final Inspection: Once assembled, centrifuges undergo a comprehensive inspection to ensure that they meet design specifications and safety standards. This includes visual checks and functional tests.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of centrifuges, as it directly impacts performance and safety. International B2B buyers should be familiar with the quality control processes and standards that manufacturers should adhere to.
International Standards
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates a commitment to quality.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: Depending on the application, additional certifications such as CE marking (for compliance with European safety standards) or API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may be relevant. These certifications ensure that the centrifuges are safe and reliable for specific industrial applications.
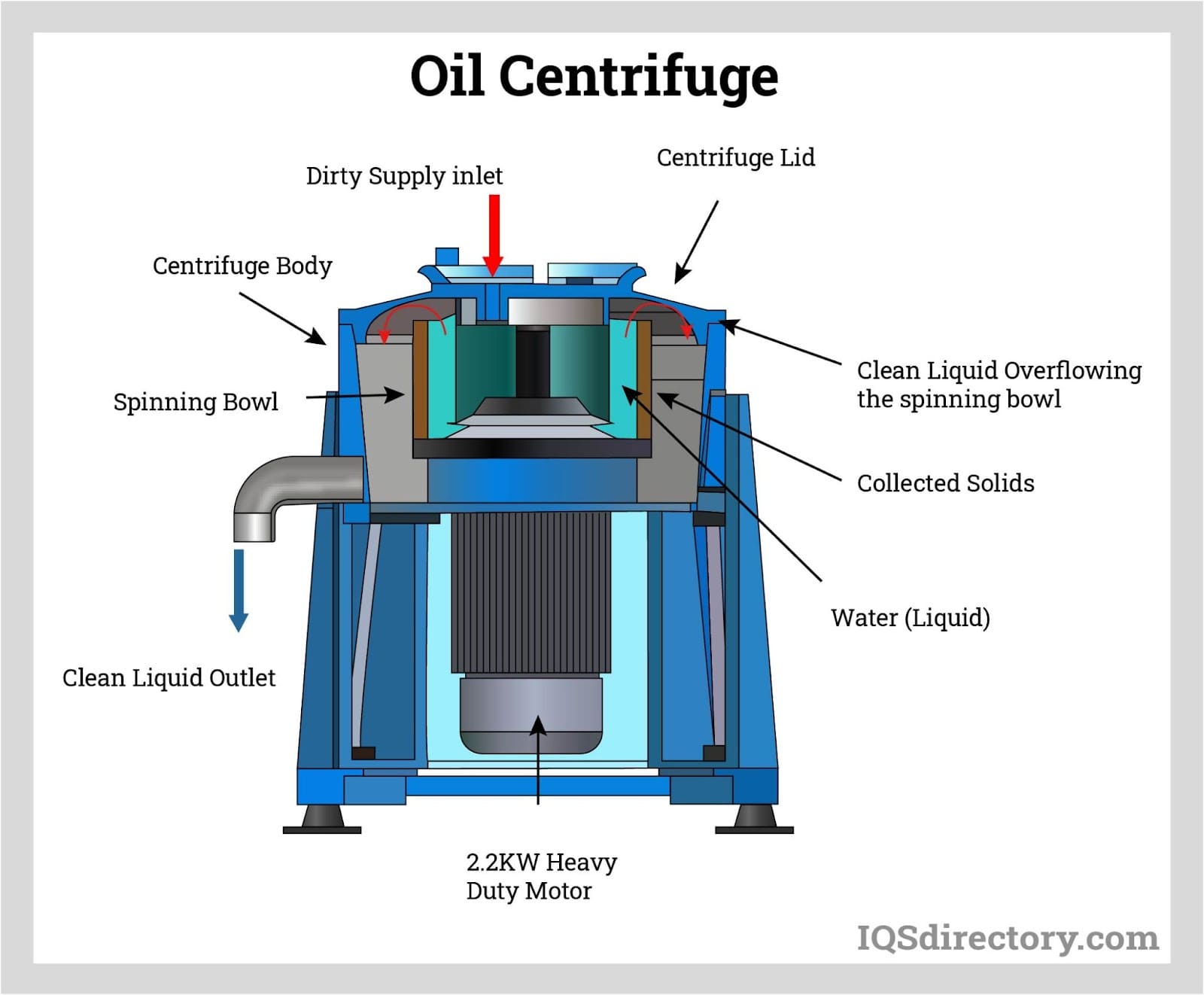
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
QC Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves testing raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, periodic checks are conducted to monitor the quality of work in progress. This includes dimensional checks and performance tests.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the final product undergoes thorough testing to confirm that it operates according to specifications. This may include performance testing under various load conditions.
Common Testing Methods
- Dynamic Balancing Tests: Ensures that rotors operate smoothly at high speeds, minimizing vibrations.
- Pressure Tests: Validates the integrity of sealed components to prevent leaks.
- Thermal Cycling Tests: Assesses the performance of centrifuges under varying temperature conditions.
Verifying Supplier QC
B2B buyers must adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality assurance processes of potential suppliers. Here are some effective methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. This can include reviewing documentation, inspecting facilities, and interviewing staff.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline testing results, certifications, and compliance with standards can provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party organizations to conduct inspections can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. This is particularly valuable for international buyers who may not be able to conduct on-site audits.
QC/Cert Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification processes:
-
Regional Compliance: Different regions may have unique compliance requirements. For example, EU regulations may necessitate additional testing or certifications that may not be required in other regions.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can influence the negotiation process regarding quality standards and certifications.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks to product integrity. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and handling procedures to mitigate these risks.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with centrifuge production, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Amazing factories | Manufacturing method and top 4 processes | Mass production process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for which best describes the function of a centrifuge Sourcing
Centrifuges are critical tools in various industries, facilitating the separation and purification of mixtures. Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will provide insights into cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for negotiating and maximizing value.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in centrifuge manufacturing include high-strength alloys, stainless steel, and specialized plastics. The choice of materials significantly impacts the durability, efficiency, and performance of the centrifuge. Higher-quality materials may lead to increased upfront costs but can reduce long-term maintenance expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in design, assembly, and testing. The complexity of the centrifuge model can influence labor hours, with more intricate designs requiring specialized skills.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs, which can be a significant part of the overall price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific centrifuge designs can incur substantial costs. Buyers seeking specialized equipment should consider these tooling costs as part of their total investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that centrifuges meet industry standards and specifications. Investing in robust QC can lead to higher initial costs but ultimately reduces the risk of failures and enhances reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs vary based on the centrifuge’s size, weight, and destination. International buyers should account for potential tariffs, taxes, and import duties, which can add significant costs to the overall purchase.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a markup to cover their expenses and generate profit. Understanding the typical margins in the centrifuge market can help buyers gauge whether they are receiving competitive pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchasing often leads to lower unit prices. Buyers should negotiate terms that allow for bulk discounts, especially if they plan to procure multiple units.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features can significantly affect pricing. Buyers need to weigh the benefits of customization against the potential cost increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can influence both the performance and price of the centrifuge. Buyers should ensure that the materials align with their operational requirements and budget.
-
Quality/Certifications: Centrifuges that meet international standards (e.g., ISO certifications) often command higher prices due to their enhanced reliability and safety. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their operations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices due to their proven track record, while newer entrants may provide lower prices to penetrate the market.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can affect the final cost. Buyers should understand these terms to avoid unexpected charges and ensure favorable shipping conditions.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing volume to negotiate better pricing and terms. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts based on bulk orders or long-term partnerships.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as maintenance, operational efficiency, and lifespan when assessing cost-effectiveness.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices may vary significantly between regions due to local market conditions, labor costs, and supply chain logistics. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct market research to understand these dynamics.
-
Disclaimer: Prices in the centrifuge market can fluctuate based on material costs, demand, and geopolitical factors. Always seek multiple quotations and perform due diligence to ensure that pricing aligns with current market conditions.
By understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of centrifuge sourcing, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their investments and enhance operational efficiency.
Spotlight on Potential which best describes the function of a centrifuge Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘which best describes the function of a centrifuge’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for which best describes the function of a centrifuge
When considering the purchase of a centrifuge, international B2B buyers must be familiar with essential technical properties and industry terminology. Understanding these aspects can significantly impact the efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of their operations.
Critical Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality of materials used in the construction of a centrifuge, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or plastic composites.
– Importance: High-grade materials ensure durability and resistance to corrosion and wear. For industries dealing with harsh chemicals or high temperatures, selecting a centrifuge made from appropriate materials is crucial for longevity and safety. -
Centrifugal Force (G-Force)
– Definition: The force exerted on the sample during centrifugation, measured in multiples of gravity (G).
– Importance: The effectiveness of separation is directly related to the G-force applied. Higher G-forces lead to faster and more efficient separation of particles, which is vital in applications like pharmaceuticals and biotechnology. -
Rotor Speed
– Definition: The maximum rotational speed of the centrifuge, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
– Importance: Different applications require specific rotor speeds for optimal results. Understanding the rotor speed capabilities helps buyers select a centrifuge that meets their operational needs. -
Sample Volume Capacity
– Definition: The maximum volume of samples that can be processed in a single run.
– Importance: Matching the centrifuge’s capacity to the volume of samples handled is essential for operational efficiency. Overloading can lead to ineffective separation and damage to the equipment. -
Temperature Control
– Definition: The ability of a centrifuge to maintain specific temperatures during operation, often ranging from -20°C to +40°C.
– Importance: For sensitive biological samples, maintaining temperature is critical to preserving sample integrity. Refrigerated centrifuges are necessary for applications like DNA and RNA extraction.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality standards and service support, especially when sourcing centrifuge components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy and inventory management, particularly for high-value equipment like centrifuges. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products.
– Relevance: Submitting an RFQ is a critical step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare options and negotiate better terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and insurance responsibilities, which can greatly affect the total cost of ownership. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Relevance: Knowing lead times is essential for planning and can influence purchasing decisions, especially in industries where timely delivery is critical.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and business objectives. Understanding the nuances of centrifuge specifications and industry jargon will facilitate smoother transactions and enhance overall procurement efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the which best describes the function of a centrifuge Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global centrifuge market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage, and environmental testing. In particular, the rise of biopharmaceuticals and personalized medicine in regions such as Africa and South America is creating a surge in the need for high-speed and ultra-centrifuges for the separation of biological compounds. Moreover, advancements in technology are leading to the development of smarter centrifuges equipped with IoT capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics. This enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, appealing to international B2B buyers focused on maximizing productivity.
Emerging trends also indicate a shift towards compact and energy-efficient centrifuge models, which cater to the needs of small and medium enterprises in developing regions. As sustainability becomes a priority, buyers are increasingly looking for centrifuge manufacturers that emphasize energy conservation and reduced waste generation. Additionally, the integration of automation and machine learning in centrifuge operations is expected to streamline processes and lower labor costs, making these technologies more accessible to businesses in Africa, the Middle East, and Europe.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming an essential factor for B2B buyers in the centrifuge market. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of centrifuge machines are under scrutiny. Buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and implementing energy-efficient technologies. Certifications like ISO 14001 can serve as a benchmark for assessing a supplier’s commitment to environmental management.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical, particularly in regions with stringent regulations regarding labor practices and environmental standards. Buyers should seek out suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and adhere to ethical labor practices. By aligning with manufacturers that are committed to sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can not only reduce their carbon footprint but also enhance their brand reputation, making them more attractive to environmentally-conscious customers.
Brief Evolution/History
Centrifuges have a storied history, originating in the late 19th century with the invention of the first laboratory centrifuge. Initially designed for simple separation tasks, such as blood component separation, the technology has evolved dramatically. The introduction of industrial centrifuges in the mid-20th century revolutionized various industries by enabling the large-scale separation of solids and liquids. As technology advanced, the development of high-speed and ultra-centrifuges allowed for more complex applications, including the purification of proteins and nucleic acids, which are crucial in modern biomedical research. This evolution reflects the growing complexity and demand for precision in separation technologies, positioning centrifuges as indispensable tools in diverse industrial applications today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of which best describes the function of a centrifuge
-
What are the critical factors to consider when vetting centrifuge suppliers?
When vetting suppliers for centrifuges, prioritize their industry experience, technical expertise, and production capacity. Verify their certifications (ISO, CE) to ensure compliance with international standards. Assess their ability to provide customization options tailored to your specific needs, especially regarding capacity, speed, and temperature control. Additionally, request references from existing clients in your region to gauge reliability and support. Understanding their logistics capabilities, including lead times for delivery, is also essential to ensure timely operations. -
Can centrifuges be customized to meet specific operational requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for centrifuges. When discussing your needs, specify the required speed, capacity, and temperature control features. It’s also important to clarify the type of materials you’ll be processing, as this can affect rotor design and construction materials. Inquire about the supplier’s experience with custom builds, and request case studies or examples of past projects. This will help you determine if they can adequately meet your unique operational demands. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for centrifuge orders?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for centrifuges can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and model. Generally, standard models may have lower MOQs, while custom or specialized units may require higher quantities. Lead times can range from a few weeks to several months based on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production schedule. Always confirm these details upfront and negotiate terms that align with your operational timelines to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification for the centrifuges I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed documentation from suppliers regarding their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, inquire about the testing processes each centrifuge undergoes before shipment. Ask for product samples or test reports to verify performance specifications. Establishing a clear understanding of these QA protocols will help mitigate risks associated with equipment failure. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing centrifuges internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include upfront deposits (20-50%), with the balance due upon delivery or prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger orders. Be cautious of the payment methods accepted; secure options like letters of credit or escrow services can help protect your investment. Always negotiate terms that are favorable and ensure they align with your cash flow needs. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing centrifuges?
When importing centrifuges, consider shipping methods (air freight vs. sea freight) based on cost and urgency. Understand the customs regulations in your country to avoid delays and additional costs. Ensure that all shipping documentation is accurate and complete, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Collaborate with a logistics partner experienced in international shipping to navigate potential challenges and streamline the delivery process. -
How can disputes with suppliers be effectively managed?
To manage disputes with suppliers, establish clear contracts that outline terms, conditions, and expectations from the outset. Include clauses for conflict resolution, such as mediation or arbitration, to provide a framework for addressing issues. Maintain open lines of communication throughout the transaction to resolve minor issues before they escalate. If disputes arise, document all correspondence and agreements to support your position and seek legal advice if necessary. -
What are the common applications of centrifuges across different industries?
Centrifuges have diverse applications across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage, and wastewater treatment. In pharmaceuticals, they are used for separating blood components and purifying biological samples. In the food industry, centrifuges help in extracting oils and clarifying liquids. Understanding these applications can help buyers select the appropriate type of centrifuge for their specific needs. Engaging with suppliers who understand your industry can also provide insights into best practices and innovative uses of centrifuge technology.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for which best describes the function of a centrifuge
In conclusion, understanding the function and capabilities of centrifuges is vital for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their operational efficiency. Centrifuges serve a crucial role in various industries, from pharmaceuticals to food processing, offering precise separation and purification of materials. By strategically sourcing the right type of centrifuge—whether it be a micro, refrigerated, or ultracentrifuge—businesses can optimize their processes, reduce waste, and ensure quality outcomes.
Key Takeaways:
– Versatility: Centrifuges can be tailored to specific applications, making them adaptable to diverse industry needs.
– Efficiency: Utilizing the right centrifuge can significantly improve throughput and reduce processing times.
– Cost-Effectiveness: Investing in high-quality centrifuges can lead to long-term savings through enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs.
As markets continue to evolve, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses should embrace innovation in their sourcing strategies. Consider integrating advanced centrifuge technologies into your operations to stay ahead of the competition. Engage with reputable suppliers who can provide the necessary support and guidance to make informed purchasing decisions. The future is bright for those who leverage the power of centrifugation to drive their business success.